The drives in a storage pool combine to form a volume to facilitate fault tolerance, scalability, and performance. Choosing a balance between all three depends on the type of workloads that run on those volumes. The following figure summarizes which workloads are a good fit for each resiliency-type, mapped with performance and efficiency.
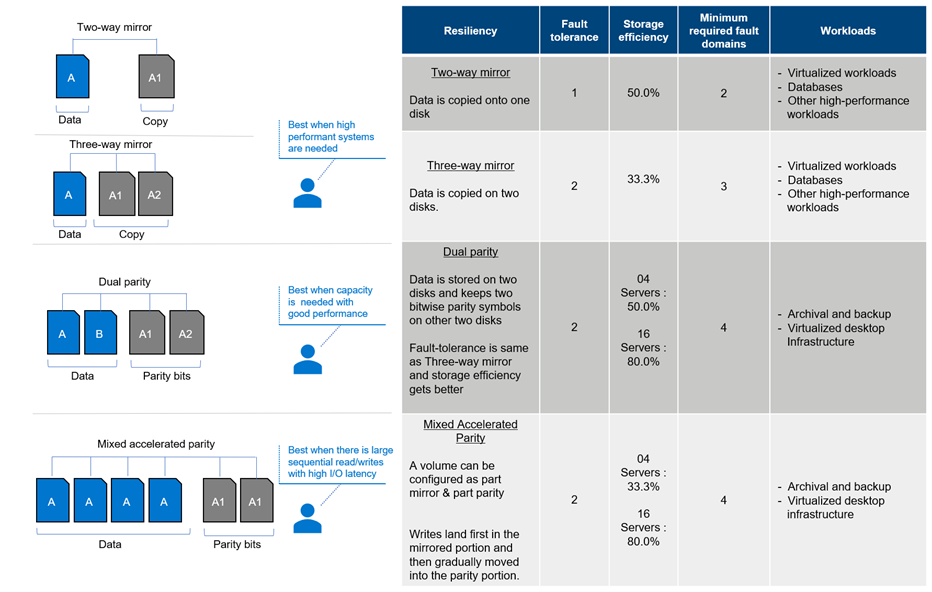
Dell Technologies recommends using a 3-way mirror for volume considerations for most workloads that highly demand performant data transfers. The reason behind this is absolute greatest performance it offers amongst all other volume options. With a 33% usable capacity, the 3-way mirror offers a great resiliency which can withstand multiple failures at the same time besides providing access to data.
For more information about best practices designed for certain workloads, see Best practices and example configurations.
If there is a need for added resiliency to the volumes, they can be configured to use nested resiliency which is explained in the further section.
The following figure describes some fault tolerance scenarios and how Azure Stack HCI can help keep the organization running. In each case, a 4-node cluster keeps on running despite one or more drive/server failures.

