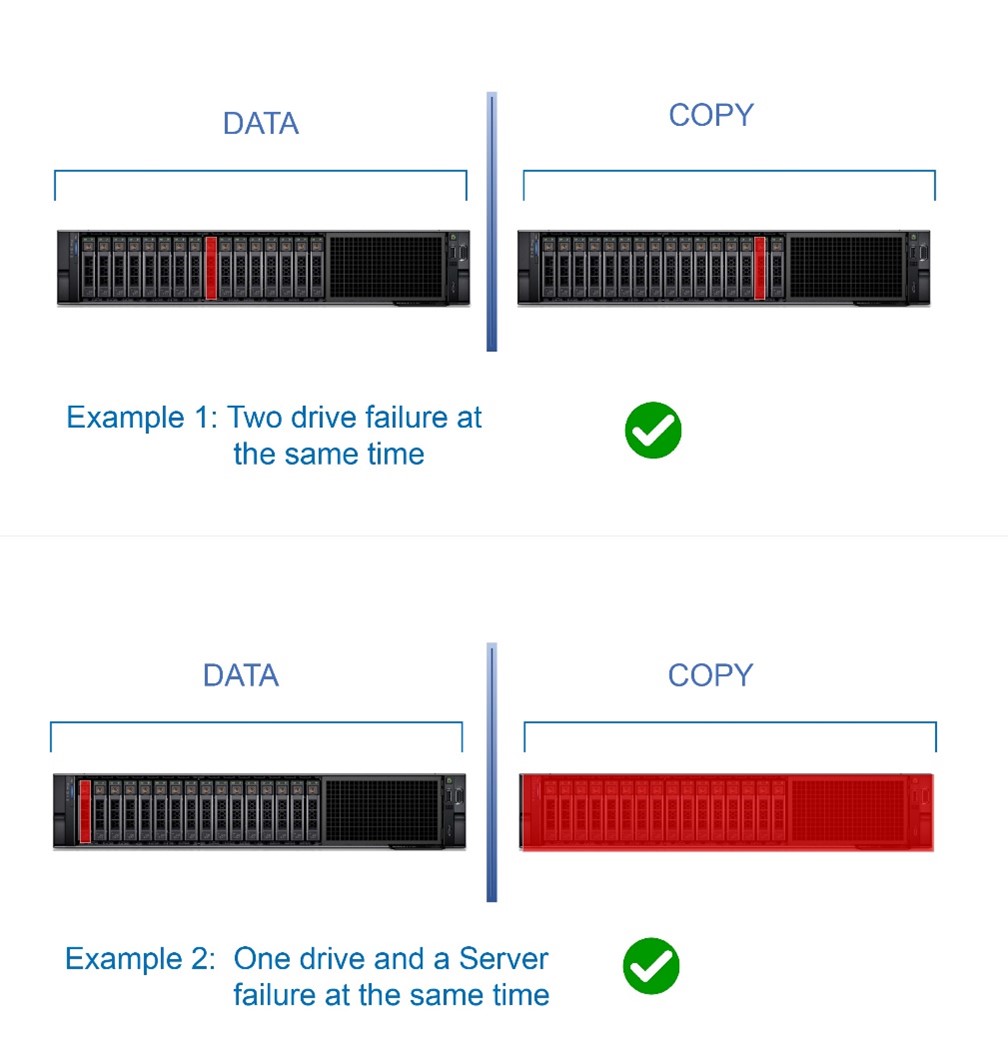
SDS powered HCI brings in a feature for a two-node cluster called nested resiliency. This feature increases uptime for applications and virtual machines providing uninterrupted access to files and resources during multiple drive, volume, or server failures. Volumes created over nested resiliency can stay online even when multiple hardware failures occur at the same time, unlike with classic two-way mirroring. The only caveat is the lower capacity efficiency, meaning less usable storage space when compared to two-way mirroring.
The following two examples show that if two drives fail at the same time, or if a complete server goes down and a drive fails simultaneously, volumes running in a nested resiliency configuration stay online and accessible.
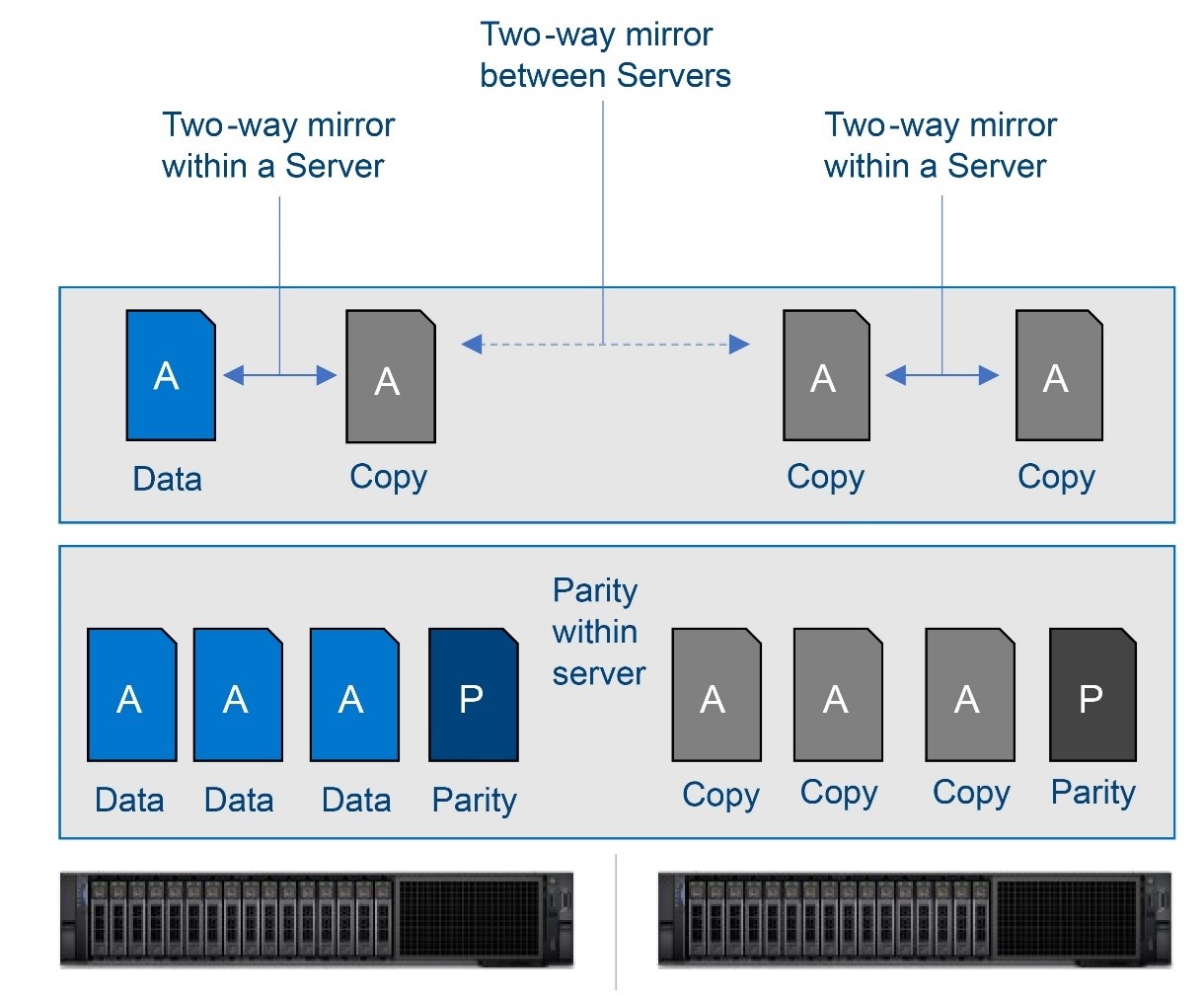
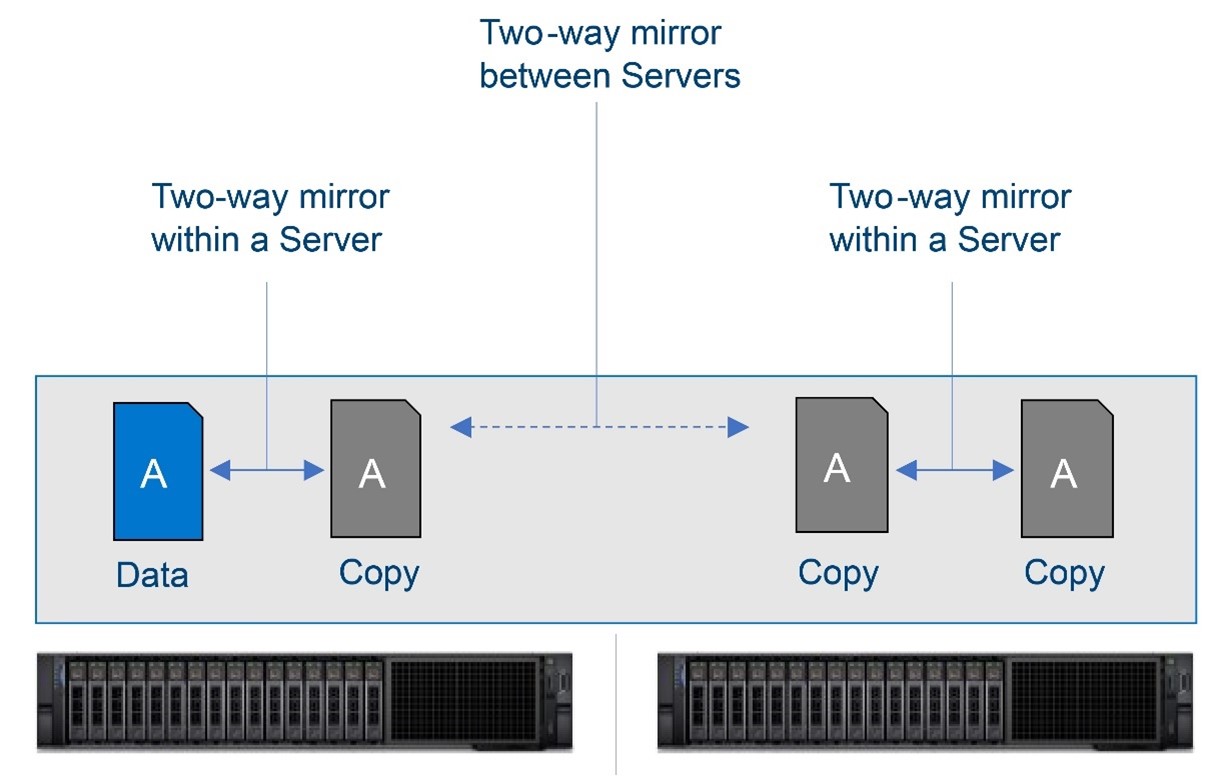
Two new resiliency options are included in Storage Spaces Direct, which uses software as a platform without the need for any hardware RAID.
Nested two-way mirror: This option works essentially as a four-way mirror with data getting written and copied, first within the server and data getting copied in between servers. This results in a volume that provides excellent performance with great resiliency.
Nested mirror-accelerated parity: This option combines the nested two-way mirroring with nested parity. First, there is parity calculation performed by S2D, that is happening locally within each server and, at the next step the two-way mirroring is happening in between the servers. This can achieve higher capacity efficiency, depending upon the number of capacity drives in each server and the mix of mirror and parity specified per volume.