Home > Storage > PowerMax and VMAX > Data Protection > Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: TimeFinder SnapVX Local Replication > Redirect-on-write
Redirect-on-write
-
SnapVX introduces redirect-on-write (ROW) technology to TimeFinder. When a source track is written to and the original data needs to be preserved for a snapshot or snapshots, the new write is accepted and asynchronously written to a new location in the Storage Resource Pool (SRP). The source volume now points to the new data while the snapshot or snapshots continue to point to the original data (the snapshot delta) in its original location.
Redirect-On-Write is illustrated in the following figures. Figure 3 shows the source volume and snapshot both pointing to the same location in the pool before the track is updated.
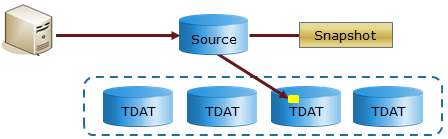
Figure 3. Source track before update
Figure 4 shows the source pointing to the new location in the pool after the host write, while the snapshot continues to point to the original location.
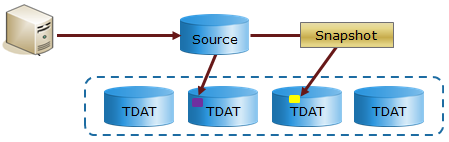
Figure 4. Source track after update and snapshot delta
Even though ROW provides many benefits, there are situations where the traditional Asynchronous Copy on First Write (ACOFW) mechanism that has been used by TimeFinder for many years is the ideal option. For example, to prevent source data from being redirected to a less than ideal performance or compression tier.
Therefore, both ROW and ACOFW are available in PowerMaxOS and HYPERMAX OS. The exact method that is selected for an operation is completely transparent to the user. As new data is written, the array will choose the appropriate mechanism to ensure source data resides in a location for ideal performance while also keeping snapshot data as efficient as possible on backend capacity.
