Home > Storage > ObjectScale and ECS > Industry Solutions and Verticals > Dell ECS and Veeam Backup & Replication > Veeam tuning
Veeam tuning
-
Compression and deduplication
Veeam Backup & Replication allows backup sets to be compressed and deduplication to be performed on them. Compression and deduplication are configured in the Veeam Backup & Replication management UI, on the Storage tab under Advanced Settings, when the backup job is created.
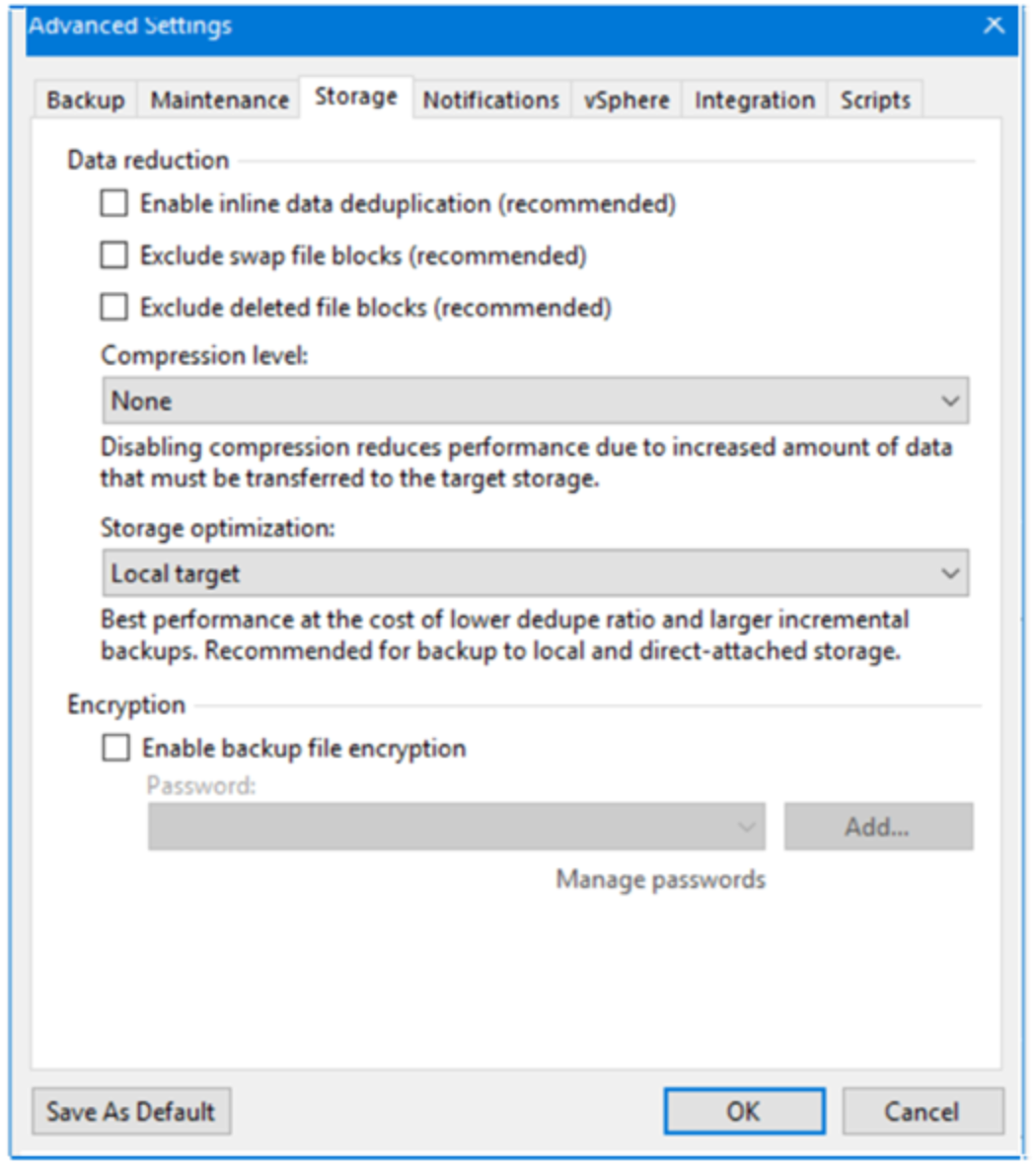
Compression
The following table lists the available compression levels.
Table 5. Veeam compression levels
Level
Description
None
No compression of backup sets.
None is a useful setting when you are using Dell ECS; ECS compresses blocks automatically using a compression algorithm based on snappy compression. For information about snappy compression, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snappy_(compression).
Dedupe-friendly
Low CPU usage.
Optimal
Recommended by Veeam; however, ECS compresses blocks as well.
High
Approximately 10x higher CPU usage over Optimal.
Extreme
High CPU overhead but produces the smallest size.
Compression levels for a job can be changed after the job is defined.
Data deduplication
With data deduplication enabled, Veeam Backup & Replication does not store identical data blocks and space that has been preallocated but not used.
For more information about compression and deduplication, see Data Compression and Deduplication in the Veeam Help Center.
Backup proxies
To allow many parallel backup tasks to run, follow these steps:
- In the Veeam Backup & Replication UI, select Backup Infrastructure > Backup Proxies, right-click VMware Backup Proxy, and then click Properties.
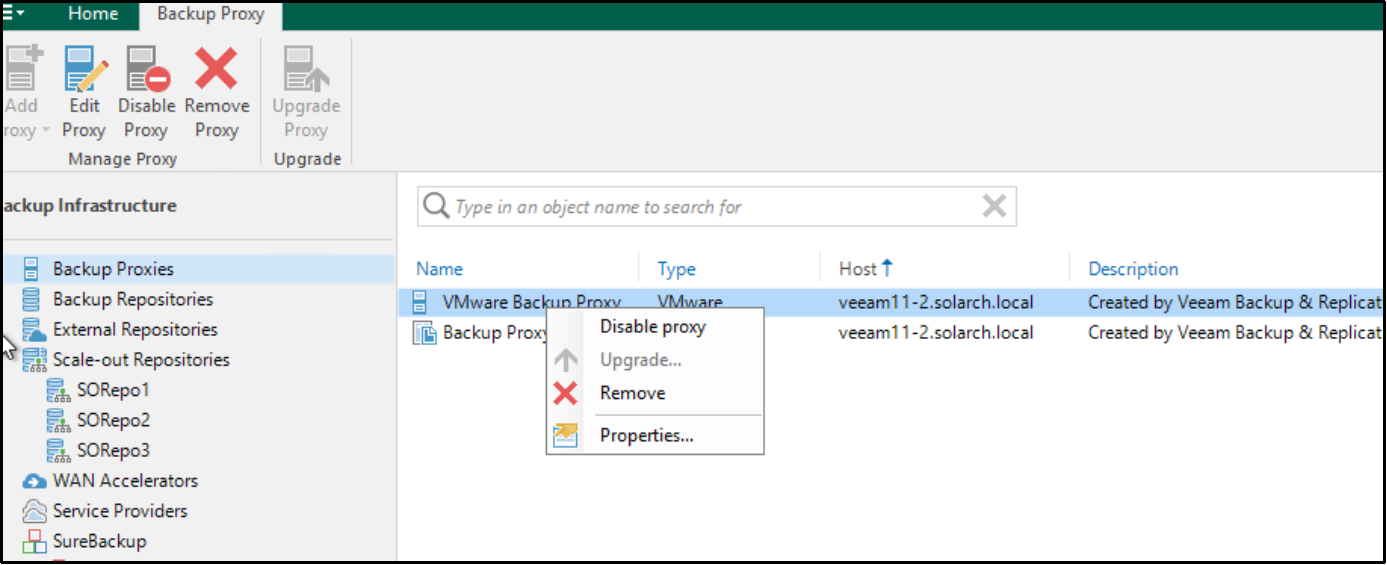
- On the Server page, Change Max concurrent tasks to increase the number of concurrent backup tasks that can run.
For example, set Max concurrent tasks to twice the number of CPUs that the Veeam backup server has.

- Click through the remaining pages, accepting the default settings.
Add Veeam Backup server proxies
You can add additional Windows or Linux servers to be Veeam Backup proxy servers under the control of the Veeam Backup and Replication server. To do this, perform the following steps.
- Install a fresh Windows or Linux server. Then, in the Veeam Backup and Replication management UI, select Backup infrastructure > Backup Proxies, right click and select Add proxy.
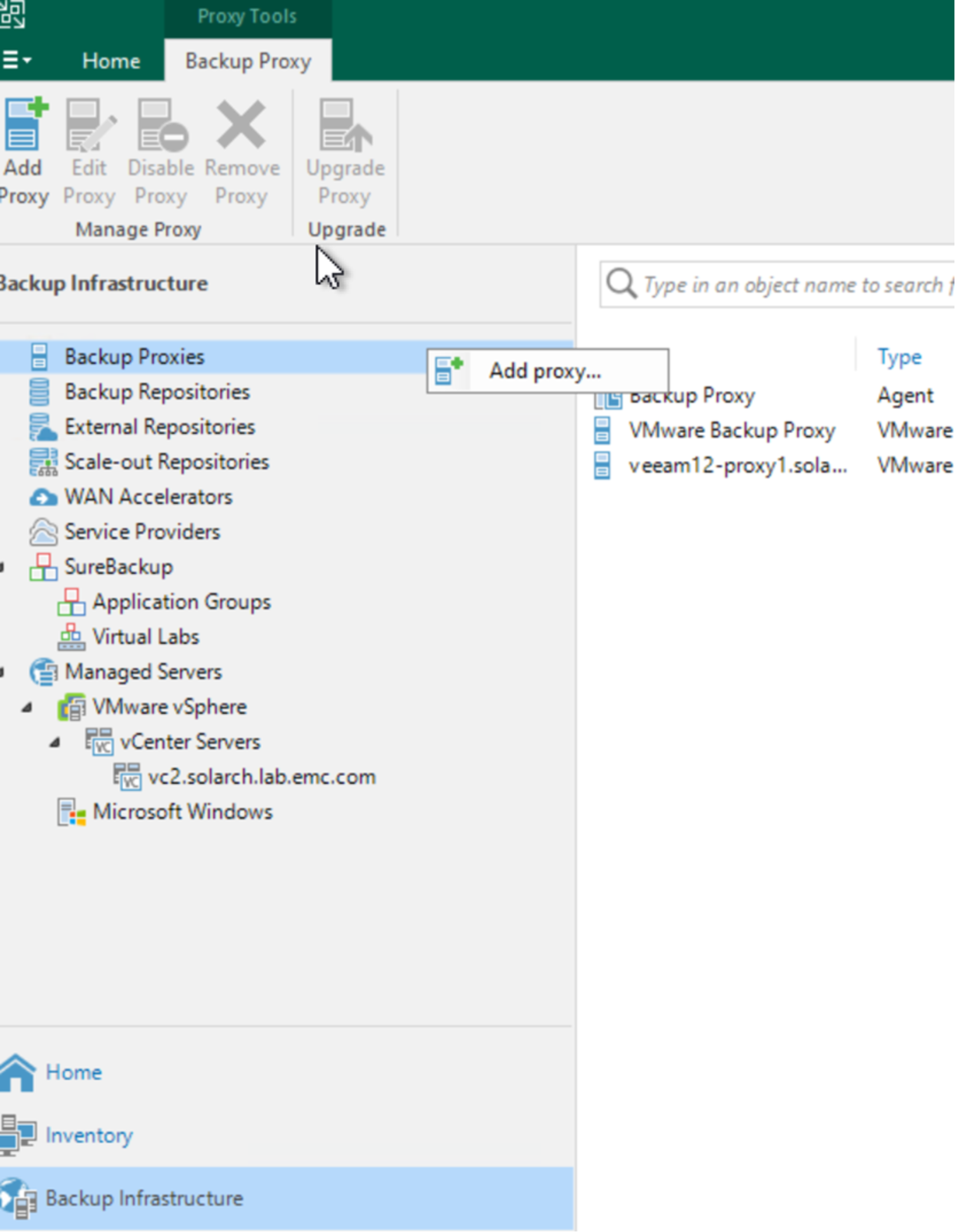
- Select VMware backup proxy.
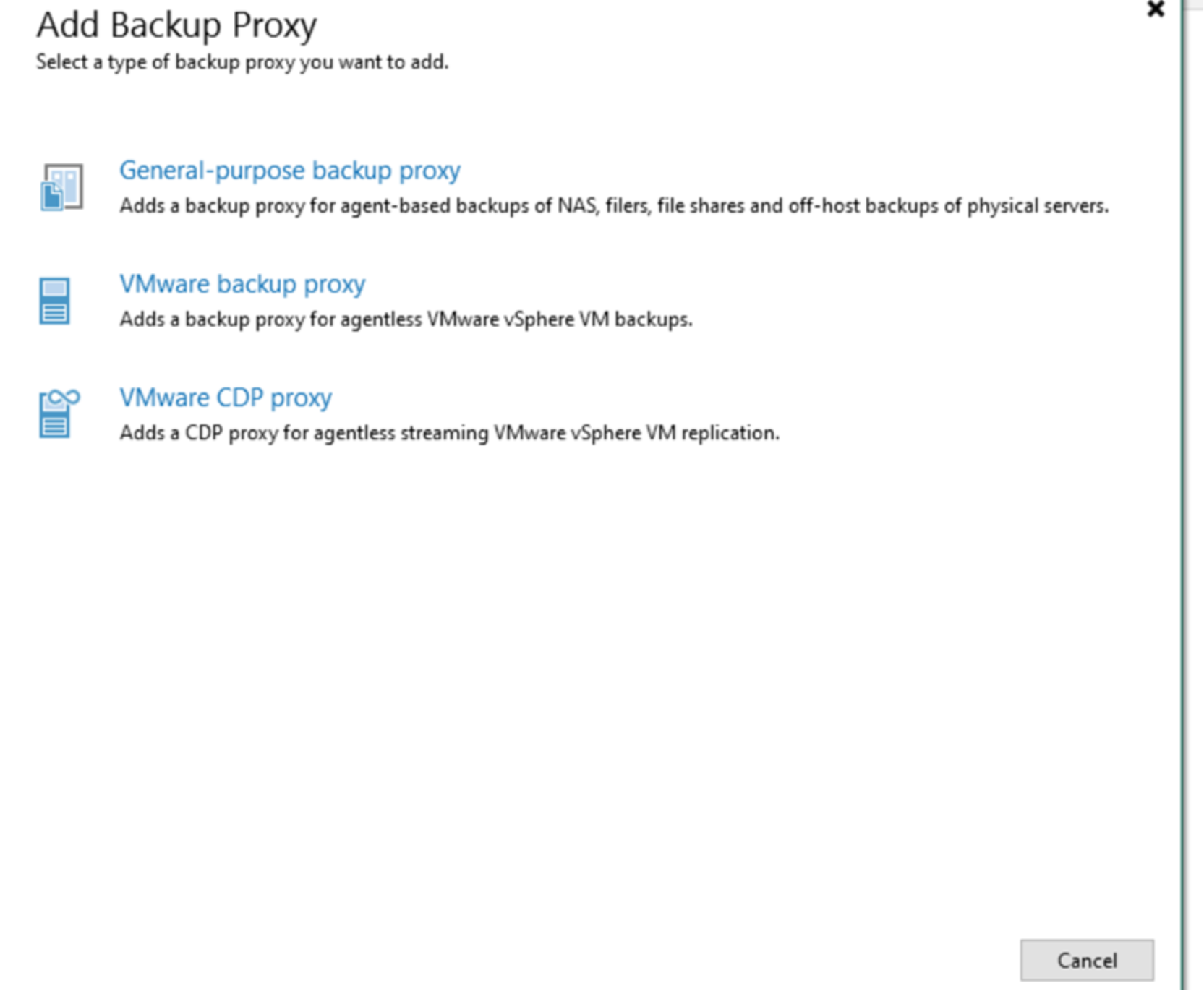
- Select Add New then Windows server.
- Enter the FQDN or IP address of the server.
- Enter the administrator credentials to use, then click Next.
- Click Apply.
- Click Next through the remaining windows to add the new Veeam backup proxy.
The new proxy has been added.
Backup block sizes
When creating a backup job in Veeam, the administrator can specify the block size that Veeam will use for the backup.
Note: To verify that this procedure has not changed, see the Veeam Backup & Replication v11 Release Information.
- In the Veeam Backup & Replication UI, when using the Job Creation form, on the Storage tab, click Advanced.

The Storage optimization menu selection governs the block size that Veeam will use for the backup.
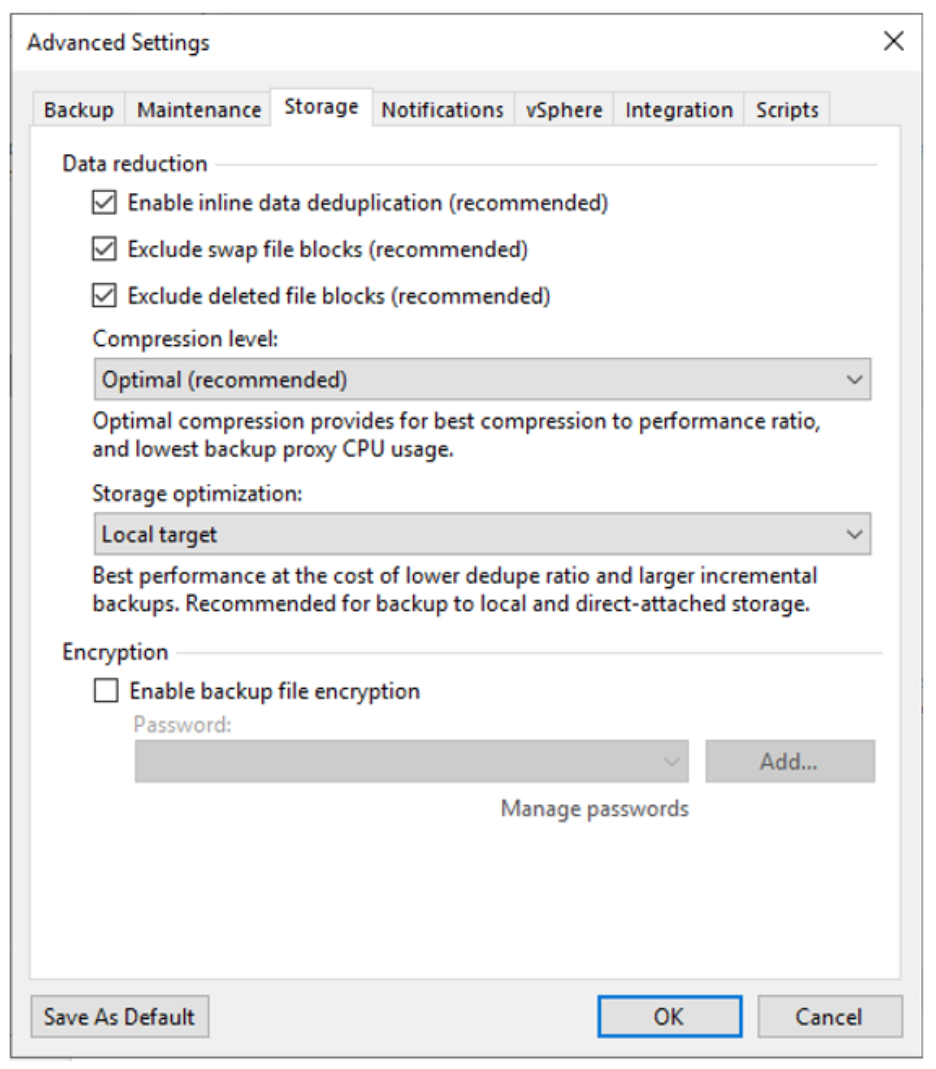
The Storage optimization menu presents the following options:
- 4 MB
- 1 MB (default)
- 512 KB
- 256 KB
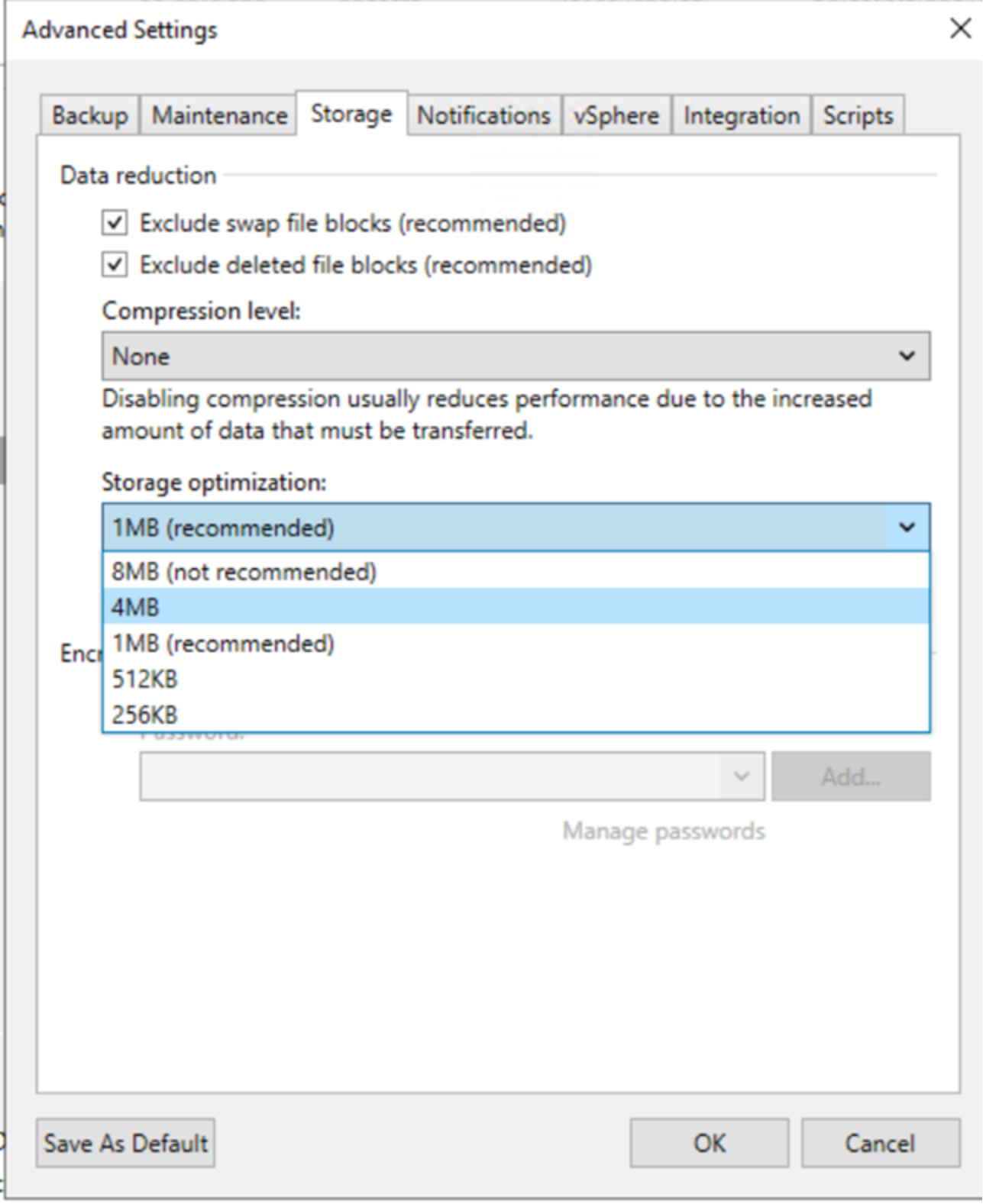
In addition, a hidden fifth option, 8MB (shown) is available.
- To enable 8 MB blocks), make a Windows Registry change:
- Under the following key:
'HKLM\SOFTWARE\Veeam\Veeam Backup and Replication'
add:
UIShowLegacyBlockSize (DWORD, 1)
- Restart the Veeam server.
The following table shows the block size for each of the storage optimization options.
Table 6. Backup block size
Block size KB
8,192
4,096
1,024
512
256
Reducing the block size increases the number of objects that are written to ECS:
# Of objects = Total size of backup job / Job block size
Backup and restore jobs elapsed time to complete will increase and the time taken to delete backup jobs will increase because there are more objects to write and subsequently delete.
ECS performance and Veeam backup block size
The ECS storage engine stores all data in logical chunks of 128 MB blocks of contiguous disk space. These chunks are initially stored with triple mirroring. Copies are written to three separate nodes, which allows transactions to be quickly acknowledged back to the application but still be protected against failure. A background task later uses erasure coding (EC) on the chunks using Reed-Solomon coding. This EC reduces the protection overhead for the objects three times to a lower level depending on the configuration of the ECS system. As object size increases, the effective throughput increases up to object sizes of 128 MB, where throughput plateaus.
Veeam storage administrators can specify a backup block size of 0.5 MB to 8 MB. The charts in this section show backup block size compared with write, restore, and delete operations.
Initially, this set of tests backs up a VM from a vSphere system to an ECS EX3000d. Each backup job offloads approximately 128 GB for the VM.
Write throughput and block size
This test backs up all three VMs to the performance tier. The backups are then offloaded to the capacity tier (ECS).
Table 7. Block size and write throughput
Block size KB
Throughput MB/s
8,192
434
4,096
418
1,024
405
The following chart shows block size and throughput.
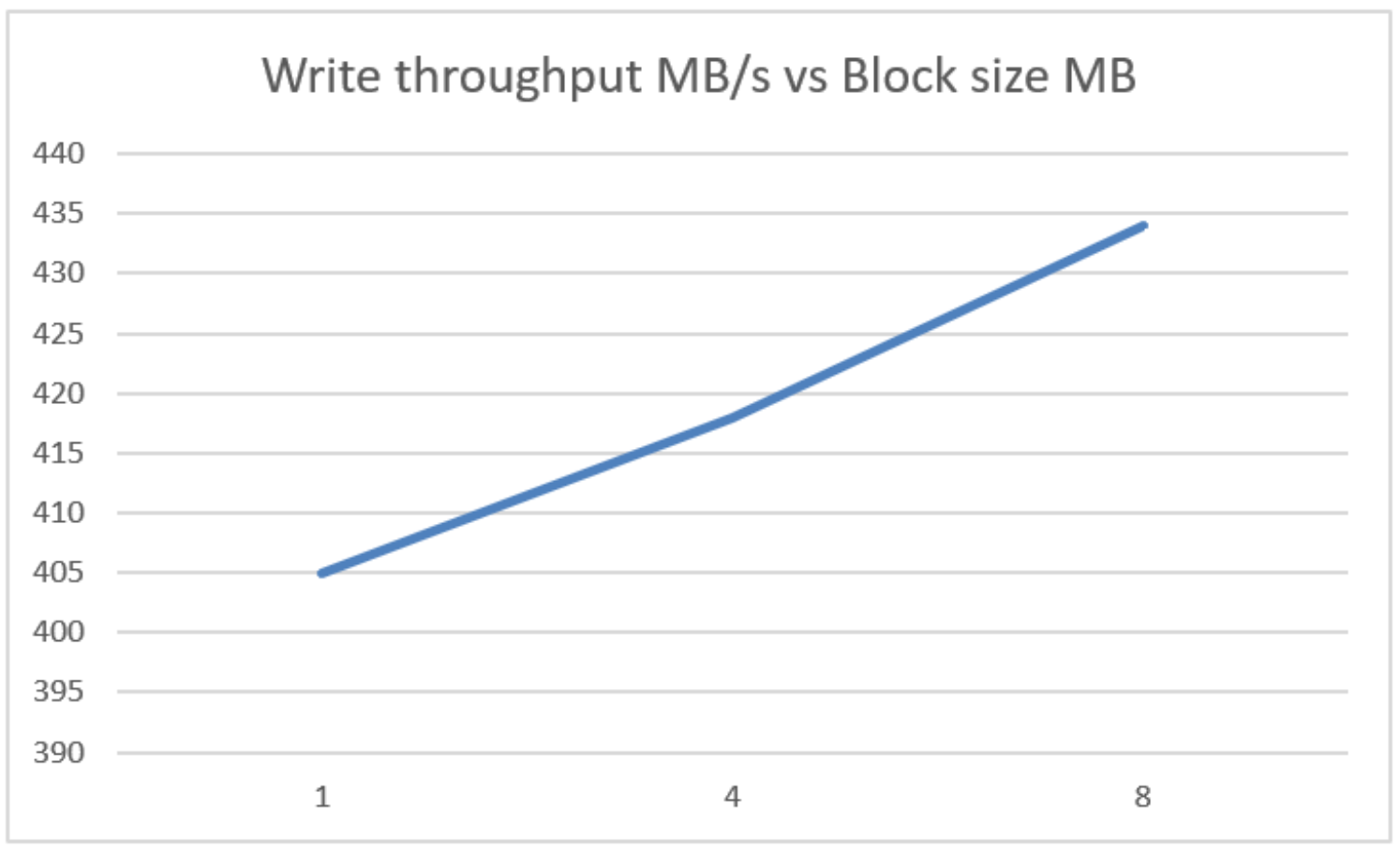
Here we can see that throughput does increase as the backup block size increases.
The default 1 MB Veeam backup block size is a good starting value, but increasing the block size to 4 MB increases throughput by only 3% and to 8MB by 7%. .
Restore throughput and block size
In this test, we restore the VM in the backup set, which was approximately 160 GB in size. This test uses a direct restore from the object repository, which was introduced in Veeam Backup & Replication v12.
Table 8. Block size and restore time
Block size KB
Restore time (secs)
8,192
117
4,096
121
1,024
165
The following chart shows restore size and block size.
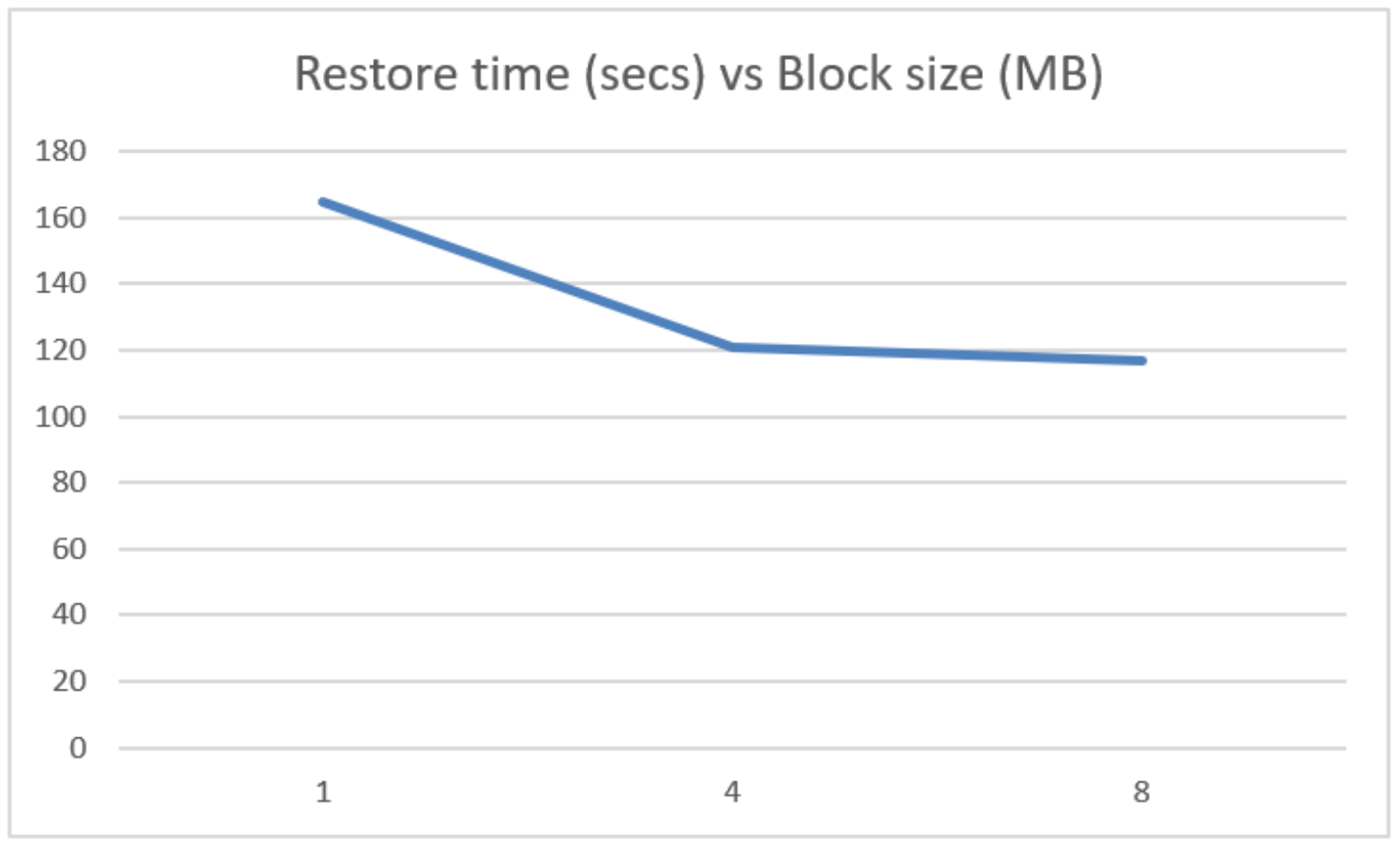
As with writes, increasing the block size from the default 1 MB to 4 MB significantly decreases the restore time for a single VM, with 8 MB block size only slightly faster.
Backup jobs deletion times and block size
In this test, each backup job is deleted from disk, which removes the backup set from the performance tier and then from the capacity tier.
Block size KB
Delete time (secs)
No. of objects
8,192
37
41,612
4,096
45
82,044
1,024
101
164,088
The following chart shows delete time and block size.
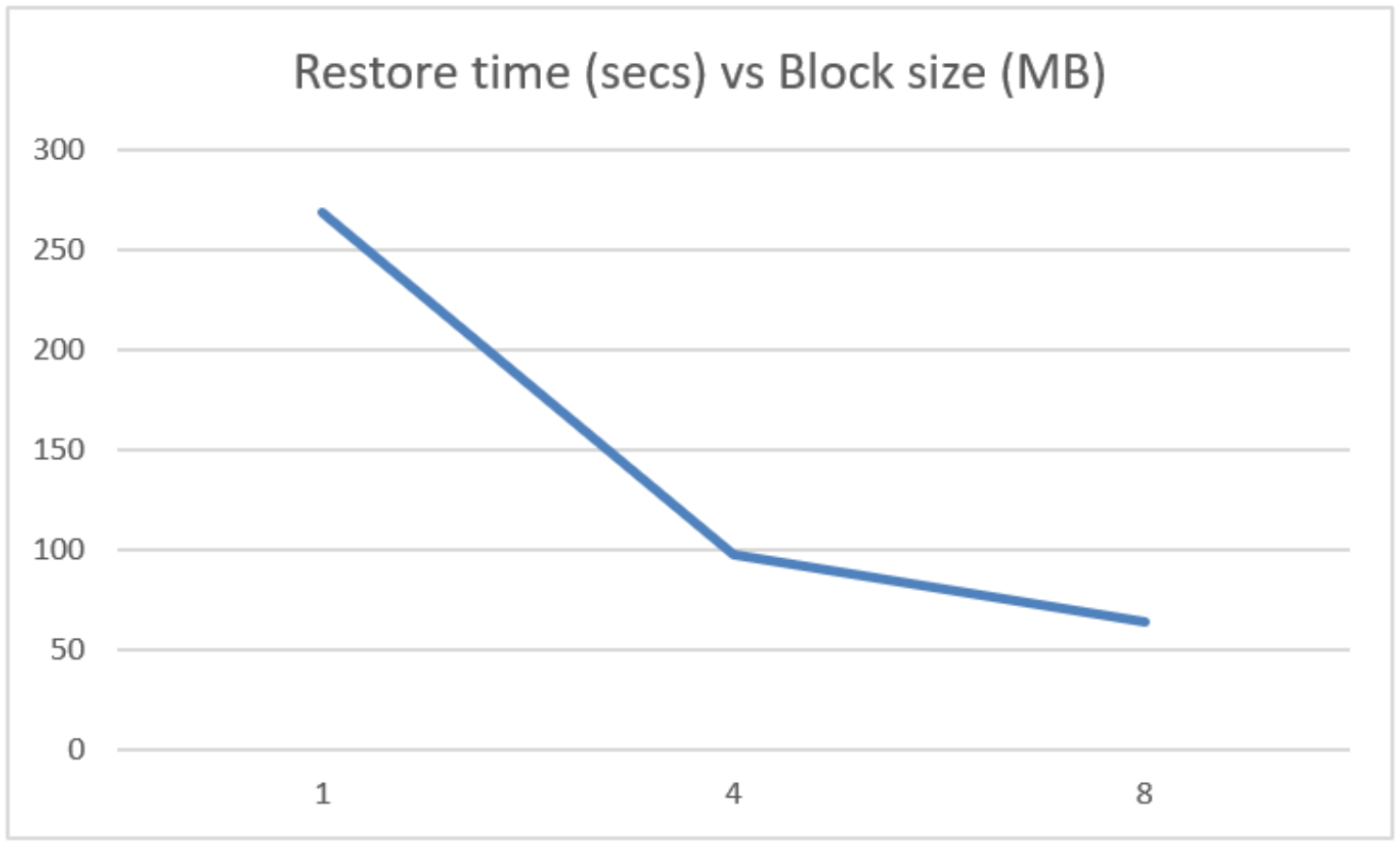
Block size has a significant effect on how long it takes to delete a backup job.
Summary
The default 1 MB block size for Veeam backup jobs is a good starting size. Increasing the block size to 4 MB does not significantly increase write throughput but read response and deletion times do improve with the increased block size and provide good backup job deletion times.
We recommend that you do not use block sizes below the 1Mb default. Although you may see improvement in backups and restores with larger block sizes, the default is usually a good starting position.
Note: For more information about setting the backup block size, see Object Storage: Impact of Job Storage Optimization Settings (in v11) on the Veeam Community site.
