Home > Storage > PowerScale (Isilon) > Product Documentation > Data Protection > High Availability and Data Protection with Dell PowerScale Scale-Out NAS > Writable snapshots
Writable snapshots
-
Introduced in OneFS 9.3, writable snapshots enable the creation and management of a space-efficient and time-efficient, modifiable copy of a regular OneFS snapshot. As such, they present a writable copy of a source snapshot, accessible at a directory path within the /ifs namespace. The snapshot can be accessed and edited through the use of any of the cluster’s file and object protocols, including NFS, SMB, and S3.
The writable snapshot architecture provides an overlay to a read-only source snapshot. This architecture allows a cluster administrator to create a lightweight copy of a production dataset using a simple CLI command, and present and use it as a separate writable namespace.
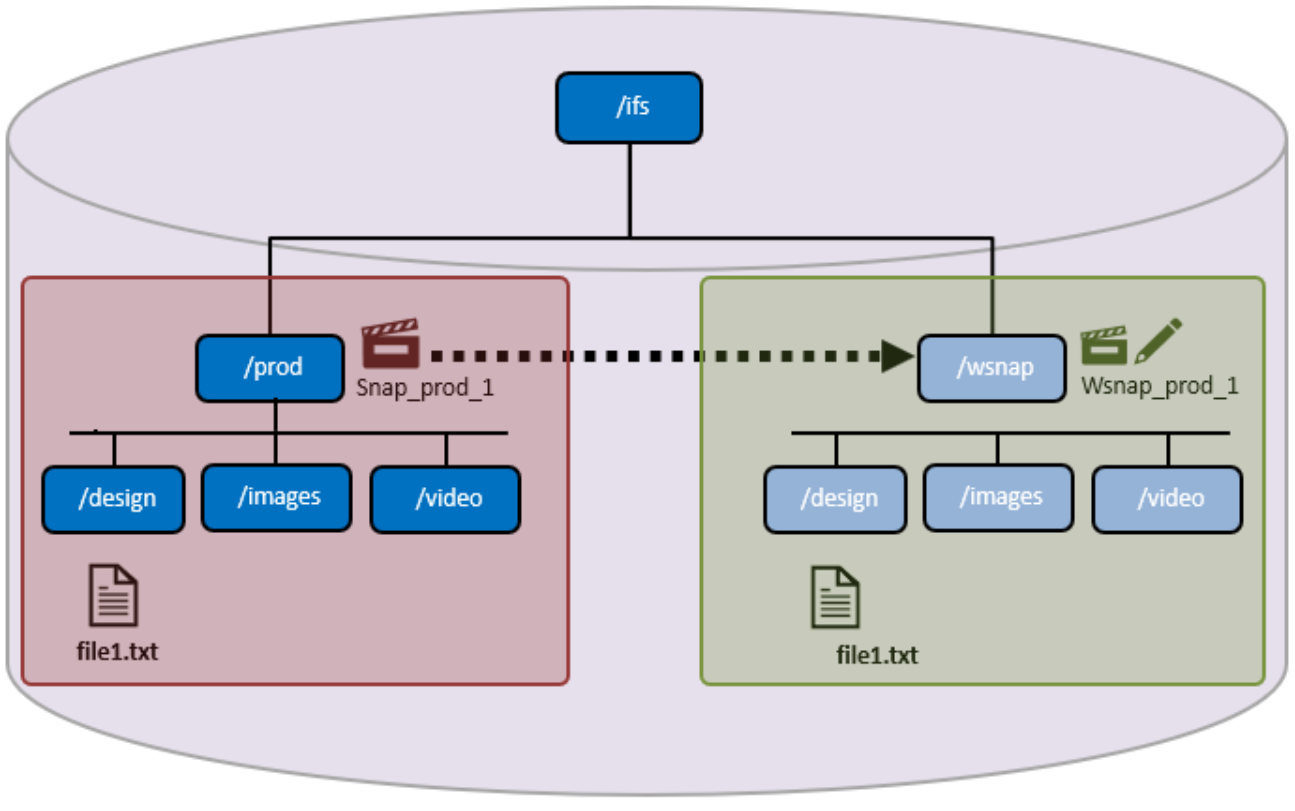
Writable snapshots
A writable snapshot contains the same subdirectory and file structure as the original prod directory, but without the added data capacity footprint.
OneFS 9.3 introduced a new protection group data structure, PG_WSNAP, which provides an overlay that allows unmodified file data to be read directly from the source snapshot while storing only the changes in the writable snapshot tree. When files within a newly created writable snapshot are first accessed, data is read from the source snapshot, populating the files’ metadata, in a process known as copy-on-read, or CoR. Unmodified data is read from the source snapshot and any changes are stored in the writable snapshot’s namespace data structure (PG_WSNAP).
Since a new writable snapshot is not copy-on-read up front, its creation is extremely rapid. As files are later accessed, they are enumerated and begin to consume metadata space.
