Home > Workload Solutions > SQL Server > Guides > Reference Architecture Guide—Consolidate and Simplify Mixed Database Workloads > NOPM
NOPM
-
NOPM is a metric that is queried from the district table at the start and end of the TPC-C-like benchmark. Some constraints qualify whether a NOPM transaction can be recognized and counted. For example, the new order, payment, and order status transactions must have a response time of 5 seconds or less to be counted in the NOPM metric.
In this guide, we examine NOPM because it has value to the customer. NOPM indicates how fast a database can process transactions across databases and different infrastructures. In the context of these validation tests, the NOPM metrics apply to an enterprise entry-level storage array such as the PowerMax 2000.
The following figure shows the NOPM metrics for the OLTP use case baseline test.
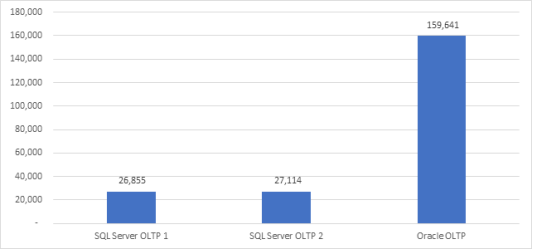
Figure 9. NOPM results for OLTP use case baseline test
We configured the two SQL Server OLTP databases identically for the TPC-C–like test, so their performance is very close in terms of NOPM. The Oracle OLTP database had four more vCPUs and 48 GB more memory allocated to the database, so its NOPM score is higher.
The DSS test does not involve running order-entry transactions. Therefore, we examine how this workload affects NOPM for the OLTP databases. The following figure shows the NOPM metrics for the OLTP and DSS tests running in parallel:
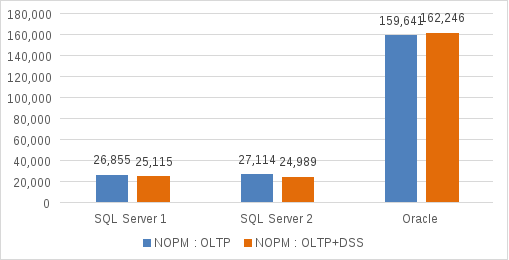
Figure 10. NOPM for OLTP workload with DSS workload running in parallel
Both SQL Server OLTP databases showed a minor loss in NOPM:
- SQL Server OLTP 1 achieved 25,115 NOPM—a difference of 1,740 from the first OLTP test.
- SQL Server OLTP 2 achieved 24,989 NOPM—a difference of 2,125 from the first OLTP test.
- The Oracle OLTP database NOPM value showed a performance improvement when the DSS workload was running in parallel. The Oracle database achieved 162,246 NOPMs—a gain of 2,605.
The snapshot OLTP databases simulated test and development activity by running a light OLTP workload on the system. The following figure shows the results:
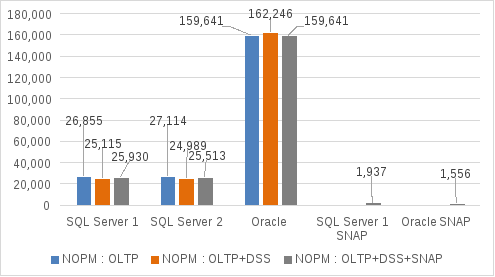
Figure 11. NOPM with OLTP, DSS, and snapshot OLTP workloads running in parallel
With all the workloads running in parallel both the OLTP SQL Server databases showed a positive performance difference:
- SQL Server OLTP 1 achieved 25,930 NOPM—a gain of 815 over the previous test.
- SQL Server OLTP 2 achieved 25,513 NOPM—a gain of 524 over the previous test.
- The Oracle OLTP database showed a slight loss of 2,605 NOPM from the previous test. (Coincidentally, that NOPM value matches that of the first test.)
The two snapshot databases on which we ran a light OLTP workload generated the following NOPM results:
- The SQL Server snapshot database achieved 1,937 NOPM.
- The Oracle snapshot database achieved 1,556 NOPM.
In terms of NOPM, the MX840c servers and PowerMax 2000 array showed consistent performance. Minor fluctuations, both positive and negative, occurred, but they did not indicate any significant performance impact. Overall, the reference architecture for mixed workloads demonstrated the consistent performance that is required for database and workload consolidation.
