Home > Integrated Products > VxRail > Guides > Design Guide—Dell Validated Design for SAP HANA Deployments with Dell VxRail Infrastructure > High availability
High availability
-
Automatic restart of SAP HANA VMs
If one of the hosts in the cluster fails, the vSphere high availability (HA) feature restarts a VM on another host that has enough free resources. We strongly recommend enabling this feature in a vSphere cluster with SAP HANA. The SAP HANA service automatic restart feature must be enabled in the SAP HANA software.
Enable the automatic restart feature during the SAP HANA installation or set autostart to 1 in the /hana/shared/<SID>/profile/<SID>_HDB<InstNo>_<hostname> file.
The minimum vSphere HA settings must be in place, as shown in the following figure:
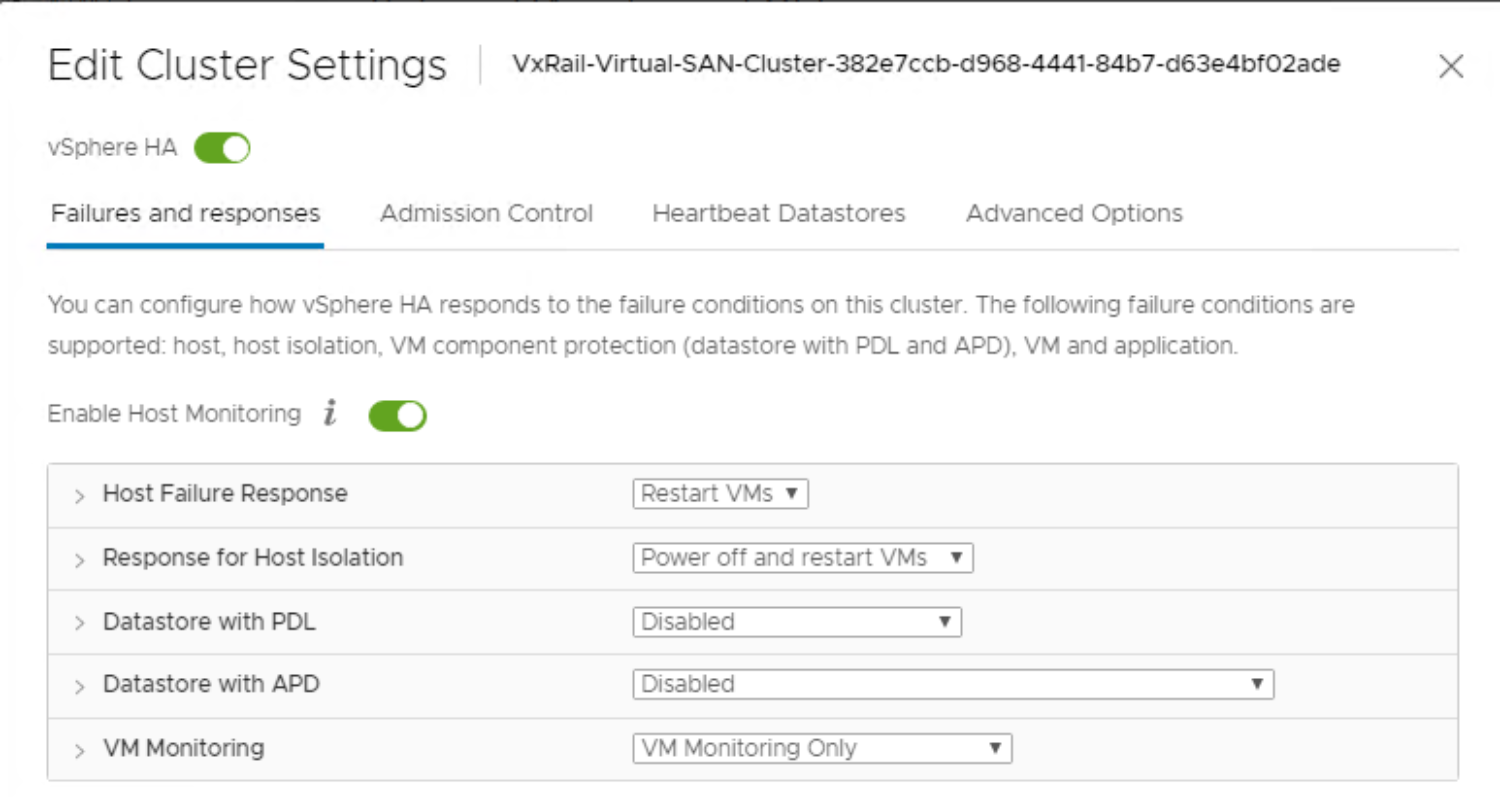
Figure 6. vSAN cluster HA settings
High availability for SAP HANA VMs
The SAP HANA service automatic restart watchdog function automatically detects a failure and restarts the corresponding SAP HANA process: nameserver, index server, and so on. This feature monitors the SAP HANA application and the associated services within a VM. The VMware HA “Guest not heartbeating” monitoring function restarts the guest operating system of the VM and SAP HANA on the same host. The monitoring feature also handles operating system failures if the SAP HANA automatic restart options are enabled.
Enable the heartbeat monitoring feature when vSphere HA is activated. The recommended setting for Heartbeat monitoring sensitivity is High, as shown in the following figure:
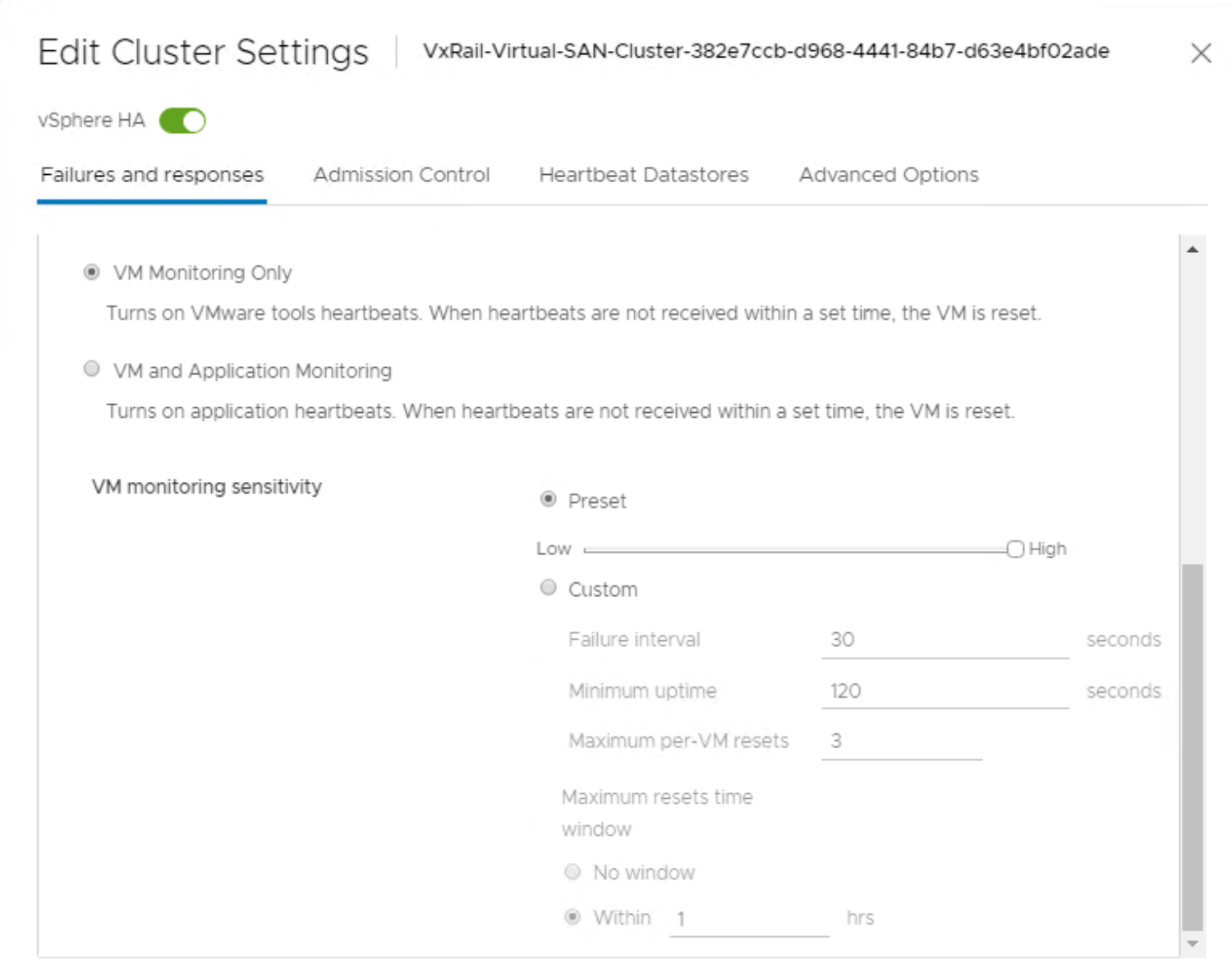
Figure 7. vSphere settings for VM monitoring
Enabling heartbeat monitoring requires that VMware Tools be installed and running in the VM. Install VMware Tools as part of the operating system open-vm-tools. Alternatively, use the vSphere web client and select Guest OS > Install VMware Tools in the VM context menu.
Note: For more information about VMware HA and virtualized SAP HANA HA best practices, see the “vSphere Clustering Service” section in the VMware vSphere best practices and reference architecture guide for SAP HANA.
VxRail vSAN stretched cluster support for SAP HANA systems
Stretched clusters extend the vSAN cluster from a single data site to a second site for a higher level of availability and cross-site load balancing. Stretched clusters are typically deployed in metropolitan or campus environments, where the distance between data centers is much smaller than in Wide Area Network (WAN) environments. Dell Technologies and VMware have collaborated to validate SAP HANA workloads in a vSAN stretched cluster environment using VxRail infrastructure. The validation was performed in Dell Technologies labs. For more information, see Appendix B: VxRail stretched cluster validation environment. As a result of the joint validation, SAP HANA is supported on VxRail vSAN stretched cluster 7.0 U1/U2 environments by Dell Technologies and VMware for vSAN-based HCI solutions.
Because stretched clusters are typically deployed in campus-wide environments, distances of up to 5 km are supported. The SAP HANA latency requirement for log file writes is less than 1 millisecond (ms). Lab tests that Dell Technologies has conducted show that it is possible to achieve distances of up to 30 km between the two sites while still achieving the SAP HANA performance throughput and latency KPIs. Note that actual distances might be lower because the network latency depends on the network components and architecture that are used across the primary and secondary sites.
The sites must be connected by a high bandwidth/low latency network. The underlying network infrastructure plays a key role for SAP HANA because the distance supported between the two sites depends solely on the ability to achieve a write log latency of 1 ms across these sites. For more information, see SAP HANA on Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) Solutions Powered by VMware vSAN.
Note: Customers must test the vSAN stretched cluster and SAP HANA performance across both sites in their own environments to ensure that the sub-ms log latency is achieved.
High availability and maintenance
Stretched clusters can be used to manage planned maintenance and avoid disaster scenarios because maintenance or loss of one site does not affect the overall operation of the cluster. In a stretched cluster configuration, both data sites are active sites. Local failures can be compensated by providing HA capacity at a site. Then, if either site fails, vSAN uses the storage on the remaining site. A site failover is achieved by providing enough compute and memory capacity at the opposite site. vSphere HA restarts any VM requiring a restart on the remaining site. Designate one site as the preferred production site. The other site becomes a secondary or nonpreferred site. If the network connection between the two active sites is lost, vSAN continues operation within the preferred site. The site that is designated as preferred is typically the site that remains in operation unless it is resynced or experiences another issue. The site that leads to maximum data availability is the site that remains in operation.
Each vSAN stretched cluster configuration requires a witness host. The witness must reside on a third site that has independent paths to each data site. While the witness host must be part of the same vCenter as the hosts in the data sites, this host must not be on the same cluster as the data site hosts.
For requirements and best practices for using stretched clusters with VxRail appliances, see the Dell EMC VxRail 7.0 vSAN Stretched Cluster Planning Guide.
SAP HANA stretched cluster VM storage policy
For an SAP HANA VM in a vSAN stretched cluster, enhance the VM storage policy to Dual site mirroring (stretched cluster) and set Failures to tolerate to 1 failure – RAID 1 (Mirroring), as shown in the following figure:

Figure 8. Setting the SAP HANA VM storage policy in a vSAN stretched cluster
When Site disaster tolerance is set to Dual site mirroring, copies of the data go to both sites. With a Primary Failures to Tolerate (PFFT) policy set to 1, writes continue to be mirrored across sites, doubling the disk capacity that is required on each site if all VMs are to be mirrored. Mirroring the storage of every VM across sites is not required. Nonproduction SAP HANA instances or supporting applications (that is, applications that are not sharing CPU sockets or cores with SAP HANA production systems) can still use a vSAN storage policy where PFTT is set to none, restricting these VMs to one of the sites. This solution might be desirable in cases where the application should not perform a site failover—for example, a site-specific backup solution or SAP application servers.
