

Analyzing How Gen4 NVMe Drive Performance Scales on the PowerEdge R7525
Download PDFMon, 16 Jan 2023 13:44:23 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
Gen4 NVMe drives double the PCIe speeds of Gen3 from 1GB/s to 2GB/s per lane, effectively increasing the performance capability by two times. However, users also need to understand how Gen4 NVMe performance scales when more than one drive is loaded into a populated server running workloads. This DfD will analyze how various IO profiles scale when more than one Gen4 NVMe drive is loaded into a PowerEdge R7525.
PCIe 4.0 History and Gen4 NVMe Scaling
PCIe 4.0 was released in 2019, following its predecessor with double the bandwidth (up to 64GB/s), bit rate (up to 16GT/s) and frequency (up to 16GHz). AMD released the first motherboards to support PCIe
4.0 in early 2020, while Intel motherboards with PCIe 4.0 support are scheduled to begin releasing by the end of 2020. Gen4 NVMe drives were introduced shortly after the release of PCIe 4.0 to capitalize on its specification improvements; allowing performance metrics to double (if the same number of lanes are used).
Although these numbers look enticing at first glance, very little data has been gathered around how Gen4 NVMe drives perform when scaled in a datacenter server running workloads. What is the sweet spot? When does the performance curve begin to plateau? The Dell Technologies engineering team constructed an in-house test setup to obtain data points that will help users understand IOPS and bandwidth trends when scaling Gen4 NVMe drives.
Test Setup
The PowerEdge R7525 was used as the host server, as it s one of the first Dell EMC servers to support PCIe 4.0.

Figure 1 - Samsung PM1733 Gen4 NVMe
The Samsung PM1733 Gen4 NVMe drive was connected using CPU direct attach and then scaled. Measurements were taken for 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 drives. The IOmeter benchmark was used to simulate data center workloads running on NVMe drives to achieve the maximum raw performance data. FIO was used as a supplemental benchmark as well. *Note that these benchmark results are not directly applicable to file systems or application workloads.
Random reads (RR) and writes (RW) were measured in Input/Output operations per second (IOPS). Online Transaction Processing (OLTP), useful for measuring database workloads, is also measured in IOPS. Sequential reads (SR) and writes (SW) were measured in mebibyte per second (MiBPs).
Test Results
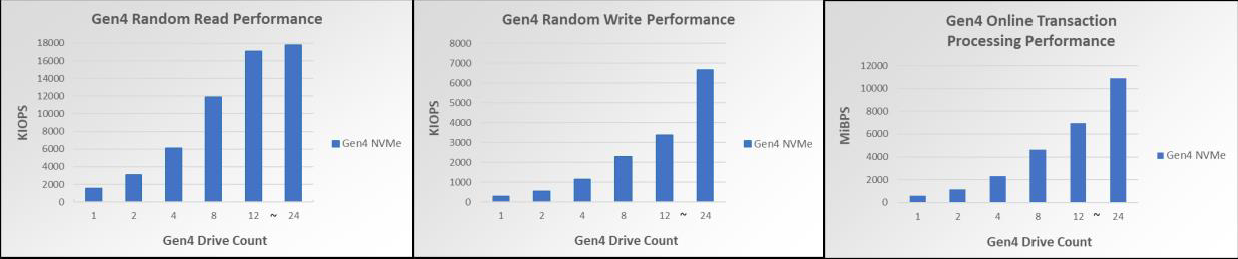
Figure 2 – Gen4 NVMe RR perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 3 –Gen4 NVMe RW perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 4 – Gen4 NVMe OLTP perf scaling per drive for up to 24 drives
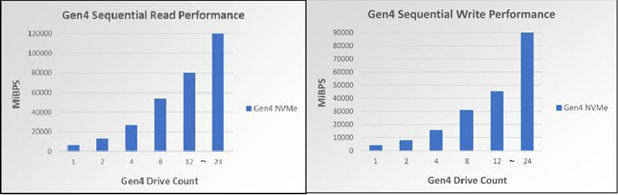
Figure 5 –Gen4 NVMe SR perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 6 –Gen4 NVMe SW perf scaling for up to 24 drives
As seen in Figures 2-6, the Gen4 NVMe drives have remarkable performance. One Gen3 NVMe drive commonly has 4K RR performance in the triple-digit KIOPS, but one Gen4 NVMe drive is within the quad-digit KIOPS for 4K RR. Scaling to 12 Gen4 NVMe drives shows 17M 4KiB RR IOPS, allowing for extraordinary amounts of data to be read randomly from the disk at one time. Scaling to 12 Gen4 NVMe drives also has a notable 80.41GiBs at 128KiB, a number very close to the theoretical maximum line rate of 94.5 128K SR GBPS. Lastly, 4K OLTP benchmark speeds are also nearly 2 times faster than Gen3 NVMe drives.
Furthermore, these bar graphs demonstrate that each profile scales linearly for up to 12 drives. The benchmarked synthetic workloads received linear performance improvements with up to 12 NVMe drives scaled, and each performance readout also scaled very closely to its theoretical maximum. However, once the jump from 12 to 24 drives is made, two of the IO profiles (in particular, the RR and SR profiles) stop scaling linearly and become less optimized. When accounting for the fact CPU utilization is at 90%, it is to be expected that scaling beyond 12 drives will not give linear performance increases for all IO profiles.
Conclusion
Customers seeking to scale their Gen4 NVMe drives will be pleased to know that all IO Profile performance readings scaled linearly for up to 12 drives, while only some of the IO Profiles did for up to 24 drives. Servers and systems running workloads like data analytics, AI, ML, DL and databases can greatly benefit from this increase in IOPS and throughput when scaling Gen4 NVMe devices for up to 12 drives.
Related Documents

Boosting Storage Performance and Resilience with the Dell PERC H755N NVMe RAID Controller
Mon, 16 Jan 2023 23:47:32 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
Hardware RAID technology adds an extra level of resilience to a server’s storage capability. RAID levels like 1, 5, and 6 allow seamless recovery from drive failures. With the Dell PERC H755N, Next Gen Dell PowerEdge servers now support hardware RAID with NVMe drives. This adds an extra level of resilience to the fantastic performance of NVMe.
Introduction
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) has been around for many years. It allows for increased resilience and reliability for critical storage applications. RAID levels of 1, 5, 6, 10, 50 and 60 offer different levels of redundancy. Depending on the application requirements and business limitations, a specific RAID level could be chosen.
With the advent of NVMe SSDs, storage performance got a tremendous boost. Hardware RAID solutions of the time were not capable of keeping up with the NVMe interface. Software RAID was a potential solution, but it lacked some key HW RAID advantages like low CPU overhead and battery backup for data in flight.
The new Dell PERC H755N changes that limitation. Sitting in a x8 PCIe Gen4 slot, each H755N RAID Controller supports up to 8 NVMe drives, connected with a x2 PCIe Gen4 interface. This ensures that the RAID Controller can keep up with the sheer bandwidth supported by NVMe drives.
The TPCx-V Benchmark
The TPCx-V Benchmark measures the performance of a virtualized server platform under a demanding database workload. It stresses CPU and memory hardware, storage, networking, hypervisor, and the guest operating system. The workload is database-centric and models many properties of cloud services, such as multiple VMs running at different load demand levels1.
This benchmark is a great real-world benchmark for a very common customer use case. It runs a variety of database workloads, and even varies the workload depending on the size of the virtual machine. One of the requirements of TPCx-V is to ensure redundancy in the system under test. This means that the system should be able to recover from hardware failures of field replaceable items including drives and/or storage controllers.
TPCx-V and the Dell PowerEdge R7525
The Dell PowerEdge R7525 is a very versatile server that can be used for a variety of applications. It can be configured with up to 2 redundant H755N NVMe RAID Controllers, and 2 of the AMD Epyc 3rd Generation of processors. The AMD Epyc 3rd Generation of processors offers up to 64 cores per socket, for a total of up to 128 cores. They also support 8 channels of DDR3200 memory per socket with up to two DIMMs per channel. This totals up to 4TB of RAM if 128GB DIMMs are used. It also features up to 160 lanes of PCie Gen4 connectivity for maximum versatility.
All of the above means that the Dell PowerEdge R7525 is a strong candidate for the TPCx-V benchmark. The number of cores and the support for high speed memory is very suited for virtualization use cases. The AMD Epyc 3rd Generation of processors has also been found to be great for database kind of workloads. The available redundant NVMe RAID Controllers ensures that the storage would be able to withstand failures while also providing exceptional NVMe type performance.
Results
The TPCx-V benchmark was run on a Dell PowerEdge R7525 with dual H755N RAID Controllers, and the AMD Epyc 7713 processors. This is 64 core processor from the AMD Epyc 3rd generation of CPUs. The system was configured with 6 NVMe drives per controller.
The output was a benchmark score of 2800 TpsV, which is 22.8% higher than the previous world record score. The previous world record was run on a platform with 2 64 core AMD Epyc 2nd generation of processors and 10 SATA SSDs per controller. The ability of the configuration to achieve the much higher score with almost half the number of drives highlights the performance advantages of the NVMe RAID Controller over a configuration with SATA SSDs
Conclusion
The Dell PowerEdge R7525 running AMD Epyc 3rd Generation of processors and leveraging the Dell PERC H755N NVMe RAID Controllers is shown to be a leading performer for database kind of workloads running in virtualized environments.

Analyzing How Gen4 NVMe Drive Performance Scales on the PowerEdge R7525
Mon, 16 Jan 2023 23:31:22 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
Gen4 NVMe drives double the PCIe speeds of Gen3 from 1GB/s to 2GB/s per lane, effectively increasing the performance capability by two times. However, users also need to understand how Gen4 NVMe performance scales when more than one drive is loaded into a populated server running workloads. This DfD will analyze how various IO profiles scale when more than one Gen4 NVMe drive is loaded into a PowerEdge R7525.
PCIe 4.0 History and Gen4 NVMe Scaling
PCIe 4.0 was released in 2019, following its predecessor with double the bandwidth (up to 64GB/s), bit rate (up to 16GT/s) and frequency (up to 16GHz). AMD released the first motherboards to support PCIe 4.0 in early 2020, while Intel motherboards with PCIe 4.0 support are scheduled to begin releasing by the end of 2020. Gen4 NVMe drives were introduced shortly after the release of PCIe 4.0 to capitalize on its specification improvements; allowing performance metrics to double (if the same number of lanes are used). Although these numbers look enticing at first glance, very little data has been gathered around how Gen4 NVMe drives perform when scaled in a datacenter server running workloads. What is the sweet spot? When does the performance curve begin to plateau? The Dell Technologies engineering team constructed an in-house test setup to obtain data points that will help users understand IOPS and bandwidth trends when scaling Gen4 NVMe drives.

Figure 1 - Samsung PM1733 Gen4 NVMe
Test Setup
The PowerEdge R7525 was used as the host server, as it is one of the first Dell EMC servers to support PCIe 4.0. The Samsung PM1733 Gen4 NVMe drive was connected using CPU direct attach and then scaled. Measurements were taken for 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 drives. The IOmeter benchmark was used to simulate data center workloads running on NVMe drives to achieve the maximum raw performance data. FIO was used as a supplemental benchmark as well. *Note that these benchmark results are not directly applicable to file systems or application workloads.
Random reads (RR) and writes (RW) were measured in Input/Output operations per second (IOPS). Online Transaction Processing (OLTP), useful for measuring database workloads, is also measured in IOPS. Sequential reads (SR) and writes (SW) were measured in mebibyte per second (MiBPs).
Test Results

Figure 2 – Gen4 NVMe RR perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 3 –Gen4 NVMe RW perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 4 – Gen4 NVMe OLTP perf scaling per drive for up to 24 drives

Figure 5 –Gen4 NVMe SR perf scaling for up to 24 drives Figure 6 –Gen4 NVMe SW perf scaling for up to 24 drives
As seen in Figures 2-6, the Gen4 NVMe drives have remarkable performance. One Gen3 NVMe drive commonly has 4K RR performance in the triple-digit KIOPS, but one Gen4 NVMe drive is within the quad-digit KIOPS for 4K RR. Scaling to 12 Gen4 NVMe drives shows 17M 4KiB RR IOPS, allowing for extraordinary amounts of data to be read randomly from the disk at one time. Scaling to 12 Gen4 NVMe drives also has a notable 80.41GiBs at 128KiB, a number very close to the theoretical maximum line rate of 94.5 128K SR GBPS. Lastly, 4K OLTP benchmark speeds are also nearly 2 times faster than Gen3 NVMe drives.
Furthermore, these bar graphs demonstrate that each profile scales linearly for up to 12 drives. The benchmarked synthetic workloads received linear performance improvements with up to 12 NVMe drives scaled, and each performance readout also scaled very closely to its theoretical maximum. However, once the jump from 12 to 24 drives is made, two of the IO profiles (in particular, the RR and SR profiles) stop scaling linearly and become less optimized. When accounting for the fact CPU utilization is at 90%, it is to be expected that scaling beyond 12 drives will not give linear performance increases for all IO profiles.
Conclusion
Customers seeking to scale their Gen4 NVMe drives will be pleased to know that all IO Profile performance readings scaled linearly for up to 12 drives, while only some of the IO Profiles did for up to 24 drives. Servers and systems running workloads like data analytics, AI, ML, DL and databases can greatly benefit from this increase in IOPS and throughput when scaling Gen4 NVMe devices for up to 12 drives.


