The New PowerEdge T350
Download PDFTue, 17 Jan 2023 07:40:19 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
The Dell EMC PowerEdge T350 offers customers peak performance and enterprise features within a significantly smaller form factor – 37% smaller to be exact. The sleek new chassis was intentionally designed for the powerful T350 tower by shrinking the unused space inside - right-sizing the box so it can reside in smaller spaces that SMB, Edge and ROBO customers intend to deploy it at. This DfD was written to brief readers of the advantages brought to the PowerEdge T350, including improved performance, new features, and its smaller form factor.
Right-Sized for Deployment Anywhere
The new Dell EMC PowerEdge T350 chassis is 37% smaller than its predecessor, the T340. This decision was pioneered by feedback from customer feedback and sales data, which consistently pointed to one clear consensus – customers valued a smaller sized box.
This value proposition pushed our development team to forego the option of leveraging the T550 chassis design (to reduce cost) and to focus on developing a right-sized T350 chassis to best accommodate customers outside of the datacenter. By shrinking unoccupied space within the server, the dimensions reduced from 17.45” x 8.6” x 23.19” (T340) to 14.6” x 6.9” x 22” (T350) – a significant decrease in volume. What’s even more impressive is that no features or hardware support were removed to enable this change!

Figure 1 – Visual aid comparing the size of the T350 (left) and the T340 (right)
Right-sizing the mainstream T350 will be most advantageous to SMB customers deploying in remote offices, as this new, smaller solution is able to deliver higher performance technologies while in a quieter and more management-friendly enclosure. As explained in the next few paragraphs, many new features implemented onto the T350 will bring new levels of performance to SMB workloads like collaboration, file sharing, database, mail/messaging and web hosting.
Latest Hardware, New Features
Despite being 37% smaller, the PowerEdge T350 is packed with the latest hardware and new features to bring higher levels of performance, versatility, and optimization to your organization:
- The latest Intel® Xeon® E-2300 Processors offer a 19% increase of IPC (instructions per cycle) while also increasing IGP cores, L1 cache speed and L2 cache speed, allowing for up to 28% faster IO speeds when compared to the Xeon® E-2200 processor family.
- Supported UDIMM speeds have increased by 20% to 3200 MT/s and the max capacity per UDIMM has doubled from 16GB to 32GB. Having more memory at faster speeds will significantly reduce data transfer times, resulting in increased productivity.
- Up to 8x 2.5” or 3.5” SATA/SAS drives can be hosted on the backplane. Additionally, up to 2x M.2 drives are now hot-swappable with Dell Technologies BOSS-S2 card, allowing the server to keep running when a critical component swap is needed.
- Support for twenty lanes of PCIe Gen4 will double I/O throughput from 8GT/s to 16GT/s, effectively cutting transfer times in half for data traveling from storage to CPU.
In addition to the latest hardware and new feature support, customers will always get the high- quality enterprise features that the PowerEdge brand is known for, including:
- iDRAC9 which provides administrators with an abundance of server operation information to a dashboard screen that can be remotely accessed and managed.
- UEFI Secure Boot which has better programmability, scalability, security, booting speeds, feature support and user-friendliness than legacy BIOS.
- Redundant fans, PSUs, and hard drives
- Storage controllers that support HW RAID for SATA, SAS and NVMe interfaces
Performance Improvements
Dell Technologies ran internal testing comparing the T350 and T340 SPECrate® 2017_int_base results, which measures the ability to process identical programs on each of its available threads in parallel (or throughput, in layman’s terms). Both configurations were identical with the processor being the independent variable. The PowerEdge T350 used the latest Intel® Xeon® E-2300 processors while the older PowerEdge T340 used Intel® Xeon® E-2200 processors. As seen in Figure 2 below, each processor SKU from top bin to bottom bin observed a performance increase ranging from 14.8% to 32.3%. More information on these studies can be read here.
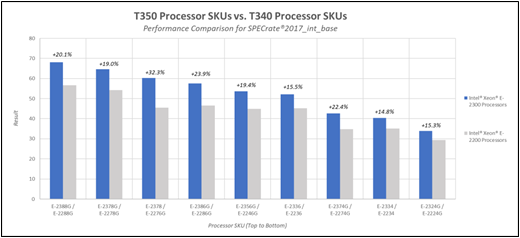
Figure 2 –SPECrate® 2017_int_base results for T350 CPUs (blue) vs. T340 CPUs (gray)
Dell Technologies also commissioned Grid Dynamics to carry out performance testing in retail and VDI environments to simulate tangible customer use-cases. Figure 3 below illustrates that, on average, the PowerEdge T350 performs I/O operations 36.1% faster than the T340 for the same amount of video streams. Figure 4 below illustrates that, on average, the PowerEdge T350 speed of transaction commits for the same size database is 37% higher than the T340. The scientific report can be read here and the executive summary can be read here.
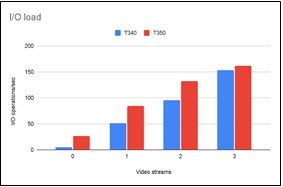
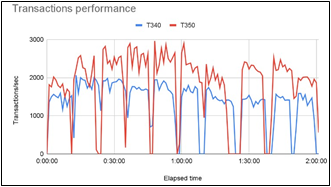
Figure 4 – Comparison of transactions committing speed
Conclusion
The Dell EMC PowerEdge T350 offers customers peak performance and new enterprise features within a right-sized form factor, so it can reside in smaller spaces to drive business growth where SMB, Edge and ROBO customers intend to deploy it at.
Related Documents
Top 5 Reasons to Migrate to the PowerEdge T550 from the Previous-Generation T440 and T640
Tue, 17 Jan 2023 08:25:05 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
The Dell EMC PowerEdge T550 is the next-generation performance mainstream tower by Dell Technologies. By consolidating the most valuable features from the previous-generation T440 and T640, the T550 is offered as the successor intended to run performance use cases and workloads in medium businesses, Edge, ROBO and enterprise data centers. This DfD will inform readers on how decision making led to merging the T440 and T640 into the T550, as well as give five top reasons why customers will be excited to transition over to this new powerhouse - the T550.
Merging the T440 and T640
Development of the PowerEdge T550 heavily focused on aligning what it would offer to what customers actually used in ROBO, Edge, SMB, and enterprise datacenter environments. Sales data from the previous-generation T440 and T640 were often used to navigate decision-making and generally pointed to a clear, general consensus. A few examples are below:
- GPU attach rates on the more-capable T640 were rarely populated in full, resulting in under-utilized space
- Specific desirable features in the T640, such as NVMe support, were not present in the T440
- Top bin CPU support was not present in the T440
These observations allowed engineering to refine what the next performance mainstream PowerEdge tower would look like. By eliminating the less desirable features and keeping the most valuable ones, the T550 has essentially merged both of its predecessors into a handcrafted, next-generation powerhouse. The remainder of this DfD will highlight the top five reasons why we believe our customers will benefit from transitioning over to the T550, a few of which are direct results from the merger.
*Please note that the T640 lifecycle is extended to mid-2022 for customers who choose to stay on 2nd Generation Xeon®, and the T440 lifecycle is extended until mid-2023 for customers who choose to bridge from 2nd Generation Xeon® to 4th Generation Xeon®
Figure 1 – Side angle of the sleek, new PowerEdge T550
Five Most Valuable Impacts
3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors
The 3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor family was designed to generate higher productivity and operational efficiency for dense workloads, such as AI, ML/DL and HPC. In addition to full-stack support for the T550, various architectural design refinements have returned significant performance improvements across multiple benchmarks, including:
- SPECrate 2017 (a throughput measurement metric) observed a 57.1% performance improvement for Floating Point when compared to 2nd Generation Xeon, as published here
- SPECspeed 2017 (a time-based measurement metric) observed a 50.3% performance improvement for Floating Point when compared to 2nd Generation Xeon, as published here
- Gen-on-Gen performance improvement average of 1.46x, as observed by Intel
Top-of-the-line features are integrated into 3rd Generation Xeon Scalable CPUs to give users more functionality. Enhanced Speed Select Technology (SST) functionalities, including base frequency, core power, and turbo frequency, offers a finer control over CPU performance for cost optimization. Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX) offers maximum privacy and protection by encrypting sections of memory to create highly secured environments to store sensitive data.
3200 MT/s Memory Speed
Memory speeds have risen by 20% over the previous-generation T440 and T640, increasing from 2666 MT/s to 3200 MT/s. Additionally, the number of supported memory slots has jumped from 6 to 8 – a 33% increase in DIMM capacity. Allowing more data to be stored in memory, with faster DIMM speeds, will significantly reduce data transfer times for memory-intensive workloads like databases, CRM, ERP, or Exchange.
PowerEdge Enterprise Features
The PowerEdge advantage lies within the robust environment offered to enterprise customers. The PowerEdge Raid Controller 11 (PERC11) now provides NVMe HW RAID, granting users the ability to back up data from their most powerful storage devices. In addition to hard drives, fans, PSUs, and Internal Dual SD Modules (IDSDM), hot-plug support is now also offered for front access BOSS (2x M.2 internal), allowing the server to keep running when a critical component swap is needed. Even the T550s smaller form factor (10% less volume than T440 and 15% less volume than T640) now allows GPUs to be used in tower format, so that max performance can be achieved whether in the datacenter or in the office closet.
Legacy Boot support has been deprecated by Intel and replaced with the superior UEFI Secure Boot (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which has better programmability, greater scalability, and higher security. UEFI Secure Boot also provides faster booting times and support for 9ZB, while legacy BIOS is limited to 2.2TB boot drives. Lastly, although not a newly supported feature, customers can continue to optimize server management with iDRAC9 (Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller), which provides administrators with an abundance of server operation information to a dashboard screen that can be remotely accessed and managed. Countless operational conditions are always monitored, giving small businesses more flexibility to allocate limited resources and manpower elsewhere.
PCIe Gen4
Support for five slots of PCIe Gen4, the fourth iteration of the PCIe standard, is now included. Compared to PCIe Gen3, the throughput per lane doubles from 8GT/s to 16GT/s, effectively cutting transfer times in half for data traveling from PCIe devices to CPU. This feature will be extremely effective for customers adopting dense components, like NVMe drives or GPUs.
MVP (Most Valuable Peripherals)
Decision making for peripheral support came as a direct result from the T440 and T640 merger. Sales data indicated what customers valued most, and the T550 achieved a perfectly balanced blend of storage, PCIe and GPU capability. To begin, the number of storage devices supported was met in the middle, with availability for up to 24x SAS/SATA drives (T440 maxed out at 16x, and the T640 maxed out at 32x). This also includes NVMe drives support, with the inclusion of an 8x SAS/SATA + 8x NVMe configuration! *Note that customers seeking 32x SAS/SATA drives can still leverage the T640 tower until mid-2022, or R740xd2 rack if that is a better suited solution.
The number of PCIe slots were also blended, with five slots available for x16 PCIe Gen4, and one slot available for x8 PCIe Gen3. This is a great compromise, as customers will still be receiving more total lanes (88 lanes on T550 vs. 64 lanes on T640). Lastly, after observing low GPU attach rates on the T640, the T550 offers up to 2x DW or 5x SW GPUs – a much more accurate representation of what customers have been using for AI/HPC workload support. The latest and greatest GPU models are now supported, including the NVIDIA T4, A10, A30 and A40. Lastly, NVLink bridging can now be utilized to create a high-bandwidth link between compatible GPUs! This will drive performance for workloads like databases, virtualization, and medium duty AI/ML.
Performance Comparison
Dell Technologies commissioned Grid Dynamics to validate the performance uplift for various T550 use cases when compared to the previous-generation T640. Figures 2-4 below illustrate just a few examples of the boosted performance seen on the T550. The full whitepaper can be seen here.
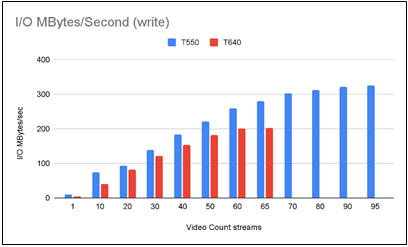
Figure 2 – I/O operations comparison for processing the same amount of retail video streams. The T550 does I/O writing 26.26% faster than T640.
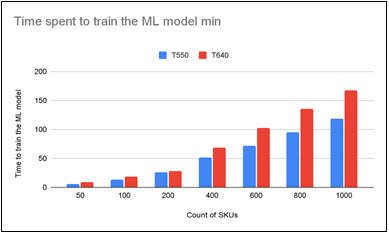
Figure 3 – Comparison of time spent to train an ML model depending on the number of SKUs for retail inventory decision making. The T550 uses 25.77% less time to train the ML model than T640.
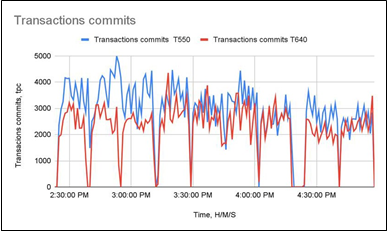
Figure 4 – Comparison of transactions committing speed when measuring database-related operations over a VM. The speed of transaction commits is 19.8% higher on the T550 compared to T640.
Final Words
The PowerEdge T550 has been handcrafted to offer a wide array of customers the most valuable features and support for performance workloads such as data analytic, virtualization, and medium duty AI/ML, in addition to more mainstream workloads such as collaboration, database, and CRM.

Memory Bandwidth for New PowerEdge Servers is Significantly Improved with Ice Lake Architecture
Tue, 17 Jan 2023 05:59:57 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
New PowerEdge servers fueled by 3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors can support sixteen DIMMs per CPU and 3200 MT/s memory speeds. This DfD will compare memory bandwidth readings observed on new PowerEdge servers with Ice Lake CPU architecture against prior-gen PowerEdge servers with Cascade Lake CPU architecture.
Ice Lake CPU Architecture
3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, known as Ice Lake processors, are the designated CPU for new Dell EMC Intel PowerEdge servers, like the R650 and R750. Compared to prior-gen 2nd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, Ice Lake architecture will support 33.3% more channels per CPU (an increase from six to eight) and 9.1% higher memory speeds (an increase from 2933 MT/s to 3200 MT/s.)
Performance Data
To quantify the impact of this increase in memory support, two studies were performed. The first study (see Figure 1) measured memory bandwidth determined by the number of DIMMs per CPU populated. The second study (see Figure 2) measured memory bandwidth determined by the number of CPU thread cores. Both STREAM bandwidth benchmarks have Ice Lake populated with eight 3200 MT/s DIMMs per channel, and Cascade Lake populated with six 2933 MT/s DIMMs per channel.
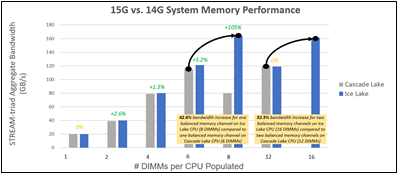
Figure 1 – Ice Lake and Cascade Lake bandwidth comparison by # of DIMMs per CPU
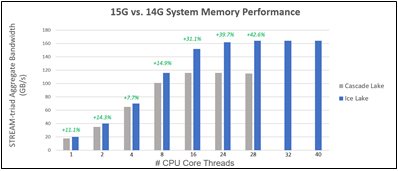
Figure 2 – Ice Lake and Cascade Lake bandwidth comparison by # of CPU core threads