
Boost Performance on Dell EMC HCI Solutions for Microsoft Server using Intel Optane Persistent Memory
Wed, 16 Jun 2021 13:35:49 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Modern IT applications have a broad range of performance requirements. Some of the most demanding applications use Online Transactional Processing (OLTP) database technology. Typical organizations have many mission critical business services reliant on workloads powered by these databases. Examples of such services include online banking in the financial sector and online shopping in the retail sector. If the response time of these systems is slow, customers will likely suffer a poor user experience and may take their business to competitors. Dissatisfied customers may also express their frustration through social media outlets resulting in incalculable damage to a company’s reputation.
The challenge in maintaining an exceptional consumer experience is providing databases with performant infrastructure while also balancing capacity and cost. Traditionally, there have been few cost-effective options that cache database workloads, which would greatly improve end-user response times. Intel Optane persistent memory (Intel Optane PM) offers an innovative path to accelerating database workloads. Intel Optane PM performs almost as well as DRAM, and the data is preserved after a power cycle. We were interested in quantifying these claims in our labs with Dell EMC HCI Solutions for Microsoft Windows Server.
Windows Server HCI running Microsoft Windows Server 2019 provides industry-leading virtual machine performance with Microsoft Hyper-V and Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct technology. The platform supports Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe), Intel Optane PM, and Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) networking. Windows Server HCI is a fully productized, validated, and supported HCI solution that enables enterprises to modernize their infrastructure for improved application uptime and performance, simplified management and operations, and lower total cost of ownership. AX nodes from Dell EMC, powered by industry-leading PowerEdge server platforms, offer a high-performance, scalable, and secure foundation on which to build a software-defined infrastructure.
In our lab testing, we wanted to observe the impact on performance when Intel Optane PM was added as a caching tier to a Windows Server HCI cluster. We set up two clusters to compare. One cluster was configured as a two-tier storage subsystem with Intel Optane PM in the caching tier and SATA Read-Intensive SSDs in the capacity tier. We inserted 12 x 128 GB Intel Optane PM modules into this cluster for a total of 1.5 TB per node. The other cluster’s storage subsystem was configured as a single-tier of SATA Read-Intensive SSDs. With respect to CPU selection, memory, and Ethernet adapters, the two clusters were configured identically.
Only the Dell EMC AX-640 nodes currently accommodate Intel Optane PM. The clusters were configured as follows:
Cluster Resources | Without Intel Optane PM | With Intel Optane PM |
Number of nodes | 4 | 4 |
CPU | 2 x Intel 6248 CPU @ 2.50 GHz (3.90 GHz with TurboBoost) | 2 x Intel 6248 CPU @ 2.50 GHz (3.90 GHz with TurboBoost) |
Memory | 384 GB RAM | 384 GB RAM |
Disks | 10 x 2.5 in. 1.92 TB Intel S4510 RI SATA SSD | 10 x 2.5 in. 1.92 TB Intel S4510 RI SATA SSD |
NICs | Mellanox ConnectX-5 EX Dual Port 100 GbE | Mellanox ConnectX-5 EX Dual Port 100 GbE |
Persistent memory | None | 12 x 128 GB Intel Optane PM per node |
Volumes were created using three-way mirroring for the best balance between performance and resiliency. Three-way mirroring protects data by enabling the cluster to safely tolerate two hardware failures. For example, data on a volume would be successfully preserved even after the simultaneous loss of an entire node and a drive in another node.
Intel Optane PM has two operating modes – Memory Mode and App Direct Mode. Our tests used App Direct Mode. In App Direct Mode, the operating system uses Intel Optane PM as persistent memory distinct from DRAM. This mode enables extremely high performing storage that is byte-addressable-like, memory coherent, and cache coherent. Cache coherence is important because it ensures that data is a uniformly shared resource across all nodes. In the four-node Windows Server HCI cluster, cache coherence ensured that when data was read or written from one node that the same data was available across all nodes.
VMFleet is a storage load generation tool designed to perform I/O and capture performance metrics for Microsoft failover clusters. For the small block test, we used VMFleet to generate 100 percent reads at a 4K block size. The baseline configuration without Intel Optane PM sustained 2,103,412 IOPS at 1.5-millisecond (ms) average read latency. These baseline performance metrics demonstrated outstanding performance. However, OLTP databases target 1 ms or less latency for reads.
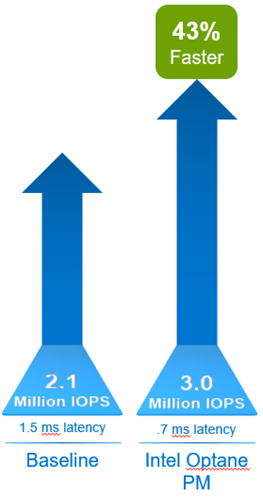
Comparatively, the Intel Optane PM cluster demonstrated 43 percent faster IOPS and decreased latency by 53 percent. Overall, this cluster sustained slightly over 3 million IOPS at .7 ms average latency. Benefits include:
- Significant performance improvement in IOPS means transactional databases and similar workloads will improve in scalability.
- Applications reading from storage will receive data faster, thus improving transactional response times.
- Intel Optane PM coherent cache provides substantial performance benefits without sacrificing availability.
When exploring storage responsiveness, testing large block read and write requests is also important. Data warehouses and decision-support systems are examples of workloads that read larger blocks of data. For this testing, we used 512 KB block sizes and sequential reads as part of the VMFleet testing. This test provided insight into the ability of Intel Optane PM cache to improve storage system throughput.

The cluster populated with Intel Optane PM was 109% faster than the baseline system. Our comparisons of 512 KB sequential reads found total throughput of 11 GB/s for the system without Intel Optane PM and 23 GB/s for the system with Intel Optane PM caching. Benefits include:
- Greater throughput enables faster scans of data for data warehouse systems, decision-support systems, and similar workloads.
- The benefit to the business is faster reporting and analytics.
- Intel Optane PM coherent cache provides substantial throughput benefits without sacrificing availability.
Overall, the VMFleet tests were impressive. Both Windows Server HCI configurations had 40 SSDs across the four nodes for approximately 76 TB of performant storage. To accelerate the entire cluster required 12 Intel Optane PM 128 GB modules per server for a total of 48 modules across the four nodes. Test results show that both OLTP and data-warehouse type workloads would exhibit significant performance improvements.
Testing 100 percent reads of 4K blocks showed:
- 43 percent performance improvement in IOPS.
- 53 percent decrease in average read latency.
- Improved scaling and faster transaction processing. Overall, application performance would be significantly accelerated, improving end-user experience.
Testing 512 KB sequential reads showed:
- 109 percent increased throughput.
- Faster reporting and faster time to analytics and data insights.
The configuration presented in this lab testing scenario will not be appropriate for every application. Any Windows Server HCI solution must be properly scoped and sized to meet or exceed the performance and capacity requirements of its intended workloads. Work with your Dell Technologies account team to ensure that your system is correctly configured for today’s business challenges and ready for expansion in the future. To learn more about Microsoft HCI Solutions from Dell Technologies, visit our Info Hub page.


