vSAN-based solutions provide flexibility as you scale, reducing the initial and future cost of ownership. Add physical and virtual servers to the server pools to scale horizontally. Add virtual resources to the infrastructure to scale vertically.
Scaling out
Each component of the solution architecture scales independently, depending on the required number of supported users. You can add appliance nodes at any time to expand the vSAN SDS pool in a modular fashion. The scaling limit for vSAN is restricted by the limits of the hypervisor at 64 nodes per block.
Sizing recommendations change over time as updates are released and qualifications are performed. See the VMware Configuration Maximums website for the latest recommendations.
A Citrix "pod architecture" consists of a virtual desktop "site" and one or more "zones" at each site. The maximum limit when using Citrix pod architecture with the LHC feature enabled would be 10,000 VDAs per zone and 40,000 VDAs per site.
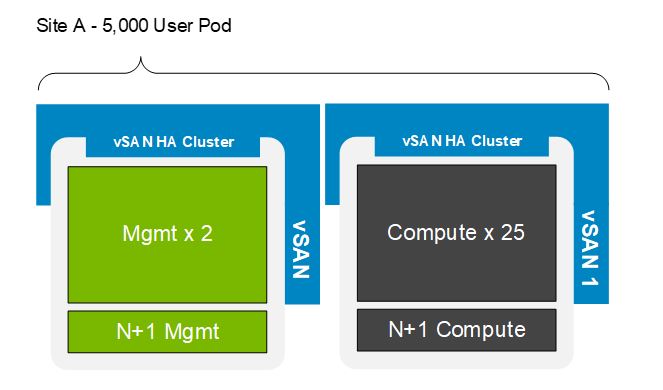
A reasonable limit to choose is 5,000 linked clone VMs per zone. With this limit in mind, 25 compute nodes with 200 task-user VMs per node would reach the maximum number of VMs for the zone. This Dell Technologies Validated Design for VDI uses MCS linked clones. The following figure shows a 5,000-user MCS linked clone/vSAN configuration, which equates to a single zone within a site:
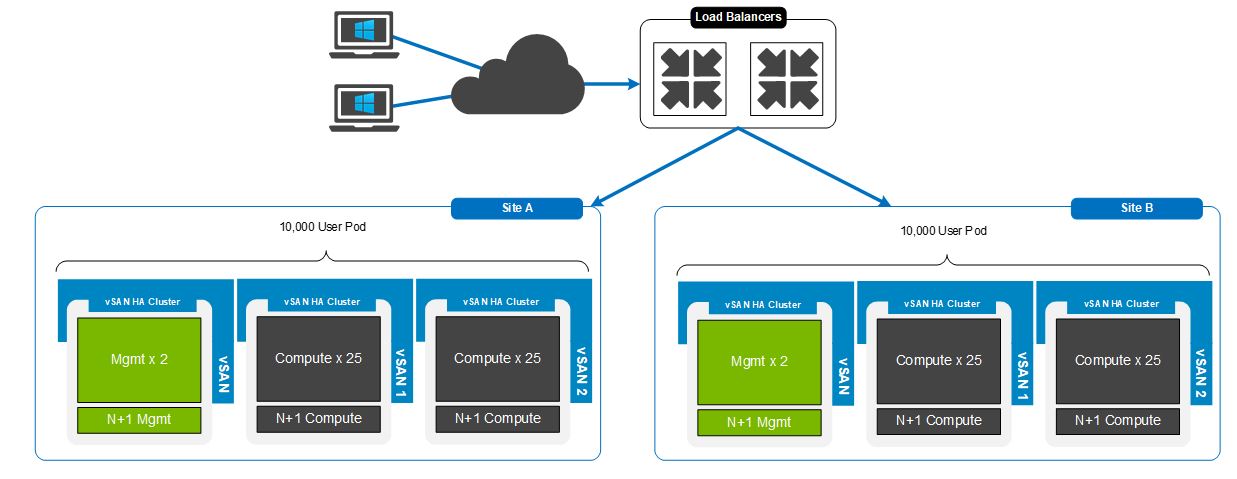
The following figure shows a scale-out of 20,000 MCS linked-clone VMs with vSAN. The recommended limit for a zone is 10,000 sessions. In this example, there are two sites with three zones each. The sites are load-balanced and presented to the users as a single entity.
Scaling up
Dell Technologies recommends a validated disk configuration for general-purpose VDI. These configurations leave drive slots available for future vertical expansion and ensure that you protect your investment as new technology transforms your organization.
For more information about Citrix best practices for scaling, see Citrix VDI Handbook and Best Practices.
