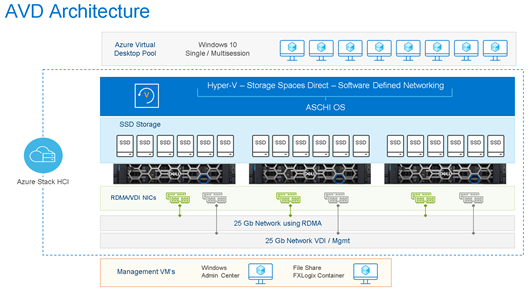
Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD), formerly Windows Virtual Desktop, is a desktop and app virtualization service that runs in public Azure. It provides IT with comprehensive controls and streamlined management experience, without any infrastructure build-up. It also provides users with a rich experience, running the latest versions of Windows and Microsoft 365 applications.
As more organizations must meet specific network and data compliance requirements, Microsoft recently extended the AVD functionality to allow virtual desktops to run on-premises on Azure Stack HCI but be managed from the centralized management plane in Azure. Azure Virtual Desktop is completely hosted and managed by Azure cloud infrastructure which means IT organizations are not required to set up and operate their own complex VDI infrastructure. To comply with data sovereignty and locality requirements, IT administrators are only required to set up and manage the Azure Stack HCI clusters, and the VMs hosted on them, in their data centers.
Besides meeting data locality requirements by keeping user data and apps on-premises, AVD for Azure Stack HCI also improves performance for users in areas with poor connectivity to the public cloud. In those cases, users access their desktops closer to their location with a low latency direct access method instead of a round trip through the cloud. This improves access to on-premises legacy applications which allows IT to provide a streamlined, cloud-consistent experience through the same rich comprehensive management plane in Azure. Best of all, organizations can reduce costs and improve user experience by providing multi-session access concurrently to VMs that are running the newest versions of Windows.