Home > Integrated Products > VxRail > Guides > Reference Architecture—Splunk Reference Architecture on VxRail > Introduction
Introduction
-
The following reference architecture describes a Dell EMC HCI VxRail coupled with a Dell EMC storage solution hosting a Splunk Enterprise environment. Dell Technologies and Splunk jointly tested and validated this architecture to meet or exceed the performance of Splunk Enterprise. This architecture is in accordance with the Splunk Validated Architectures white paper.
VxRail is a fully integrated, preconfigured, and pretested HCI. Powered by industry-leading vSAN and vSphere software, VxRail is the easiest and fastest way to streamline and extend a VMware environment while dramatically simplifying IT operations.
We deployed two reference architectures representing Splunk instances as virtual machines on a VMware vSphere 7.0 cluster following Splunk’s documented virtualization best practices. VxRail uses VMware vSAN technology as the storage layer to build vSAN on groups of locally attached disks. This configuration provides a low latency read and writes disk I/O by using an all-flash array.
The following figure shows the four layers in this solution:
- Application layer
- Virtualization layer
- Infrastructure layer
- vSAN layer
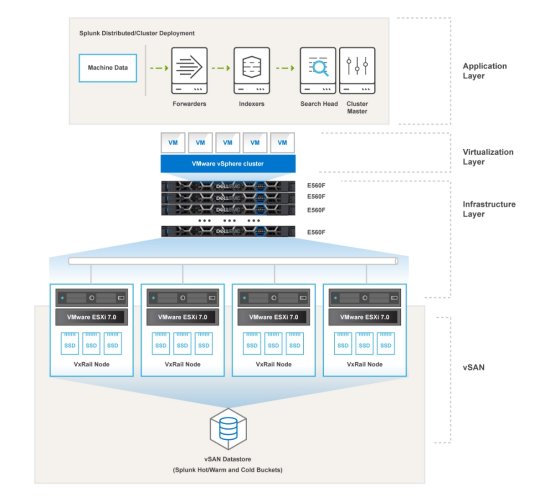
Figure 1. Splunk Enterprise on VxRail reference architecture
In the application layer, there are four Splunk components: forwarder, indexer, search head, and management node. The VxRail cluster forms a vSAN as shared storage on all-flash disks that is used to hold all virtual machines and indexed data in directories referred to as "buckets" as it moves through its life cycle in Splunk.
The following figure shows a reference architecture that is similar to Figure 1, except with differences in the number of VxRail nodes and Splunk bucket placements:
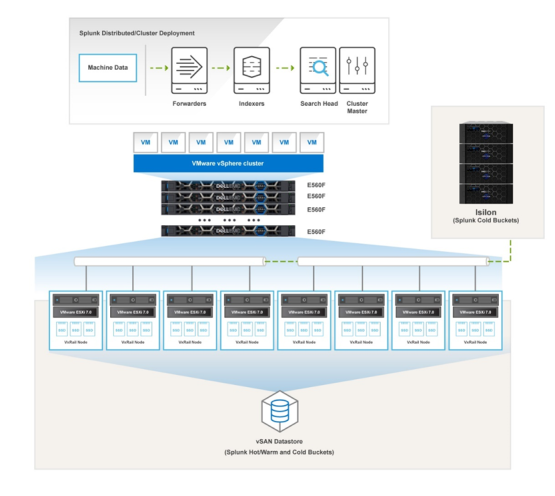
Figure 2. Splunk Enterprise on VxRail with Isilon reference architecture
In this example, vSAN is used to store all virtual machines and Splunk hot/warm buckets, while PowerScale storage is used to store the Splunk cold bucket for long-term data retention.
Note: For information about the hot/warm and cold bucket concept, see Splunk's Managing Indexers and Clusters of Indexers document.
