Home > Workload Solutions > SQL Server > White Papers > Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Big Data Cluster on Dell EMC VxRail > Container-based virtualization
Container-based virtualization
-
Two primary options for enabling applications to run on virtual hardware are:
- VMs and a hypervisor
- Container-based virtualization (also referred to as operating system virtualization or containerization)
The older and more pervasive virtualization method using VMs and a hypervisor was first developed by Burroughs Corporation in the 1950s. That method was replicated with the commercialization of IBM mainframes in the early 1960s. The primary virtualization method that is used by platforms such as IBM VM/CMS, VMware ESXi, and Microsoft Hyper-V starts with a hypervisor layer that abstracts the physical components of the computer. The abstraction enables sharing of the components by multiple VMs, each running a guest operating system. A more recent development is container-based virtualization, where a single host operating system supports multiple processes that are running as virtual applications.
The following figure contrasts VM-based virtualization with container-based virtualization. In container-based virtualization, the combination of the guest operating system components and any isolated software applications constitutes a container running on the host server, as indicated by the App 1, App 2, and App 3 boxes in the figure.
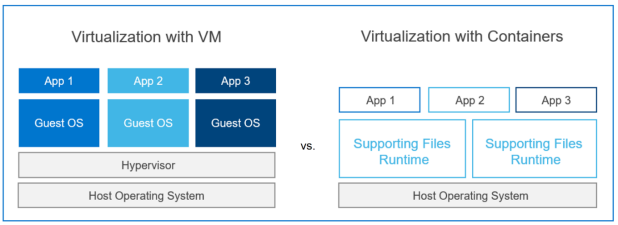
Figure 1. Primary virtualization methods
Both types of virtualization increase the efficiency of computer hardware investments by supporting multiple users and applications in parallel. Containerization further improves IT operations productivity by simplifying application portability. Application developers most often work outside the server environments in which their programs will run. To minimize conflicts in library versions, dependencies, and configuration settings, the production environment must be re-created multiple times for development, testing, and preproduction integration. IT professionals have found containers easier to deploy consistently across multiple environments because the core operating system can be configured independently of the application container.
