Home > Storage > ObjectScale and ECS > Product Documentation > ECS: Overview and Architecture > Storage protection overhead
Storage protection overhead
-
Each VDC member in an RG is responsible for its own EC protection of data at the local level. That is, data is replicated but not any related coding segments. Although EC is more storage efficient than other forms of protection, such as full copy drive mirroring, it does incur an inherent storage cost overhead at the local level. However, when it is required to have secondary copies replicated offsite, and to have all sites have access to data when a single site becomes unavailable, the storage costs become more extensive than when using traditional site-to-site data copying protection methods. This is especially true when unique data is distributed across three or more sites.
ECS provides a mechanism in which storage protection overhead efficiency can increase as three or more sites are federated. In a two-VDC replicated environment ECS replicates chunks from the primary, or owner VDC to a remote site to provide high availability and resiliency. There is no way to evade the 100% cost of protection overhead of a full copy of data in a two-site federated ECS deployment.
Now, consider three VDCs in a multi-site environment, VDC1, VDC2, and VDC3, where each VDC has unique data replicated to it from each of the other VDCs. VDC2 and VDC3 may send a copy of their data to VDC1 for protection. VDC1 would therefore have its own original data, plus replicate data from VDC2 and VDC3. This means that VDC1 would be storing 3X the amount of data written at its own site.
In this situation ECS can perform an XOR operation of VDC2 and VDC3 data locally stored at VDC1. This mathematical operation compares equal quantities of unique data, chunks, and renders a result in new chunk which contain enough characteristics of the two original data chunks to make it possible to restore either of the two original sets. So, where previously there were three unique sets of data chunks stored on VDC1, consuming 3X the available capacity, there is now only two - the original local data set, and the XOR reduced protection copies.
In this same scenario, if VDC3 becomes unavailable, ECS can reconstruct VDC3 data chunks by using chunk copies recalled from VDC2 and the (C1 ⊕ C2) data from VDC3 stored locally at VDC1. This principle applies to all three sites participating in the RG and is dependent upon each of the three VDC’s having unique data sets. The following figure shows an XOR calculation with two sites replicating to a third site.
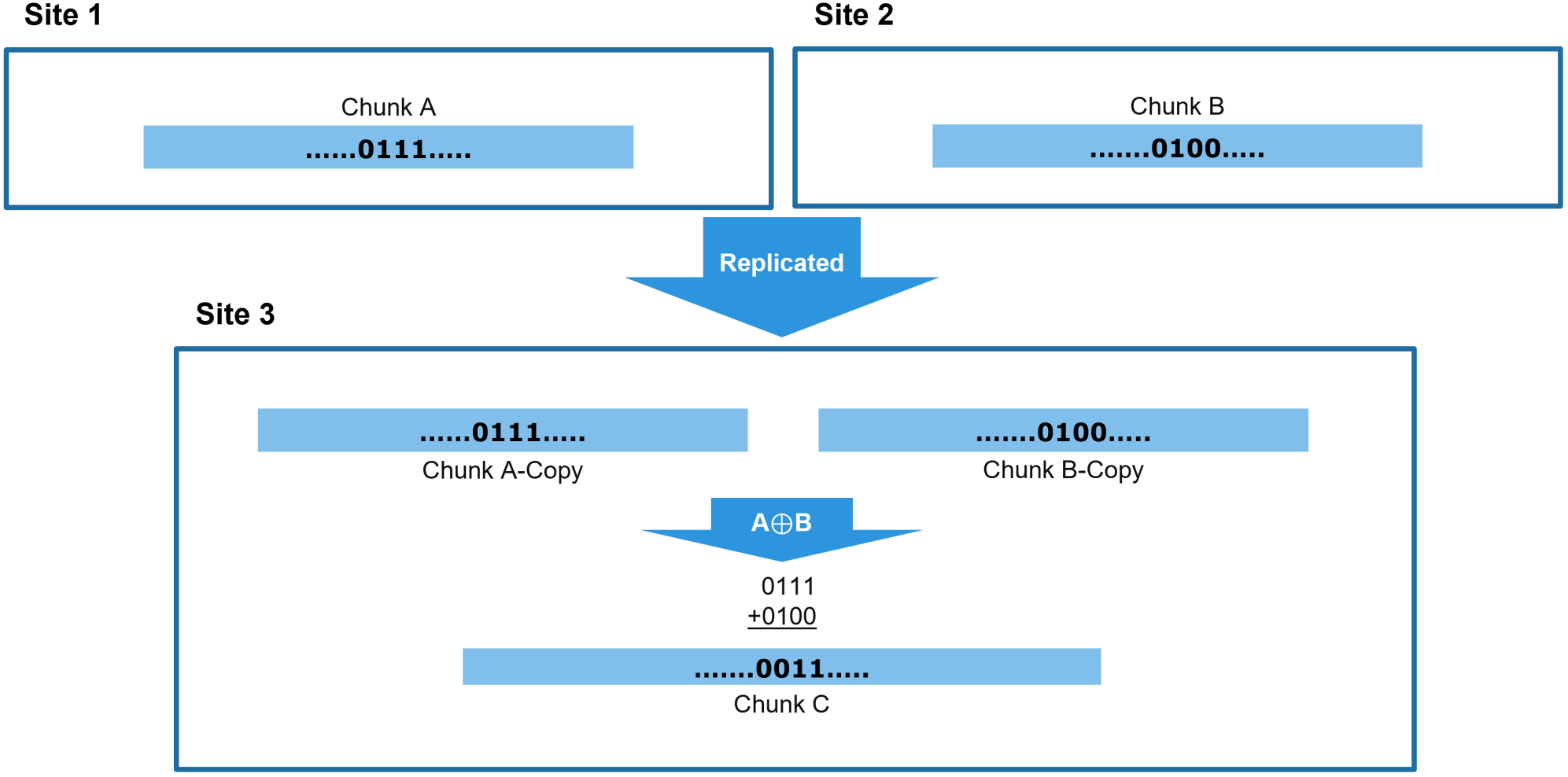
Figure 29. XOR data protection efficiency
If business service level agreements require optimum read access speeds even in the event of a full site failure, then the replicate to all sites setting forces ECS to revert to full copies of replicated data to be stored at all sites. Expectedly, this drives up the storage costs in proportion to the number of VDCs participating in the RG. Therefore a 3-site configuration would revert to 3X storage protection overhead. Replicate to All Sites setting is available during RG creation and cannot be toggled back and forth.
As the number of federated sites increases, the XOR optimization is more efficient in reducing the storage protection overhead due to replication. The following table provides information about the storage protection overhead based on the number of sites for normal EC of 12+4 and cold archive EC of 10+2, illustrating how ECS can become more storage efficient as more sites are linked.
Note: To lower replicated data overhead across three, and up to eight sites, unique data must be written relatively equally at each site. By writing data in equal amounts across sites, each site will have a similar number of replica chunks. Similar numbers of replica chunks at each site lead to similar number of XOR operations that can occur at each site. Maximum multisite storage efficiency is gained by reducing the maximum number of replica chunks stored by using XOR.
Table 11. Storage protection overhead
# sites in RG
12+4 EC
10+2 EC
1
1.33
1.2
2
2.67
2.4
3
2.00
1.8
4
1.77
1.6
5
1.67
1.5
6
1.60
1.44
7
1.55
1.40
8 (Max # sites in RG)
1.52
1.37
