Home > Storage > PowerStore > Data Protection > Dell PowerStore: Replication Technologies > Theory of operation
Theory of operation
-
The configuration of asynchronous replication for vVol-based VMs requires a remote system pair, as described in an earlier section configured for two PowerStore clusters running PowerStoreOS 3.0 or later. Each of the PowerStore clusters for vVol replication must have a registration in vCenter as a storage provider because the VASA 3.0 API is used to exchange information between the PowerStore cluster and the associated vCenter.
The VMware Storage Policy, which can be assigned to VMs in vCenter, leverages the same replication rules in PowerStore Manager as used for other PowerStore asynchronous replication sessions. Asynchronous replication for vVol based VMs also uses the same snapshot based asynchronous replication technology as native block replication, which is described in the section native asynchronous replication.
When a VMware Storage Policy with PowerStore replication is assigned to a vVol-based VM, a replication session is created on PowerStore for the vVol resources in the same resource group. VMware resource groups can be selected when a VMware Storage Policy is configured for a VM. VMware SRM uses these VMware resource groups to manage the protected VMs in Replication Groups. An SRM Recovery Plan controls the PowerStore replication session for vVols in a replication group during test failover, failover, and reprotection. After a VM has a VMware Storage Policy assigned, and the Resource Group is in a Replication Group with a Protection Plan in SRM, a placeholder VM on destination vCenter and PowerStore is created. The storage container for placeholder VM is part of the site pair configuration in SRM.
Supported replication flows
For replicating Resource Groups on PowerStore, different combinations of source and destination vVol Storage Containers are possible:
- One or more Resource Groups from a single Storage Container to a single Storage Container on a different PowerStore cluster
- One or more different Resource Groups on a single Storage Container to different Storage Containers on different PowerStore clusters
- Resource Groups from Storage Containers on different PowerStore clusters to a single Storage Container
- Multiple replications in different directions
- Any combination of these replication flows
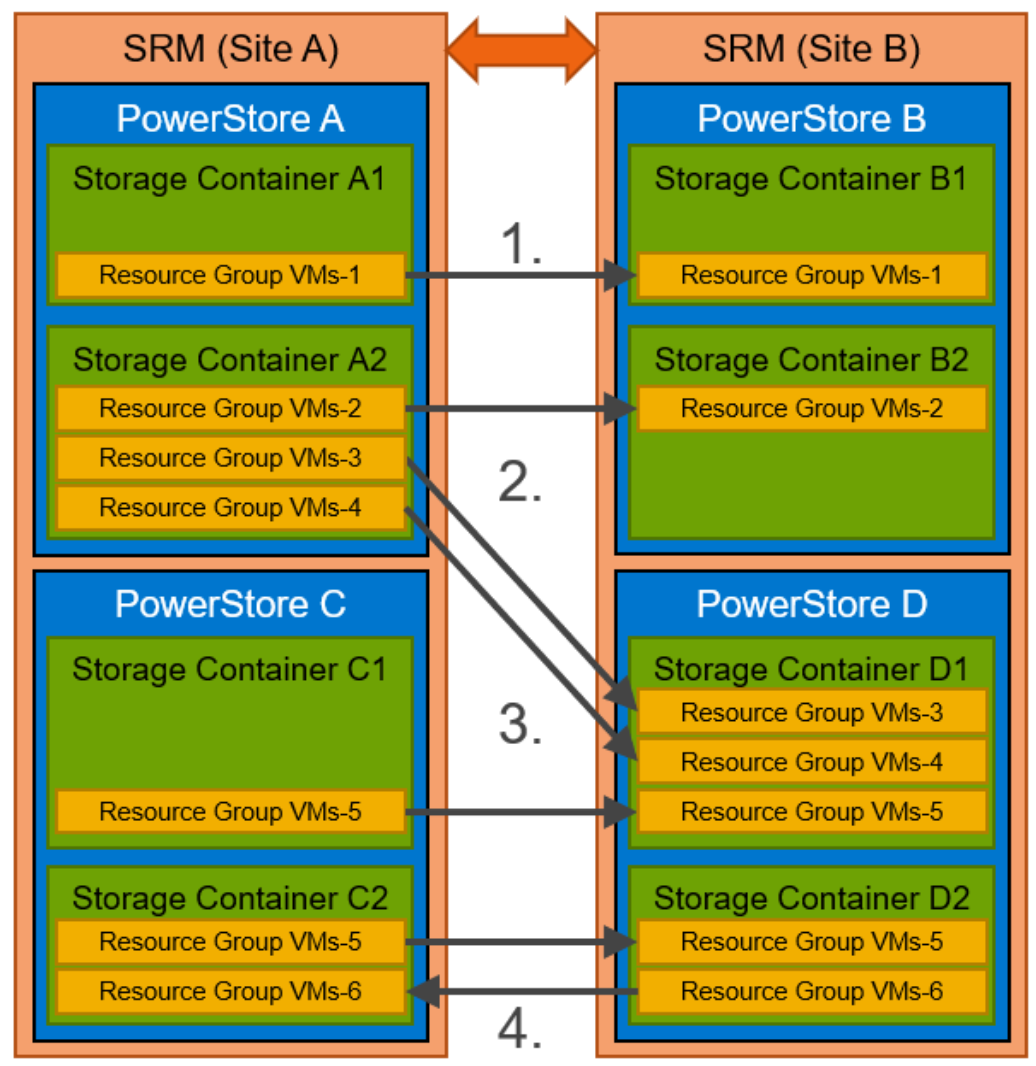
Figure 50. Supported replication flows
