Home > Storage > PowerStore > Databases and Data Analytics > Dell PowerStore: Oracle Best Practices > Multiple client interfaces for dNFS
Multiple client interfaces for dNFS
-
If multiple network paths are intended for NFS traffic, consider using one path for NFS control/management traffic and the remaining NFS paths for NFS data traffic. This ensures that the NFS data path is only used for NFS data traffic.
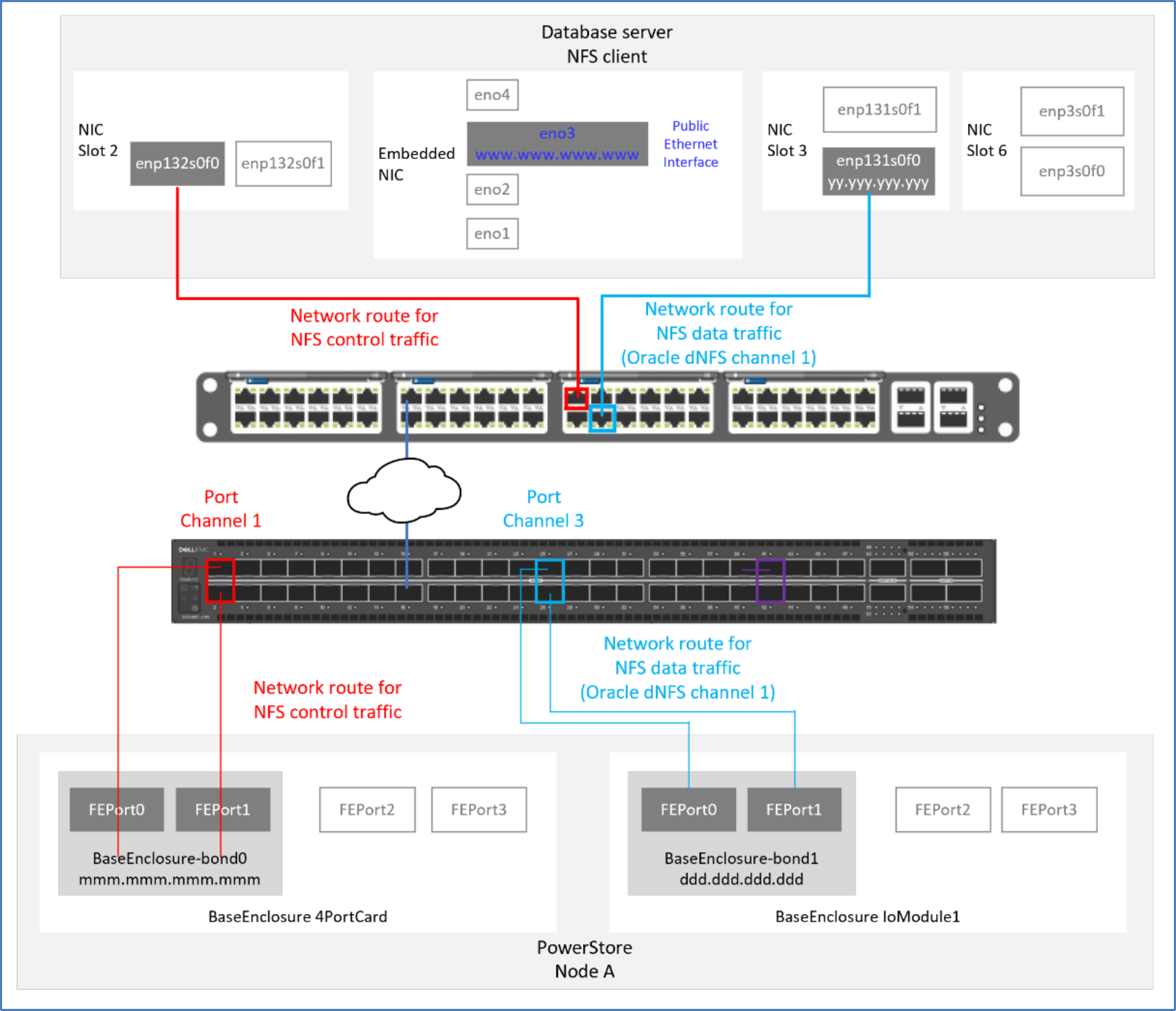
Figure 54. Network routes using dedicated interfaces for NFS control and data traffic
If multiple dNFS paths are defined for data traffic, when a dNFS data path fails, dNFS reissues requests over any of the remaining dNFS data paths, improving database availability. Multiple data paths also provide Oracle the ability to automatically tune the paths to the NFS storage devices, and manually tuning NFS is unnecessary. Because dNFS implements multipath I/O internally, Oracle recommends not configuring LACP and channel-bonded interfaces on the database server (NFS client) for dNFS data traffic.
If a single interface is used for the NFS mount on the NFS client (see Figure 54), NFS control traffic can be blocked if the interface is down. This blocked NFS traffic causes the database to appear unavailable. To mitigate this single point of failure in the network, configure LACP on multiple interfaces to create a channel-bonded interface for NFS control/management traffic (see Figure 55).
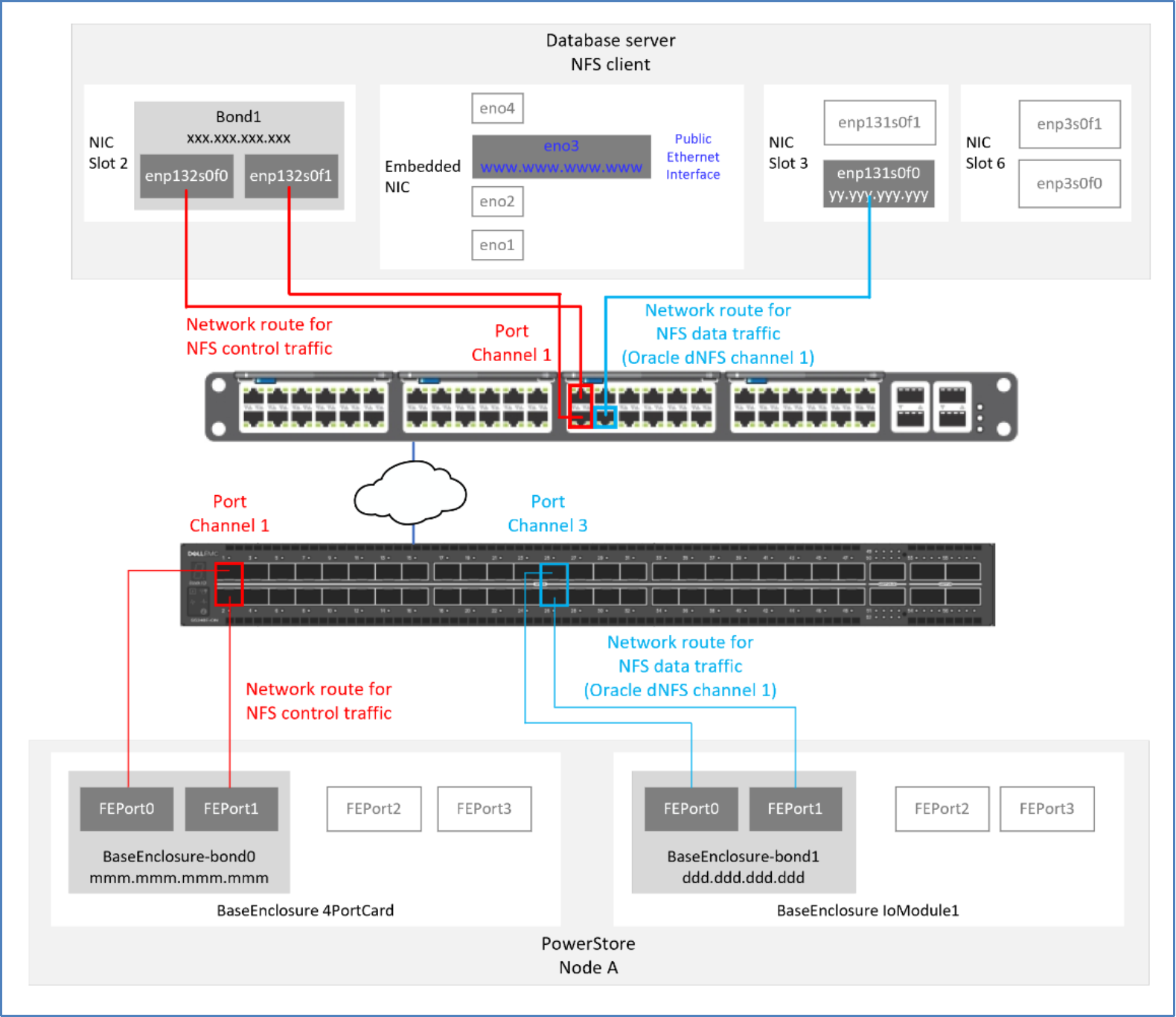
Figure 55. Network route using bonded client interface for NFS control traffic
When configuring dNFS with multiple network paths, use a unique network for each of the paths if possible. When multiple unique networks are not available, a different IP address from the same subnet can be used for each of the network paths.
