
Yes Virginia, Data Quality Matters to AI & Data Analytics
Thu, 15 Sep 2022 14:22:23 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
How often do we hear a project has failed? Projected benefits were not achieved, ROI is less than expected, predictability results are degrading, and the list goes on.
Data Scientists blame it on not having enough data engineers. Data engineers blame it on poor source data. DBAs blame it on data ingest, streaming, software and such…Scape goats are easy to come by.
Have you ever thought why? Yes there are many reasons but one I run across constantly is data quality. Poor data quality is rampant through the vast majority of enterprises. It remains largely hidden. From what I see most companies say we’re a world class organization with top notch talent and we make lots of money and have happy customers therefore we must have world class data with high data quality. This is a pipe dream. Iif you’re not measuring it it’s almost certainly bad leading to inefficiencies, costly mistakes, bad decisions, high error rates, rework, lost customers and many other maladies.
When I’ve built systems & databases in past lives I’ve looked into data, mostly with a battery of SQL queries and found many a data horror, poor quality, defective items, wrong data and many more.
So if you want to know where you stand you must measure your data quality and have a plan to measure the impact of defects and repair them as justified. I think most folks that start down this path quit as they attempt to boil the ocean and fix all the problems they find. I think the best approach is to rank your data items in terms of importance and then measure perhaps the top 1-3% of them. In that way one can make the most impactful improvements with the least effort.
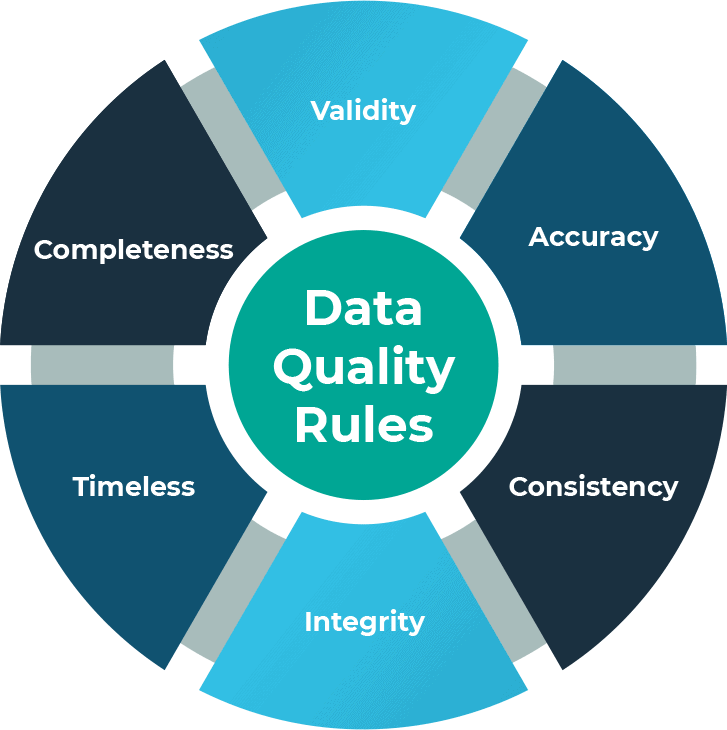
The dimensions of data are varied and can be complex but from a data quality perspective they fall into six or more categories:
- Completeness
- Validity
- Accuracy
- Consistency
- Integrity
- Timeliness
Using a tool is highly recommended. Yes, you probably have to pay for one. I won’t get into all the players here.
So, if you don’t have a data quality program then you should get started today because you do have poor data quality.
In a future post I’ll go into more about data quality measures.
If you like a free consultation on your particular situation please do contact me at Mike.King2@Dell.com
Related Blog Posts

Simplifying Machine Learning with Omnia and Polyaxon
Wed, 11 Aug 2021 20:52:33 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Managing data science projects can be a nightmare
Tracking data science projects can be a nightmare. Making sense of a sea of experiments, models that are all scattered across multiple workstations with no sense of order, different software environments, and other complexities create ever more hurdles to making sense of your data. Then when you add in limited documentation availability plus the intricate interplay of the different technologies being leveraged it's no wonder that reproducing results becomes a tricky task. Fortunately, machine learning (ML) platforms are helping to automate and manage these complexities, leaving data scientists and data science managers to solve the real problem – getting value from the data.
Polyaxon makes developing models easier
Polyaxon is a platform for developing machine learning and deep learning models that can be used on an enterprise scale for all steps of the machine learning and deep learning model development process: building, training, and monitoring. Polyaxon accomplishes this by leveraging a built-in infrastructure, set of tools, trusted algorithms, and industry models, all of which lead to faster innovation. Polyaxon enables data scientists to easily develop and manage experiments and manages the entire workflow with smart containers and advanced scheduling. It is also language and framework agnostic, allowing data scientists to work with popular libraries and frameworks such as R, Python, SAS, Jupyter, RStudio, Tensorflow, and H2O.
Managing multiple data scientists and experiment artifacts
One feature that data scientist managers will find especially useful is Polyaxon’s ease of knowledge distribution. With fast onboarding of new team members and a documented and searchable knowledge base, any new hire can quickly pick up where others left off using each project's artifacts and history. Additionally, Polyaxon includes risk management capabilities and a built-in auto-documentation engine to remove risk and create a searchable knowledge base, avoiding the problem of laptop-centric and scattered scripts-oriented development.
For the executives of an organization, Polyaxon provides improved insights on model development and measuring time to market. By enabling a virtuous experimentation life cycle and giving data-driven feedback, all based on a centralized dashboard, Polyaxon optimizes and the time spent on projects. This means data science teams spend more time producing value, rather than trying to maintain infrastructure and documentation.
Deploying Polyaxon with Omnia
Omnia is an open‑source framework for deploying and managing high-performance clusters for HPC, AI, and data analytics workloads. Omnia not only automates the installation of Slurm and/or Kubernetes for managing your server infrastructure, it also deploys and configures many other packages and services necessary for running diverse workloads on the same converged solution. It also automates the deployment of ML platforms, like Polyaxon. This gives IT infrastructure teams the ability to quickly spin up and offer new capabilities to an organization’s data science and applications teams, giving them more time to do the company’s business.
Automation is key to any data-driven organization
The ability to automate the infrastructure stack, from the server, storage, and network resources up to the data science platforms that help you derive value from their data, is key to the success of modern data-driven organizations. Tools change quickly and frequently, and spending weeks deploying IT solutions for a company’s data science teams is time not spent finding critical value. Omnia simplifies the process of infrastructure deployment, allowing IT groups to get their data science teams up and running in minutes. What could be more transformative than that?
Learn More
Learn more about Polyaxon
Learn more about Omnia

Omnia: Open-source deployment of high-performance clusters to run simulation, AI, and data analytics workloads
Mon, 12 Dec 2022 18:31:28 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
High Performance Computing (HPC), in which clusters of machines work together as one supercomputer, is changing the way we live and how we work. These clusters of CPU, memory, accelerators, and other resources help us forecast the weather and understand climate change, understand diseases, design new drugs and therapies, develop safe cars and planes, improve solar panels, and even simulate life and the evolution of the universe itself. The cluster architecture model that makes this compute-intensive research possible is also well suited for high performance data analytics (HPDA) and developing machine learning models. With the Big Data era in full swing and the Artificial Intelligence (AI) gold rush underway, we have seen marketing teams with their own Hadoop clusters attempting to transition to HPDA and finance teams managing their own GPU farms. Everyone has the same goals: to gain new, better insights faster by using HPDA and by developing advanced machine learning models using techniques such as deep learning and reinforcement learning. Today, everyone has a use for their own high-performance computing cluster. It’s the age of the clusters!
Today's AI-driven IT Headache: Siloed Clusters and Cluster Sprawl
Unfortunately, cluster sprawl has taken over our data centers and consumes inordinate amounts of IT resources. Large research organizations and businesses have a cluster for this and a cluster for that. Perhaps each group has a little “sandbox” cluster, or each type of workload has a different cluster. Many of these clusters look remarkably similar, but they each need a dedicated system administrator (or set of administrators), have different authorization credentials, different operating models, and sit in different racks in your data center. What if there was a way to bring them all together?
That’s why Dell Technologies, in partnership with Intel, started the Omnia project.
The Omnia Project
The Omnia project is an open-source initiative with a simple aim: To make consolidated infrastructure easy and painless to deploy using open open source and free use software. By bringing the best open source software tools together with the domain expertise of Dell Technologies' HPC & AI Innovation Lab, HPC & AI Centers of Excellence, and the broader HPC Community, Omnia gives customers decades of accumulated expertise in deploying state-of-the-art systems for HPC, AI, and Data Analytics – all in a set of easily executable Ansible playbooks. In a single day, a stack of servers, networking switches, and storage arrays can be transformed into one consolidated cluster for running all your HPC, AI, and Data Analytics workloads. Omnia project logo
Omnia project logo
Simple by Design
Omnia’s design philosophy is simplicity. We look for the best, most straightforward approach to solving each task.
- Need to run the Slurm workload manager? Omnia assembles Ansible plays which build the right rpm files and deploy them correctly, making sure all the correct dependencies are installed and functional.
- Need to run the Kubernetes container orchestrator? Omnia takes advantage of community supported package repositories for Linux (currently CentOS) and automates all the steps for creating a functional multi-node Kubernetes cluster.
- Need a multi-user, interactive Python/R/Julia development environment? Omnia takes advantage of best-of-breed deployments for Kubernetes through Helm and OperatorHub, provides configuration files for dynamic and persistent storage, points to optimized containers in DockerHub, Nvidia GPU Cloud (NGC), or other container registries for unaccelerated and accelerated workloads, and automatically deploys machine learning platforms like Kubeflow.
Before we go through the process of building something from scratch, we will make sure there isn’t already a community actively maintaining that toolset. We’d rather leverage others' great work than reinvent the wheel.
Inclusive by Nature
Omnia’s contribution philosophy is inclusivity. From code and documentation updates to feature requests and bug reports, every user’s contributions are welcomed with open arms. We provide an open forum for conversations about feature ideas and potential implementation solutions, making use of issue threads on GitHub. And as the project grows and expands, we expect the technical governance committee to grow to include the top contributors and stakeholders from the community.
What's Next?
Omnia is just getting started. Right now, we can easily deploy Slurm and Kubernetes clusters from a stack of pre-provisioned, pre-networked servers, but our aim is higher than that. We are currently adding capabilities for performing bare-metal provisioning and supporting new and varying types of accelerators. In the future, we want to collect information from the iDRAC out-of-band management system on Dell EMC PowerEdge servers, configure Dell EMC PowerSwitch Ethernet switches, and much more.
What does the future hold? While we have plans in the near-term for additional feature integrations, we are looking to partner with the community to define and develop future integrations. Omnia will grow and develop based on community feedback and your contributions. In the end, the Omnia project will not only install and configure the open source software we at Dell Technologies think is important, but the software you – the community – want it to, as well! We can’t think of a better way for our customers to be able to easily setup clusters for HPC, AI, and HPDA workloads, all while leveraging the expertise of the entire Dell Technologies' HPC Community.
Omnia is available today on GitHub at https://github.com/dellhpc/omnia. Join the community now and help guide the design and development of the next generation of open-source consolidated cluster deployment tools!



