How Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks are Simplifying 5G RAN Cloud Transformation
Thu, 08 Dec 2022 20:01:48 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
5G is a technology that is transforming industry, society, and how we communicate and live in ways we’ve yet to imagine. Communication Service Providers (CSPs) are at the heart of this technological transformation. Although 5G builds on existing 4G infrastructure, 5G networks deployed at scale will require a complete redesign of communication infrastructure. 5G network transformation is undergoing, where more than 220 operators in more than 85 countries have already launched services, and they have realized that operational agility and accelerated deployment model in such a decentralized and cloud-native landscape are considered a must-have to meet customer demands for new innovative capabilities, services, and digital experiences for both Telecom and vertical industries. This is accompanied by the promise of cloud native architectures and open and flexible deployments, which enable CSPs to scale and enable new data-driven architectures in an open ecosystem. While the initial deployments of 5G are based on the Virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN), which offers CSPs enhanced operational efficiency and flexibility to fulfill the needs of 5G customers, Open RAN expands vRAN's design concepts as well as goals and is truly considered the future. Although O-RAN disaggregates the network, providing network operators more flexibility in terms of how their networks are built and allowing them the benefits of interoperability, the trade-off for the flexibility is typically increased operational complexity, which incurs additional costs of continuous testing, validation, and integration of the 5G RAN system components, which are now provided by a diverse set of suppliers.
Another aspect of this growing complexity is the need for denser networks. Although powerful, new 5G antennas and RAN gear required to attain maximum bandwidth cover substantially less distance than 4G macro cells operating at lower frequencies. This means similar coverage requires more 5G hardware and supporting software. Adding the essential gear for 5G networks can dramatically raise operational costs, but the hardware is only a portion of these costs. The expenses of maintaining a network include the time and money spent on configuration changes, testing, monitoring, repairs, and upgrades.
For most nationwide operators, Edge and RAN cell sites are widely deployed and geographically dispersed across the nation. As network densification increases, it becomes impractical to manually onboard thousands of servers across multiple sites. CSPs need to create a strategy for incorporating greater automation into their network and continue service operations to ensure robust connectivity, manage to expand network complexities, and preserve cost efficiencies without the need for a complete "rip and replace" strategy.
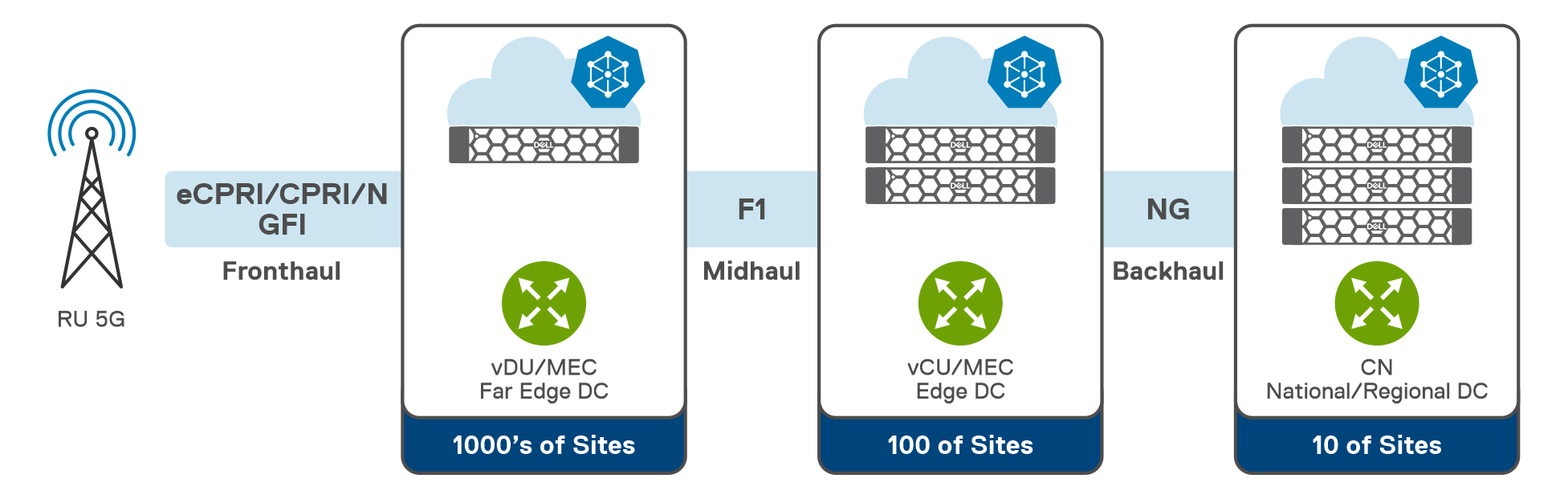
As CSPs migrate to an edge-computing architecture, a new set of requirements emerges. As workloads move closer to the network's edge, CSPs must still maintain ultra-high availability often 5-6 nines. Legacy technology is incapable of attaining this degree of availability.
Scalability, specifically down to a single node with a small footprint at the edge. When a single network reaches tens of thousands of cell sites, you simply cannot afford to have a significant physical footprint with many servers. As a result, the need for a new architecture that can scale up and down grew. As applications grow more real-time, ultra-low latency at the edge is required. CSPs need in-built lifecycle management to perform live software upgrades and manage this environment. Finally, CSPs are demanding more and more open-source software for their networks. Wind River Studio addresses each of these network issues.
Wind River Studio Cloud Platform, which is the StarlingX project with commercial support, provides a production-grade distributed Kubernetes solution for managing edge cloud infrastructure. In addition to the Kubernetes-based Wind River Studio Cloud Platform, Studio also provides orchestration (Wind River Studio Conductor) and analytics (Wind River Studio Analytics) capabilities so operators can deploy and manage their intelligent 5G edge networks globally.
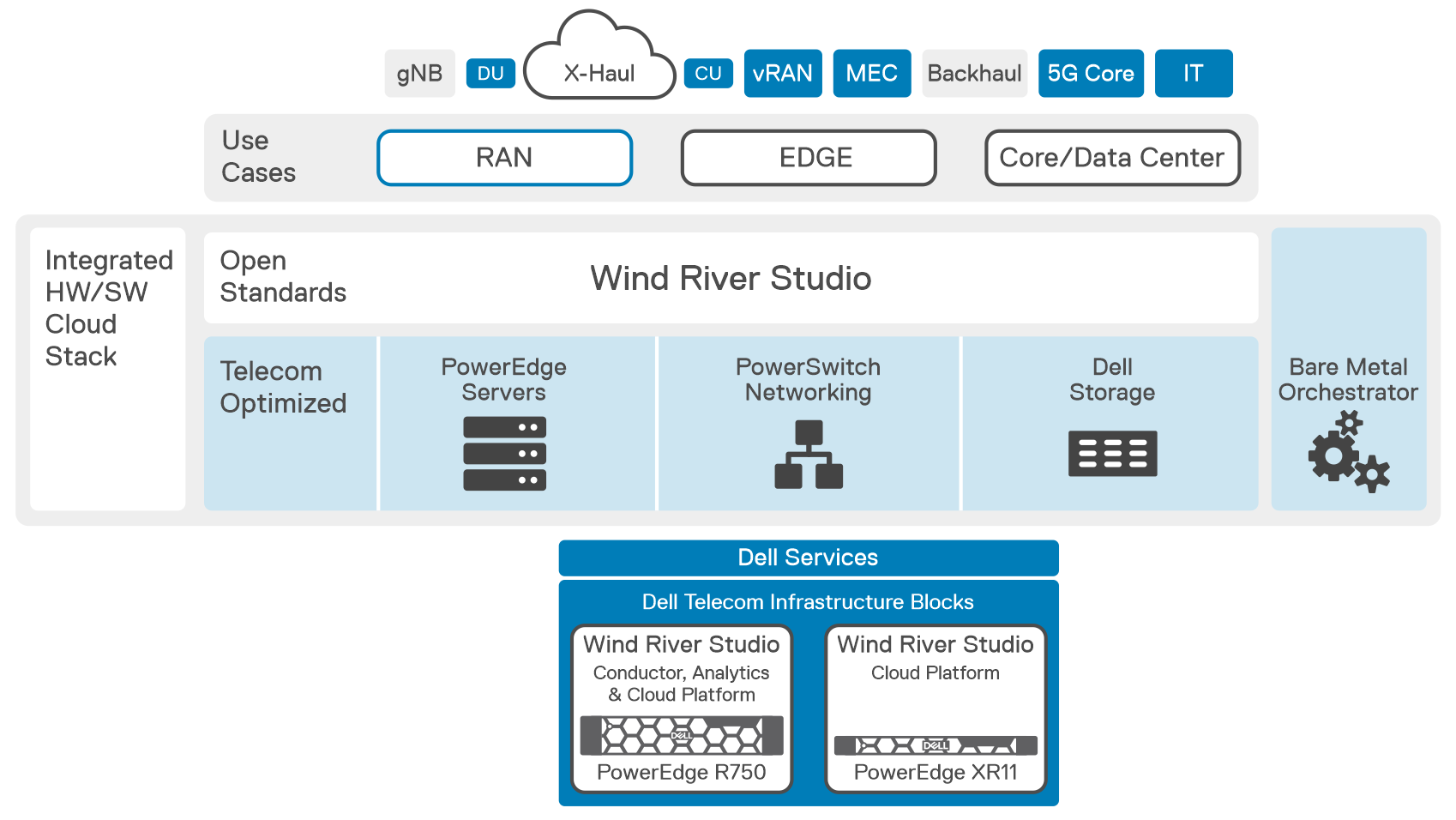
Mobile Network Operators who adopt vRAN and Open RAN must integrate cloud platform software on optimized and tuned hardware to create a cloud platform for vRAN and Open RAN applications. Dell and Wind River have worked together to create a fully engineered, pre-integrated solution designed to streamline 5G vRAN and Open RAN design, deployment, and lifecycle management. Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River integrate Dell Bare Metal Orchestrator (BMO) and Wind River Studio on Dell PowerEdge servers to provide factory-integrated building blocks for deploying ultra-low latency, vRAN and Open RAN networks with centralized, zero-touch provisioning and management capabilities.
Key Advantages:
- Reduces the complexity of integration and lifecycle management in a highly distributed, disaggregated network, allowing lower operating costs while reducing time to deploy new services while accelerating innovation.
- Dell's comprehensive, factory-integrated solution simplifies supply chain management by reducing the number of components and suppliers needed to build out the network. In addition, to back-haul optimization by preloading all software needed for day-0 and day-1 automation.
- It has been thoroughly tested and includes design guidance for building and scaling out a network that provides low latency, redundancy, and High Availability (HA) for carrier-grade RAN Applications.
- Simplified support with Dell providing single contact support for the whole stack including all hardware and software from Dell and Wind River with an option for carrier-grade support.
- Reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO) for CSPs by deploying a fully integrated, validated, and production-ready vRAN/O-RAN cloud infrastructure solution with a smaller footprint, low latency, and operational simplicity.

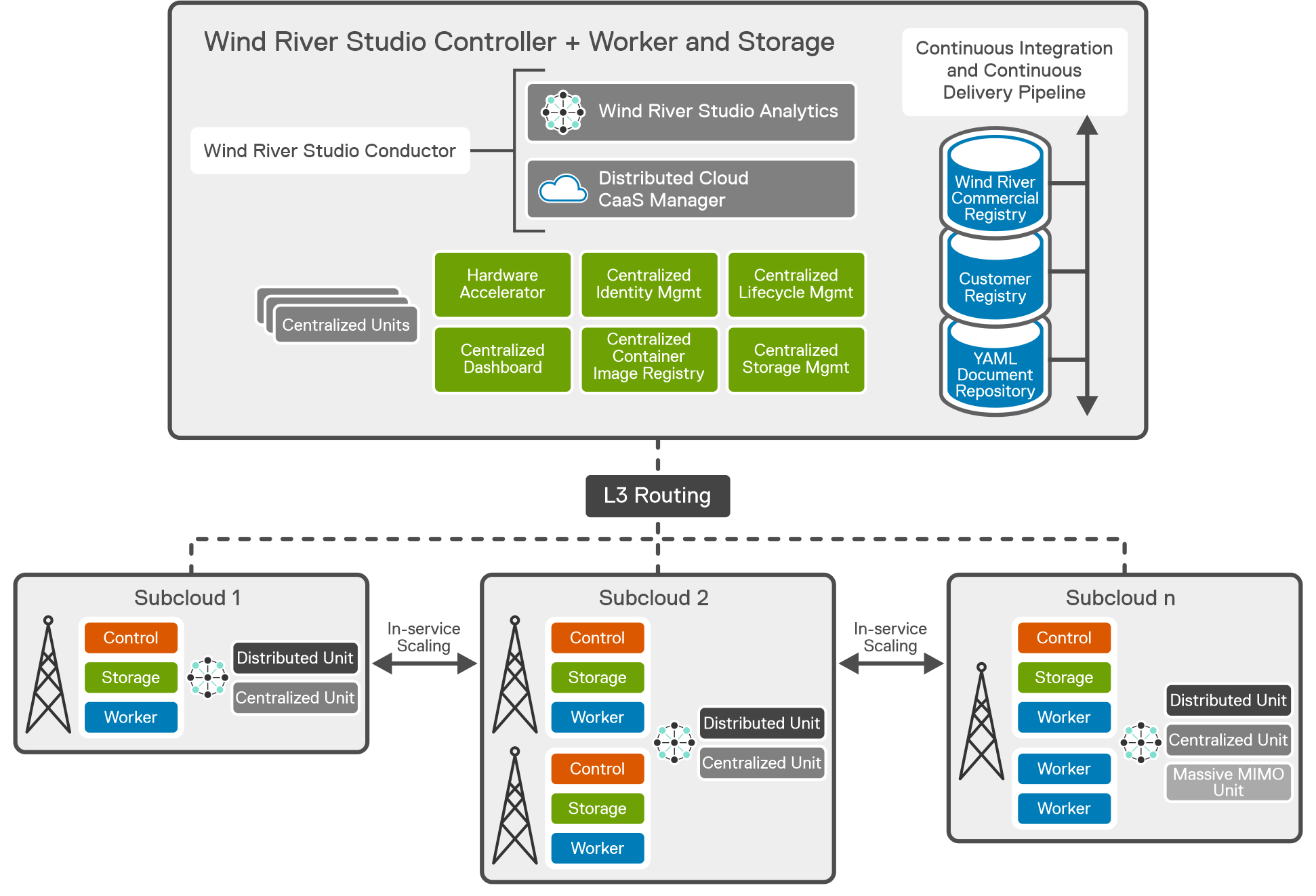
Wind River Studio Cloud Platform Architecture
Wind River Studio Cloud Platform Distributed Cloud configuration supports an edge computing solution by providing central management and orchestration for a geographically distributed network of cloud platform systems with easy installation with support for complete Zero Touch Provisioning of the entire cloud, from the Central Region to all the Sub-Clouds
The architecture features a synchronized distributed control plane for reduced latency, with an autonomous control plane such that all sub-cloud local services are operational even during loss of Northbound connectivity to the Central Region (Distributed cloud system controllers cluster location) which is quite important because Studio Cloud Platform can scale horizontal or vertical independent from the main cloud in the regional data center (RDC) or in National Data center (NDC).
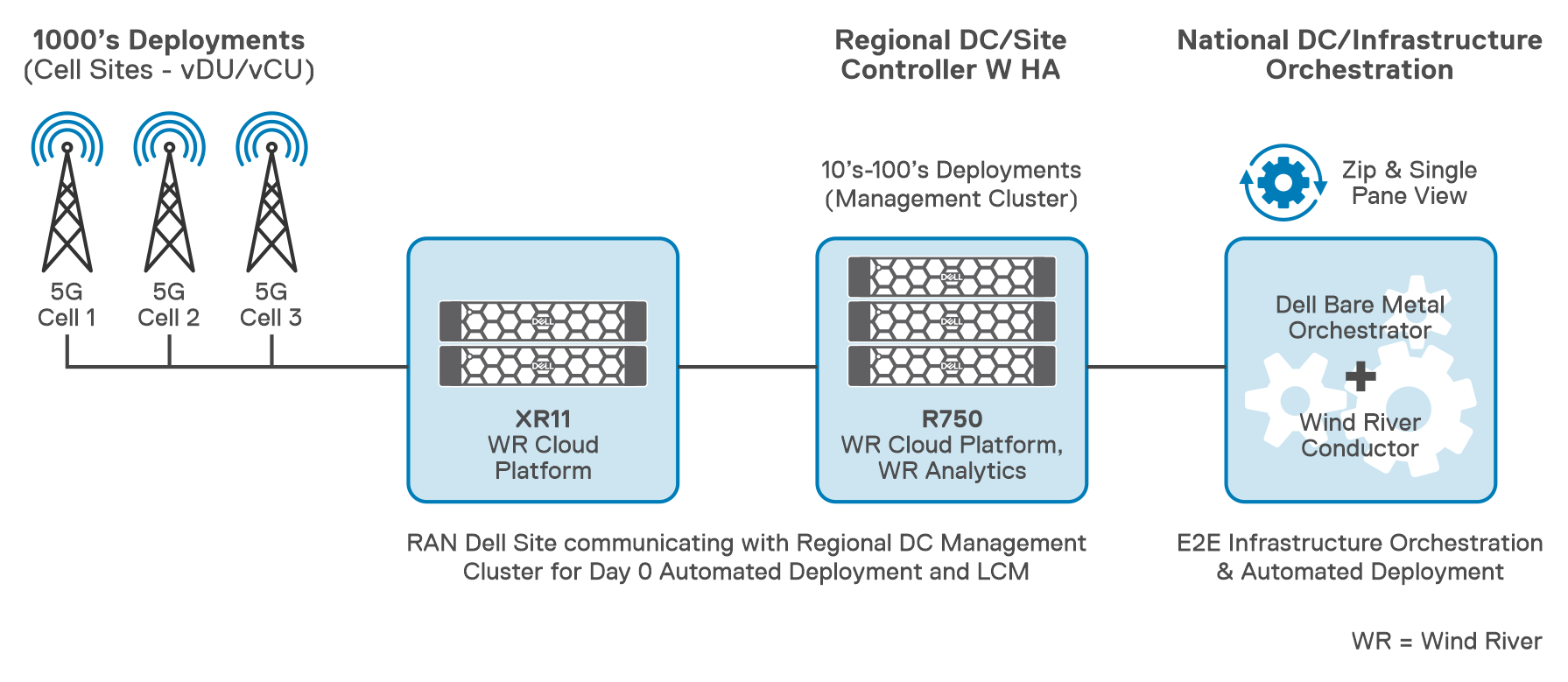
Cell Sites, or sub-clouds, are geographically dispersed edge sites of varying sizes. Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River cell site installations can be either All-in-One Simplex (AIO- SX), AIO Duplex (DX), or All-in-One (AIO) DX + workers. For a typical AIO SX deployment, at least one server is needed in a sub-cloud. Remote worker sites running Bare Metal Orchestrator are where sub-clouds are set up.
- AIO-SX (All-In-One Simplex) - A complete hyper-converged cloud with no HA, with ultra-low cloud platform overhead of 2 physical cores and 64G Memory, and 500G Disk, which is required to run the cloud, while the rest of the CPU cores, memory, and disk are used for the applications.
- AIO-DX (All-In-One Duplex) - Same as AIO-SX except that it runs on 2 servers to provide High Availability (HA) up to 6-9's.
- AIO-DX (All-In-One Duplex) +Workers - Two nodes plus a set of worker nodes (starting small and growing as workload demands increase)
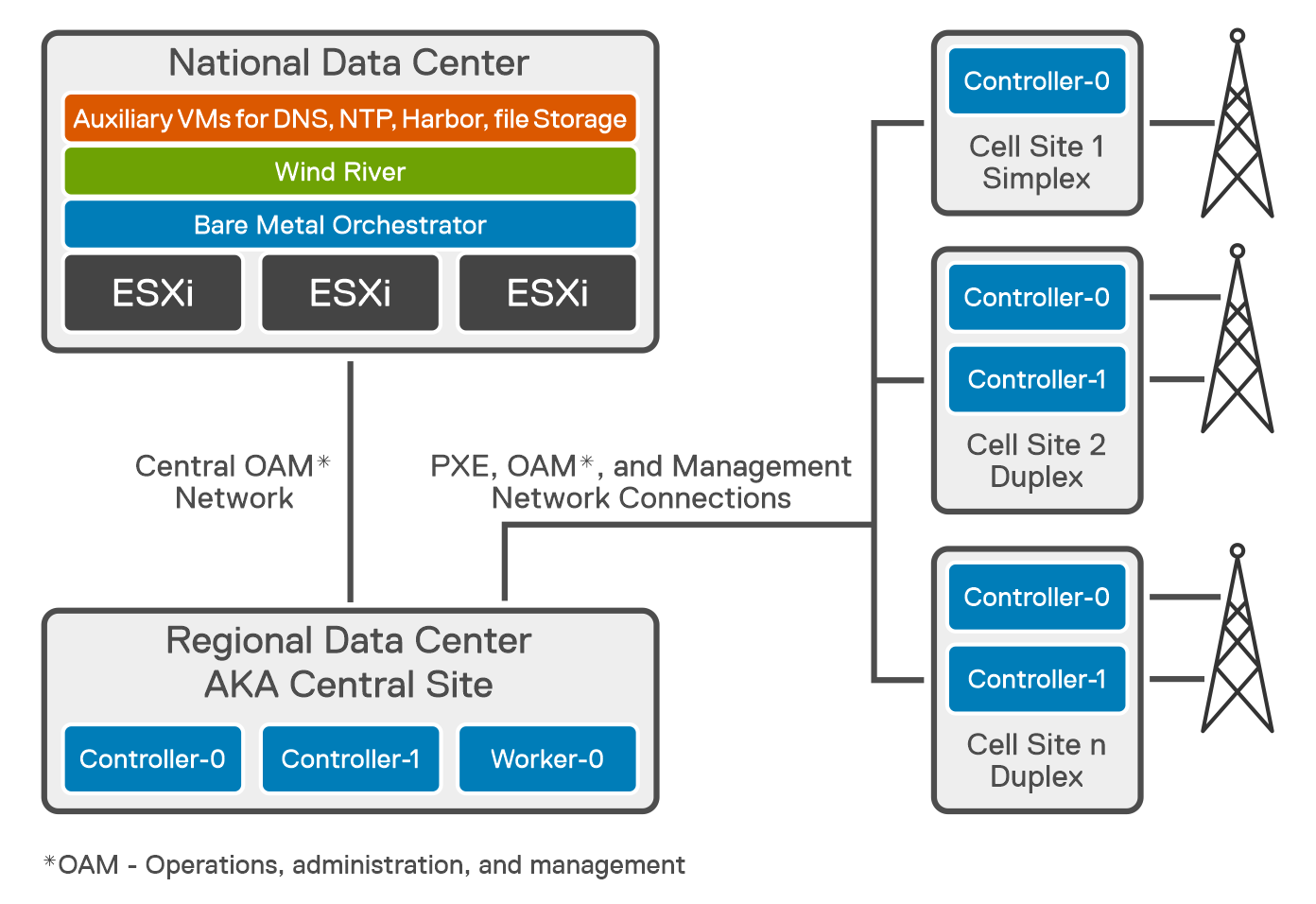
The Central Site at the RDC is deployed as a standard cluster across three Dell PowerEdge R750 servers, two of which are the controller nodes and one of which is a worker node, The Central Site also known as the system controller, provides orchestration and synchronization services for up to 1000 distributed sub-clouds, or cell sites. Controller-0, Controller-1, and Workers-0 through n are the various controllers in the system. To implement AIO DX, both Controller-0 and Controller-1 are required.
Wind River Studio Conductor runs in the National Data Center (NDC) as an orchestrator and infrastructure automation manager. It integrates with Dell's Bare Metal Orchestrator (BMO) to provide complete end-to-end automation for the full hardware and software stack. Additionally, it provides a centralized point of control for managing and automating application deployment in an environment that is large-scale and distributed.
Studio Conductor receives information from Bare Metal Orchestrator as new cell sites come online. Studio Conductor instructs the system controller (CaaS manager) to install, bootstrap, and deploy Studio Cloud Platform at the cell sites. It supports TOSCA (Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Application) based blueprint modeling. (Blueprints are policies that enable orchestration modeling.) Studio Conductor uses blueprints to map services to all distributed clouds and determine the right place to deploy. It also includes built-in secret storage to securely store password keys internally, reducing threat opportunities.
Studio Conductor can adapt and integrate with existing orchestration solutions. The plug-in architecture allows it to accommodate new and old technologies, so it can easily be extended to accommodate evolving requirements.
Wind River Studio Analytics is an integrated data collection, monitoring, analysis, and reporting tool used to optimize distributed network operations. Studio Analytics specifically solves a unique use case for the distributed edge. It provides visibility and operational insights into the Studio Cloud Platform from a Kubernetes and application workload perspective. Studio Analytics has a built-in alerting system with the ability to integrate with several third-party monitoring systems. Studio Analytics uses technology from Elastic. co as a foundation to take data reliably and securely from any source and format, then search, analyze, and visualize it in real time. Studio Analytics also uses the Kibana product from Elastic as an open user interface to visually display the data in a dashboard.
Dell Telecom Multi-Cloud Foundation Infrastructure Blocks provides a validated, automated, and factory integrated engineered system that paves the way for the zero-touch deployment of 5G Telco Cloud Infrastructure, to operation and management of the lifecycle of vRAN and Open RAN sites, all of which contribute to a high-performing network that lessens the cost, time, complexity, and risk of deploying and maintaining a telco cloud for the delivery of 5G services.
To learn more about our solution, please visit the Dell Telecom Multi-Cloud Foundation solutions site
Authored by:
Gaurav Gangwal
Senior Principal Engineer – Technical Marketing, Product Management
About the author:
Gaurav Gangwal works in Dell's Telecom Systems Business (TSB) as a Technical Marketing Engineer on the Product Management team. He is currently focused on 5G products and solutions for RAN, Edge, and Core. Prior to joining Dell in July 2022, he worked for AT&T for over ten years and previously with Viavi, Alcatel-Lucent, and Nokia. Gaurav has an engineering degree in electronics and telecommunications and has worked in the telecommunications industry for about 14 years. He currently resides in Bangalore, India.

Related Blog Posts

Cloud-native or Bust: Telco Cloud Platforms and 5G Core Migration
Wed, 24 May 2023 12:45:00 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Breaking down barriers with an open, disaggregated, and cloud-native 5G Core
As 5G network rollouts accelerate, communication service providers (CSPs) around the world are shifting away from purpose-built, vertically integrated solutions in favor of open, disaggregated, and cloud-native architectures running containerized network functions. This allows them to take advantage of modern DevSecOps practices and an emerging ecosystem of telecom hardware and software suppliers delivering cloud-native solutions based on open APIs, open-source software, and industry-standard hardware to boost innovation, streamline network operations, and reduce costs.
To take advantage of the benefits of cloud-native architectures, many CSPs are moving their 5G Core network functions onto commercially available cloud native application platforms like Red Hat OpenShift, the industry's leading enterprise Kubernetes platform. However, building an open, disaggregated telco cloud for 5G Core is not easy and it comes with its own set of challenges that need to be tackled before large scale deployments.
In an disaggregated network, the system integration and support tasks become the CSP's responsibility. To achieve their objectives for 5G, they must:
Accelerate the introduction and management of new technologies by simplifying and streamlining processes from Day 0, network design and integrations tasks, to Day 1 deployment, and Day 2 lifecycle management and operations.
Break down digital silos to deploy a horizontal cloud platform to reduce CapEx and OpEx while lowering power consumption
Deploy architectures and technologies that consistently meet strict telecom service level agreements (SLAs).
Digging into the challenges of deploying 5G Core network functions on cloud infrastructure
This will be a five-part blog series that addresses the challenges when deploying 5G Core network functions on a telco cloud.
In this first blog, we will highlight CSPs’ key challenges as they migrate to an open, disaggregated, and cloud-native ecosystem;
The next blog will explore the 3GPP 5G Core network architecture and its components;
The third blog in the series will discuss how Dell Technologies is working with Red Hat to streamline operator processes from initial technology onboarding through Day 2 operations when deploying a telco cloud to support core network functions;
The fourth blog will focus on how Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Red Hat can help CSPs move to a horizontal cloud platform to reduce costs and power consumption;
The final blog in the series will discuss how Dell is integrating Intel technology that consistently meets CSP SLAs for 5G Core network functions.
Accelerating the introduction and simplifying the management of 5G Core network functions on cloud infrastructure
Cloud native architectures offer the potential to achieve superior performance, agility, flexibility, and scalability, resulting in easily updated, scaled, and maintained Core network functions with improved network performance and lower operational costs. Nevertheless, operating 5G Core network functions on a telco cloud can be difficult due to new challenges operators face in integration, deployment, lifecycle management, and developing and maintaining the right skill sets.
Different integration and validation requirements
Open multi-vendor cloud-native architectures require the CSP to take on more ownership of design, integration, validation, and management of many complex components, such as compute, storage, networking hardware, the virtualization software, and the 5G Core workload that runs on top. This increases the complexity of deployment and lifecycle management processes while requiring investment in development of new skill sets.
Complexity of the deployment process demands automation
5G Core deployment on a telco cloud platform can be a complex process that requires integrating multiple systems and components into a unified whole with automated deployment from the hardware up through the Core network functions. This complexity creates the need for automation that not only to streamlines processes, but also ensures a consistent deployment or upgrade each time that aligns with established configuration best practices. Many CSPs may lack deployment experience with automation and cloud native tools making this a difficult task.
Lifecycle management and orchestration of a disaggregated 5G Core
The size and complexity of the 5G Core can make lifecycle management and orchestration challenging. Every one of the components starts a new validation cycle and increases the risk of introducing security vulnerabilities and configuration issues into the environment.
Lack of cloud-native skills and experience
Managing a telco cloud requires a different set of skills and expertise than operating traditional networks environments. CSPs often need to acquire additional staff and invest in cloud native training and development to obtain the skills and experience to put cloud native principles into practice as they build, deploy, and manage cloud-native applications and services.
Breaking down vertical silos with a horizontal, 5G telco cloud platform
In recent years, many CSPs embarked on a journey away from vertically integrated, proprietary appliances to virtualized network functions (VNFs). One of the goals when adopting network functions virtualization was to obtain greater freedom in selecting hardware and software components from multiple suppliers, making services more cost-effective and scalable. However, CSPs often experiences difficulties in designing, integrating and testing their individual stacks, resulting in higher integration costs, interoperability issues and regression testing delays leading to less efficient operations.
Despite efforts to move to virtualized network functions, silos of vertically integrated cloud deployments can emerge where the virtual network functions suppliers define their own cloud stack to simplify their process of meeting the requirements for each workload. These vertical silos prevented CSPs from pooling resources, which can reduce infrastructure utilization rates and increase power consumption. It also increases the complexity of lifecycle management as each layer of the stack for each silo needs to be validated whenever a change to a component of the stack is made.
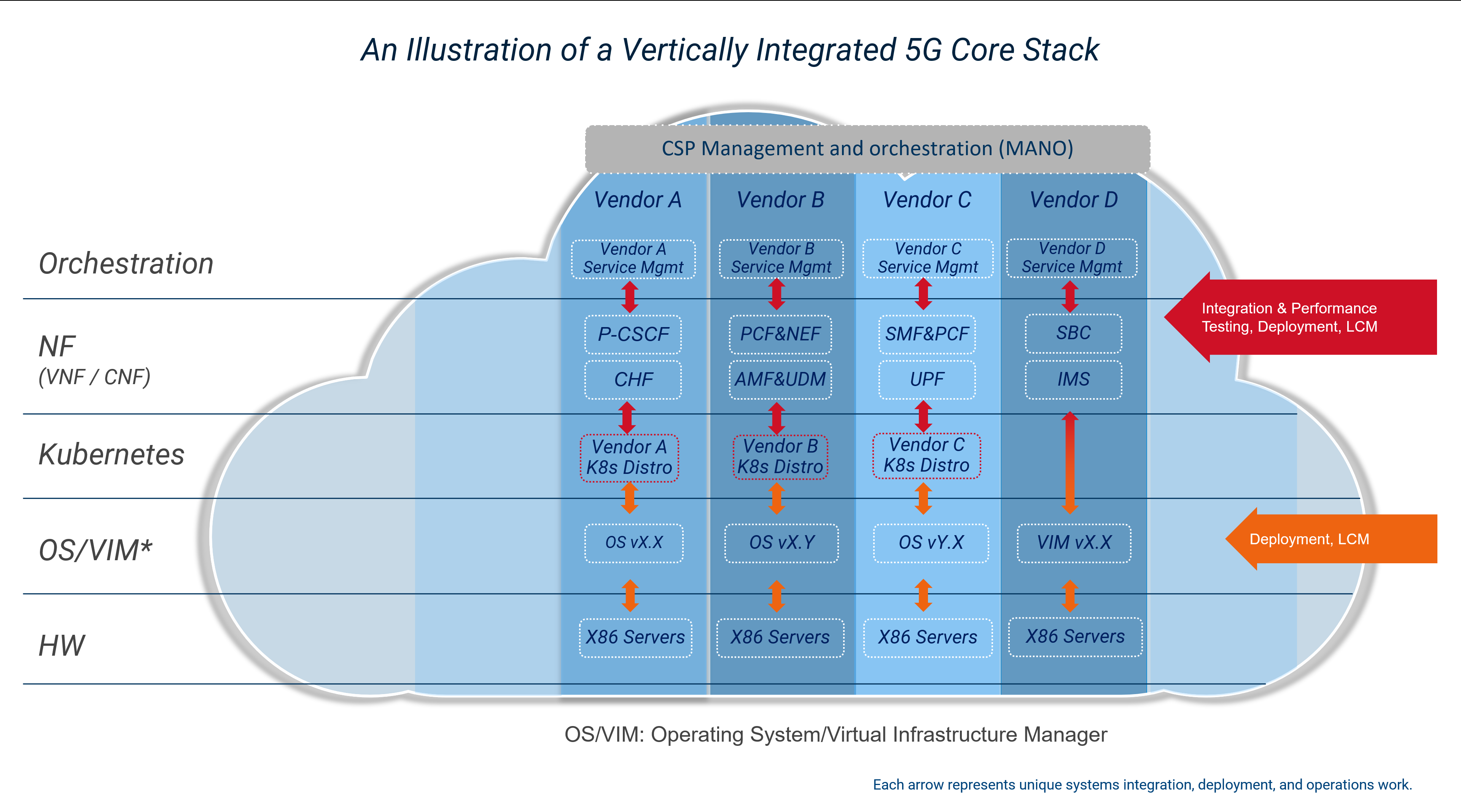 Vertically integrated 5G Core stack on a telco cloud
Vertically integrated 5G Core stack on a telco cloud
CSPs are now looking to implement a horizontal platform that can provide a common cloud infrastructure to help break down these silos to lower costs, reduce power consumption, improve operational efficiency, and minimize complexity allowing CSPs to adopt cloud native infrastructure from the core to the radio access network (RAN).
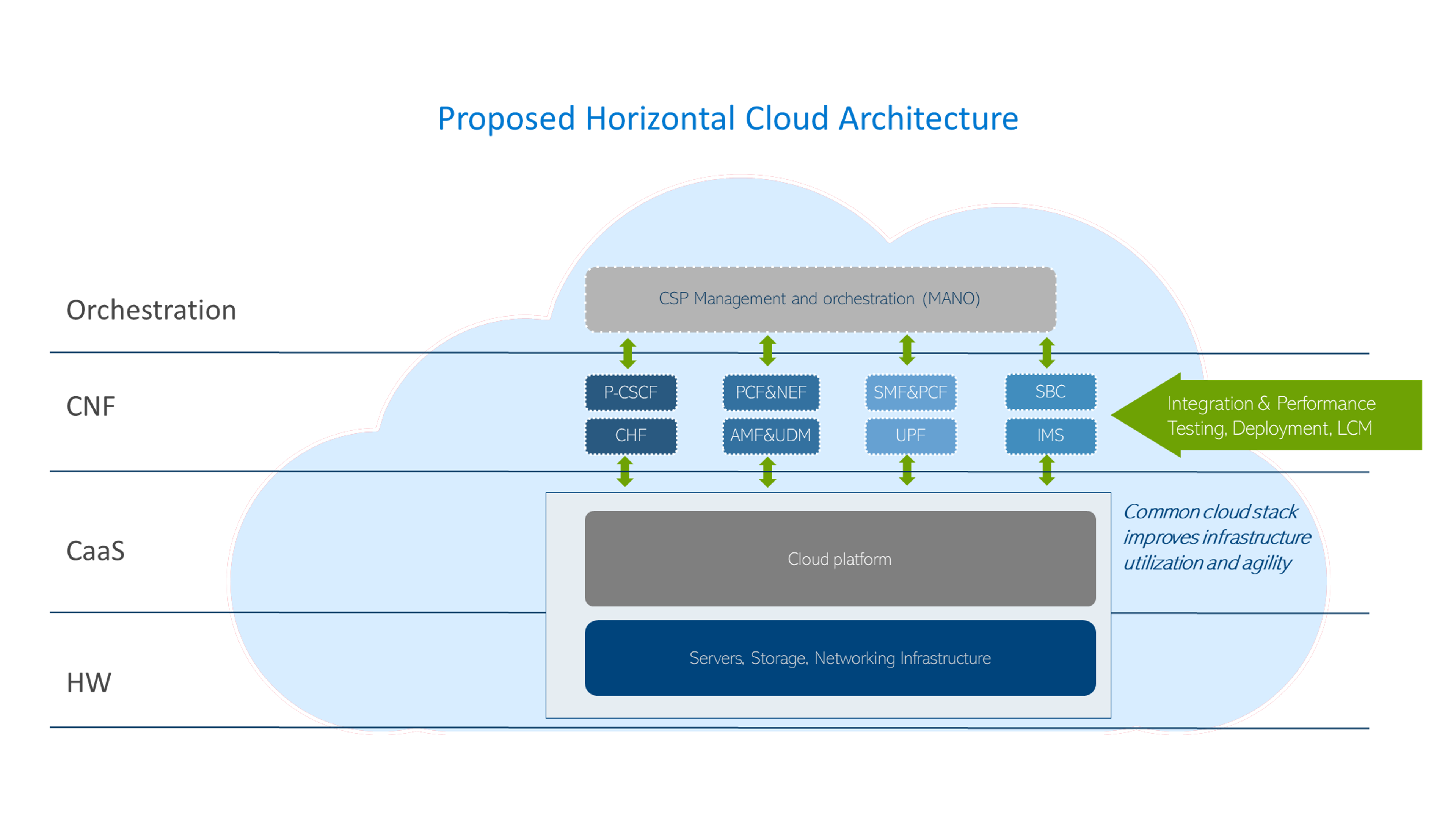 Horizontal platform for 5G telco workloads
Horizontal platform for 5G telco workloads
Maintaining compliance with telecom industry SLAs
Creating and managing a geographically dispersed telco cloud based on a broad range of suppliers while consistently adhering to CSP SLAs takes a lot of effort, resources and time and can introduce new complications and risks. To meet these SLAs and accelerate the introduction of new technologies, CSPs will need a novel approach when working with vendors that reduces integration and deployment times and costs while simplifying ongoing operations. This will include developing a tighter relationship with their supply base to offload integration tasks while maintaining the flexibility provided by an open telecom ecosystem. As an example, Vodafone recently introduced a paper outlining their vision for a new operating model to improve systems integrations with their supply base to help achieve these objectives. It would also include following a proven path in enterprise IT by adopting engineered systems, similar to the converged and hyper converged systems used by IT today, that have been optimized for telecom use cases to simplify deployment, scaling and management.
Short-term total cost of ownership (TCO)
When it comes to optimizing short-term TCO, there are several options available to CSPs. One such option is to work closely with vendors in order to reduce integration, deployment times and costs while simplifying ongoing operations. This approach can help CSPs leverage the expertise of vendors who specialize in the software and hardware components required for a disaggregated telco cloud. By working with skilled vendors, CSPs can reduce the risk of validating and integrating components themselves, which can lead to cost savings in the short term.
Another option that CSPs can consider is to adopt a phased approach to implementation. This involves deploying disaggregated telco cloud technologies in stages, starting with the most critical components and gradually expanding to include additional components over time. This approach can help to mitigate the initial costs associated with disaggregated telco cloud adoption while still realizing the benefits of increased flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
CSPs can also take advantage of initiatives like Vodafone's new operating model for improving systems integrations with their supply base. This model aims to simplify the process of integrating components from multiple vendors by providing a standardized framework for testing and validation. By adopting frameworks like this, CSPs can reduce the time and costs associated with integrating components from multiple vendors, which can help to optimize short-term TCO.
Although implementing a disaggregated telco cloud can increased investment in the short term, there are several options available to CSPs for optimizing short-term TCO. Whether it's working closely with trusted vendors, adopting a phased approach, or leveraging standardized frameworks, CSPs can take steps to reduce costs and maximize the benefits of a disaggregated telco cloud.
Your partners for simplifying telco cloud platform design, deployment, and operations
Dell and Red Hat are leading experts in cloud-native technology used in building 5G networks and are working together to simplify their deployment and management for CSPs. Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Red Hat is a solution that combines Dell's hardware and software with Red Hat OpenShift, providing a pre-integrated and validated solution for deploying and managing 5G Core workloads. This offering enables CSPs to quickly launch and scale 5G networks to meet market demand for new services while minimizing the complexity and risk associated with deploying cloud-native infrastructure.
Next steps
In the next blog we will dive deeper into the the service-based architecture of the 5G Core architecture and how it was developed to support cloud native principles. To learn more about how Dell Technologies and Red Hat are partnering to simplify the deployment and management of a telco cloud platform built to support 5G Core workloads, see the ACG Research Industry Directions Brief: Extending the Value of Open Cloud Foundations to the 5G Network Core with Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Red Hat.
Authored by:
Gaurav Gangwal
Senior Principal Engineer – Technical Marketing, Product Management
About the author:
Gaurav Gangwal works in Dell's Telecom Systems Business (TSB) as a Technical Marketing Engineer on the Product Management team. He is currently focused on 5G products and solutions for RAN, Edge, and Core. Prior to joining Dell in July 2022, he worked for AT&T for over ten years and previously with Viavi, Alcatel-Lucent, and Nokia. Gaurav has an Engineering degree in Electronics and Telecommunications and has worked in the telecommunications industry for about 14+ years. He currently resides in Bangalore, India.

Kevin Gray
Senior Consultant, Product Marketing – Product Marketing
About the author:
Kevin Gray leads marketing for Dell Technologies Telecom Systems Business Foundations solutions. He has more than 25 years of experience in telecommunications and enterprise IT sectors. His most recent roles include leading marketing teams for Dell’s telecommunications, enterprise solutions and hybrid cloud businesses. He received his Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from the University of Massachusetts in Amherst and his MBA from Bentley University. He was born and raised in the Boston area and is a die-hard Boston sports fan.


Accelerate Telecom Cloud Deployments with Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks
Mon, 31 Oct 2022 16:48:10 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
During MWC Vegas, Dell Technologies announced Dell’s first Telecom Infrastructure Blocks co-engineered with our partner Wind River to help communication service providers (CSPs) reduce complexity, accelerate network deployments, and simplify life cycle management of 5G network infrastructure. Their first use cases will be focused on infrastructure for virtual Radio Access Network (vRAN) and Open RAN workloads.
Deploying and supporting open, virtualized, and cloud-native 5G RANs is one of the key requirements to accelerate 5G adoption. The number of options available in 5G RAN design makes it imperative that infrastructures supporting them are flexible, fully automated for distributed operations, and maximally efficient in terms of power, cost, the resources they consume, and the performance they deliver.
Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River are designed and fully engineered to provide a turnkey experience with fully integrated hardware and software stacks from Dell and Wind River that are RAN workload-ready and aligned with workload requirements. This means the engineered system, once delivered, will be ready for RAN network functions onboarding through a simple and standard workflow avoiding any integration and lifecycle management complexities normally expected from a fully disaggregated network deployment.
The Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River are a part of the Dell Technologies Multi-Cloud Foundation, a telecom cloud designed specifically to assist CSPs in providing network services on a large scale by lowering the cost, time, complexity, and risk of deploying and maintaining a distributed telco-cloud. Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River are comprised of:
- Dell hardware that has been validated and optimized for RAN
- Dell Bare Metal Orchestrator and a Bare Metal Orchestrator Module (a combination of a Bare Metal Orchestrator plug-in and a Wind River Conductor integration plug-in)
- Wind River Studio, which is comprised of:
- Wind River Conductor
- Wind River Cloud Platform
- Wind River Analytics
How do Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River make infrastructure design, delivery, and lifecycle management of a telecom cloud better and easier?
From technology onboarding to Day 2+ operations for CSPs, Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks streamline the processes for technology acquisition, design, and management. We have broken down these processes into 4 stages. Let us examine how Dell Telecom Infrastructure Blocks for Wind River can impact each stage of this journey.
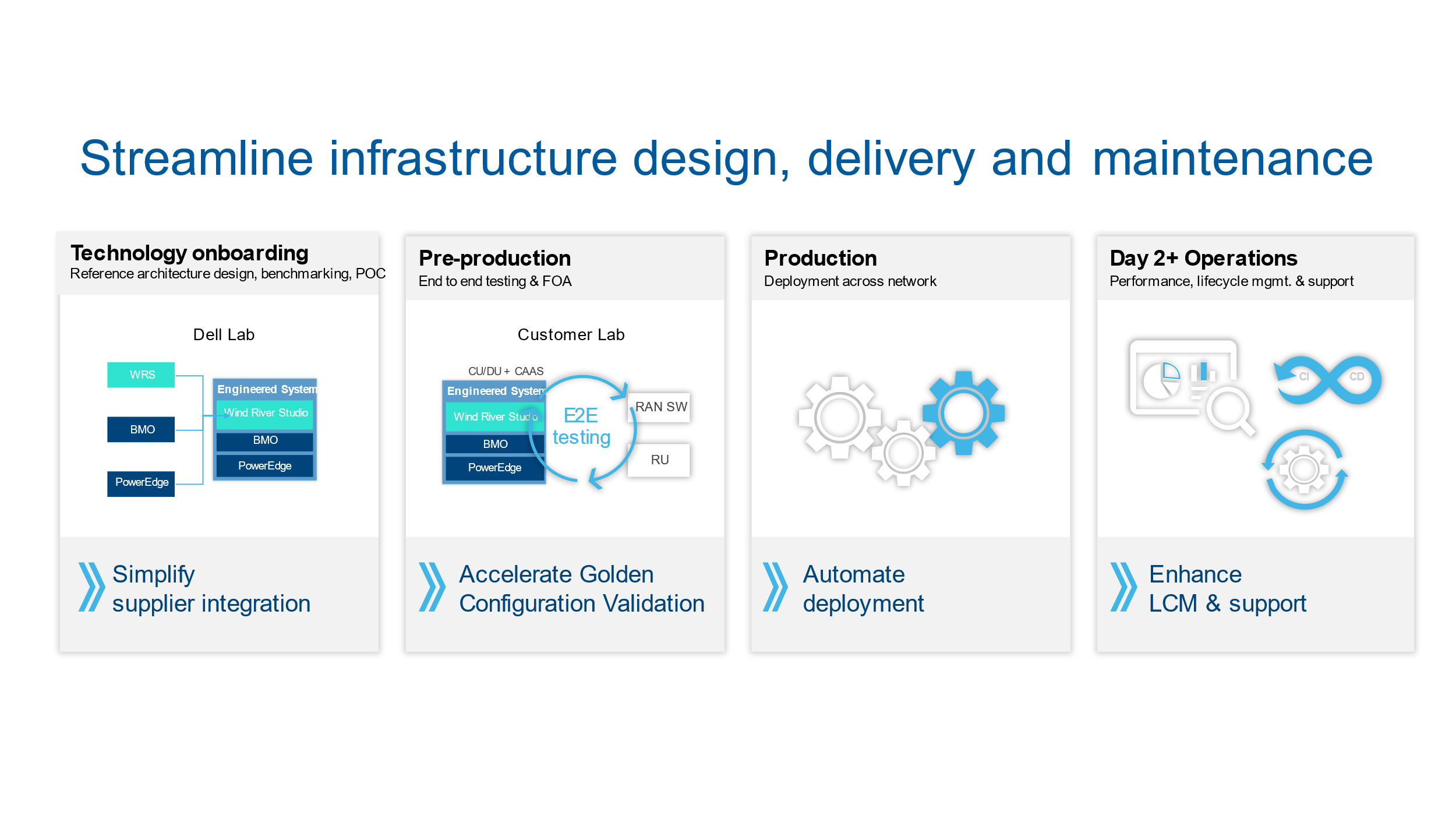
Stage 1: Technology onboarding | Faster Time to Market
The first stage is the Technology onboarding, where Dell Technologies works with Wind River in Dell’s Solution Engineering Lab to develop the engineered system. Together we design, validate, build, and run a broad range of test cases to create an optimized engineered system for 5G RAN vCU/vDU and Telecom Multi-Cloud Foundation Management clusters. During this stage, we conduct extensive solution testing with Wind River performing more than 650 test cases. This includes validating functionality, interoperability, security, scalability, high availability, and test cases specific to the workload’s infrastructure requirements to ensure this system operates flawlessly across a range of scale and performance points.
We also launched our OTEL Lab (Open Telecom Ecosystem Lab) to allow telecom ecosystem suppliers (ISVs) to integrate or certify their workload applications on Dell infrastructure including Telecom Infrastructure Blocks. Customers and partners working in OTEL can fine-tune the Infrastructure Block to a given CSP’s needs, marrying the efficiency of Infrastructure Block development with the nuances presented in meeting a CSP’s specific requirements.
Continuous improvement in the design of Infrastructure Blocks is enabled by ongoing feedback on the process throughout the life of the solution which can further streamline the design, validation, and certification. This extensive process produces an engineered system that streamlines the operator’s reference architecture design, benchmarking, proof of concept, and end-to-end validation processes to reduce engineering costs and accelerate the onboarding of new technology.
All hardware and software required for this Engineered system are integrated in Dell’s factory and sold and supported as a single system to simplify procurement, reduce configuration time, and streamline product support.
This "shift left" in the design, development, validation, and integration of the stacks means readiness testing and integration are finished sooner in the development cycle than they would have been with more traditional and segregated development and test processes. For CSPs, this method speeds up time to value by reducing the time needed to prepare and validate a new solution for deployment.
Now we go from Technology onboarding to the second phase, pre-production.
Stage 2: Pre-production | Accelerated onboarding
From Dell’s Solution Engineering Labs, the engineered system moves into the CSPs pre-production environment where the golden configuration is defined. Rather than receiving a collection of disaggregated components, (infrastructure, cloud stacks, automation, and so on.) CSPs start with a factory-integrated, engineered system that can be quickly deployed in their pre-production test lab. At this stage, customers leverage the best practices, design guidance, and lessons learned to create a fully validated stack for their workload. The next step is to pre-stage the Telco Cloud stack including the workload and start preparing for Day 1 and Day 2 by integrating with the customer CI/CD pipeline and defining/agreeing on the life-cycle management process to support the first office application deployment.
Stage 3: Production | Automation enables faster deployment
Advancing the flow, deployment into production is accelerated by:
- Factory integration that reduces procurement, installation, and integration time on-site.
- Embedded automation that reduces time spent configuring hardware or software. This includes validating configurations and streamlining processes with Customer Information Questionnaires (CIQs). CIQs are YAML files that list credentials, management networks, storage details, physical locations, and other relevant data needed to set the telco cloud stack at different physical locations for CSPs.
- Streamlining support with a unified single call carrier-grade support model for the full cloud stack.
Automating deployment eliminates manual configuration errors to accelerate product delivery. Should the CSP need assistance with deployment, Dell's professional services team is standing by to assist. Dell provides on-site services to rack, stack, and integrate servers into their network.
Stage 4: Day 2+ Operations | Performance, lifecycle management, and support
Day 2+ operations are simplified in several ways. First, the automation provided, combined with the extensive validation testing Dell and Wind River perform, ensure a consistent, telco-grade deployment, or upgrade each time. This streamlines daily fault, configuration, performance, and security management in the fully distributed cloud. In addition, Dell Bare Metal Orchestrator will automate the detection of configuration drift and its remediation. And, Wind River Studio Analytics utilizes machine learning to proactively detect issues before they become a problem.
Second, Dell’s Solutions Engineering lab validates all-new feature enhancements to the software and hardware including new updates, upgrades, bug fixes, and security patches. Once we have updated the engineered system, we push it via Dell CI/CD pipeline to Dell factory and OTEL Lab. We can also push the update to the CSP's CI/CD pipeline using integrations set up by Dell Services to reduce the testing our customers perform in their labs.
We complement all this by providing unified, single-call support for the entire cloud stack with options for carrier-grade SLAs for service response and restoration times.
Proprietary appliance-based networks are being replaced by best-of-breed, multivendor cloud networks as CSPs adapt their network designs for 5G RAN. As CSPs adopt disaggregated, cloud-native architectures, Dell Technologies is ready to lend a helping hand. With Dell Telecom Multi-Cloud Foundation, we provide an automated, validated, and continuously integrated foundation for deploying and managing disaggregated, cloud-native telecom networks.
Ready to talk? Request a callback.
To learn more about our solution, please visit the Dell Telecom Multi-Cloud Foundation solutions site
Authored by:
Gaurav Gangwal
Senior Principal Engineer – Technical Marketing, Product Management
About the author:
Gaurav Gangwal works in Dell's Telecom Systems Business (TSB) as a Technical Marketing Engineer on the Product Management team. He is currently focused on 5G products and solutions for RAN, Edge, and Core. Prior to joining Dell in July 2022, he worked for AT&T for over ten years and previously with Viavi, Alcatel-Lucent, and Nokia. Gaurav has an engineering degree in electronics and telecommunications and has worked in the telecommunications industry for about 14 years. He currently resides in Bangalore, India.