Home > Storage > PowerFlex > White Papers > Reference Architecture: Google Cloud Anthos and GDC Virtual on Dell PowerFlex > PowerFlex deployment architectures
PowerFlex deployment architectures
-
PowerFlex software defined infrastructure excels in deployment flexibility. PowerFlex can be deployed in a two-layer (independent compute and storage layers), single-layer (Hyperconverged Infrastructure, or HCI), or a mixture of the two architectures (Mixed).
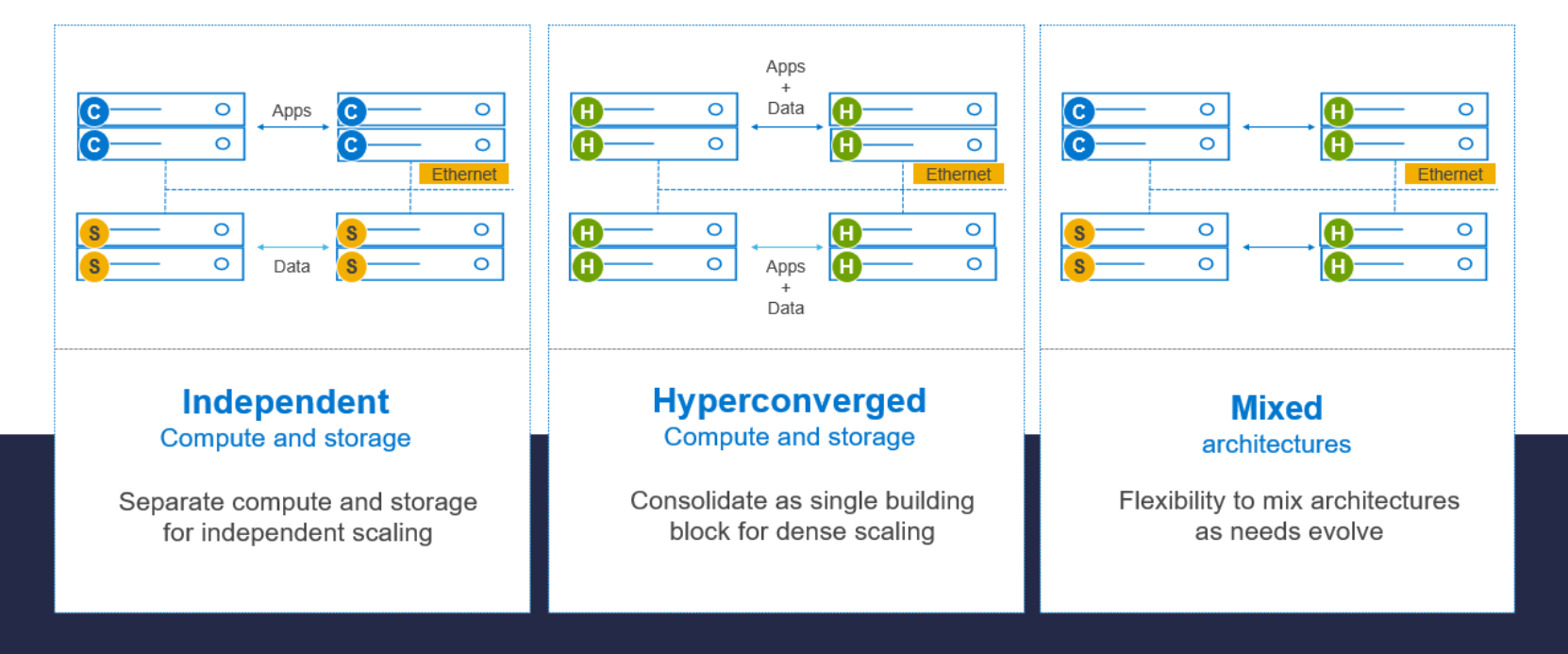 Figure 2: PowerFlex deployment architectures
Figure 2: PowerFlex deployment architecturesIndependent architecture
In an independent architecture, or two-layer architecture, some nodes provide storage capacity for applications data while other separate and independent nodes provide compute resources for applications and workloads. Compute and storage resources can be scaled independently by adding nodes to the cluster while it remains active. This separation of compute and storage resources can help minimize software licensing costs in certain situations. This architecture can be ideal for high-performance databases and application workloads.
Hyperconverged architecture
In an HCI architecture, each node in the cluster contributes storage and compute resources simultaneously to the applications and workloads. This architecture allows you to scale your infrastructure uniformly with building blocks that add both storage and compute resources. This architecture is appropriate for data center and workload consolidation.
Mixed architecture
In a mixed architecture we have a combination of both the HCI and Independent architectures. As shown in Figure 2 there would be some storage only nodes, compute only nodes, and HCI nodes as a part of the same PowerFlex cluster. This is a desirable architecture when working with an existing compute infrastructure and adding high-performance software defined infrastructure. This can also be a starting point for a two-layer deployment design as external workloads are migrated to PowerFlex.
