Home > Storage > PowerStore > Databases and Data Analytics > Dell EMC PowerStore Metro Node with Microsoft SQL Server > SQL Server with PowerStore metro node Metro
SQL Server with PowerStore metro node Metro
-
PowerStore metro node Metro enables metro node capabilities over distance. By adding a second metro node cluster in another location, storage resiliency can be stretched between data centers or multiple buildings. This provides an alternative for product-specific data replication mechanisms for extended cluster or geo-cluster applications.
For example, in a metro node Metro configuration, one metro node cluster is placed at Site A and another is placed at Site B as shown in the example below.
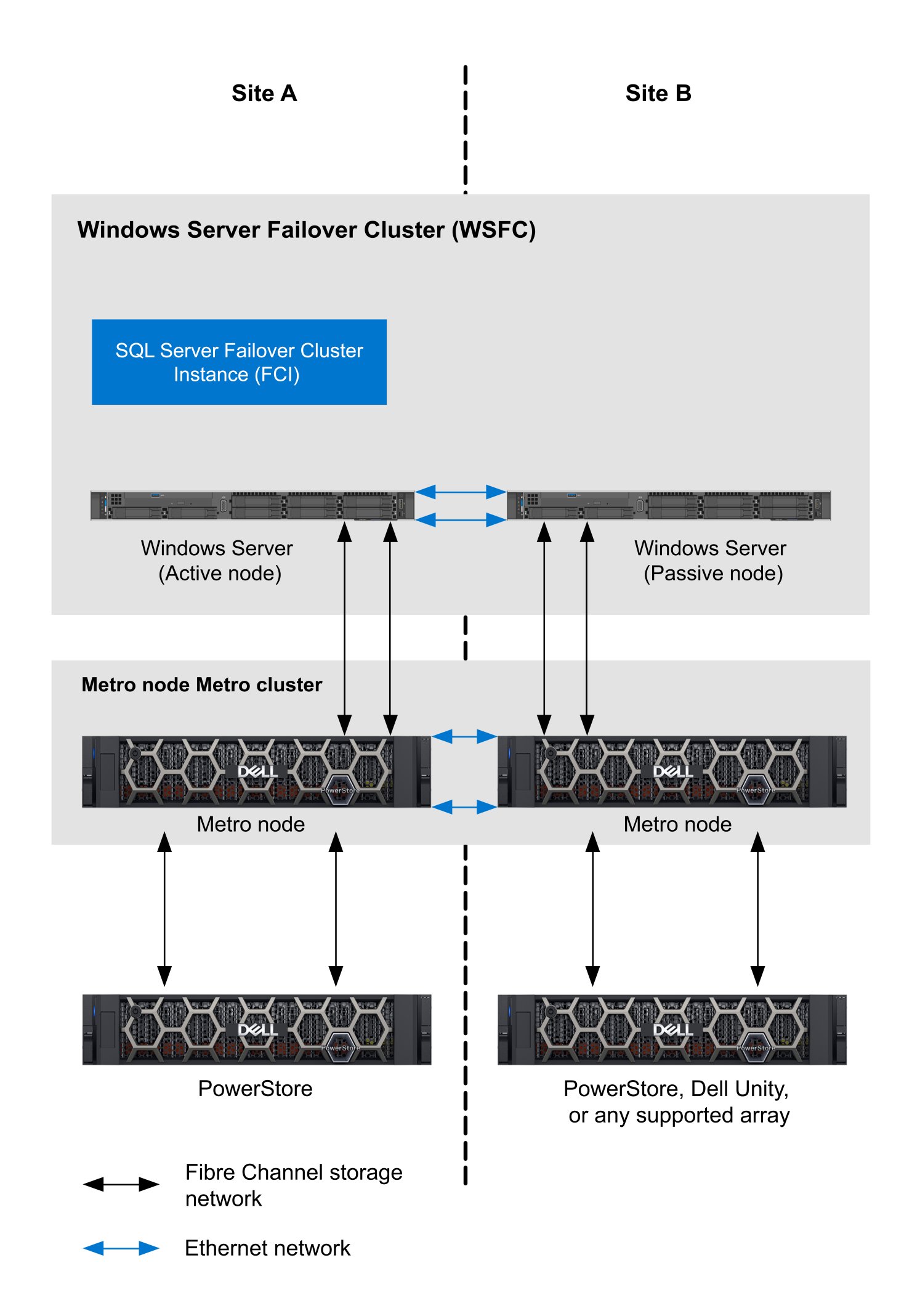
Figure 7. WSFC storage configuration with Metro node Metro
In a metro node Metro configuration, storage network traffic is local to the site and cross-site communication is handled by the Ethernet network. In this example, in the case of a local storage failure at Site A, IO traffic would flow across the ethernet network between metro node clusters and access storage at Site B. At this point an administrator could decide whether to failover the compute to Site B as a planned event, or to wait until the storage issue at Site B is resolved, metro node performs automatic resynchronization, and all IO traffic is returned to normal at Site A.
The same architecture pattern can be applied to SQL Server Always On Availability Groups (AG). In this way, additional protection against site failure is added while maintaining persistent storage connectivity to the applications in the event of a single site storage failure that would otherwise introduce a SQL Server instance failover and likely an unplanned outage.
It is recommended that distance between metro node Metro clusters is less that 100km and the Round Trip Time (RTT) over the inter-cluster link is no more than 10ms. See the Dell Metro Node Product Guide for more information.
