Briefs

Dell PowerScale: Data Protection with Dell NetWorker using NDMP
Fri, 23 Feb 2024 22:05:51 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
NetWorker for PowerScale data protection
Dell NetWorker is an enterprise-class cross-platform data protection software solution for file servers, application servers, and database management systems across the network. NetWorker supports a wide range of data protection options, including Network Data Management Protocol (NDMP) support for NAS storage devices. Dell PowerScale NAS storage integration with NetWorker software provides esteemed data protection and recovery capabilities for enterprises of all sizes in a secure way.
NetWorker software uses NDMP functionality to enable access to storage in a heterogeneous network environment. NDMP uses TCP/IP to control the movement of the data and specifies various device drivers to store the data on devices.
Three main components support NDMP data operations with the NetWorker software: NDMP Data Server (PowerScale), NDMP Tape Server (the host with the backup device to which NetWorker writes the NDMP data), and the Data Management Agent or DMA (in which the NetWorker server is the DMA).
NDMP Features with Dell NetWorker
Multistreaming
NetWorker 9.0.1 and later supports multistreaming for up to 32 streams for Isilon OneFS 8.0 and later backups. NetWorker uses the client parallelism value that is defined for a PowerScale client to determine how many backups run concurrently.
IPv6
NetWorker storage nodes support IPv6 communications with a NetWorker server. By default, NDMP backup and recovery operations use IPv6 to create the data connection between the NDMP data server and mover server.
Checkpoint restart
The PowerScale filers create a snapshot of the file system before the backup. The save set is generated from the snapshot.
Volume Based Backup (vbb) supports
Data Access in Real Time (DART) version 5.5 and later.
Direct Access Recovery (DAR) and Dynamic Direct Access Recovery (DDAR)
DAR and DDAR send file information from the NAS filer to the NetWorker server.
Methods to configure the NDMP Data Server and the NDMP Tape Server to perform backups and recoveries
NDMP local backup (Direct-NDMP)
In an NDMP local backup (Direct-NDMP), the NDMP Data Server (NAS) sends data to a locally attached tape device or library.
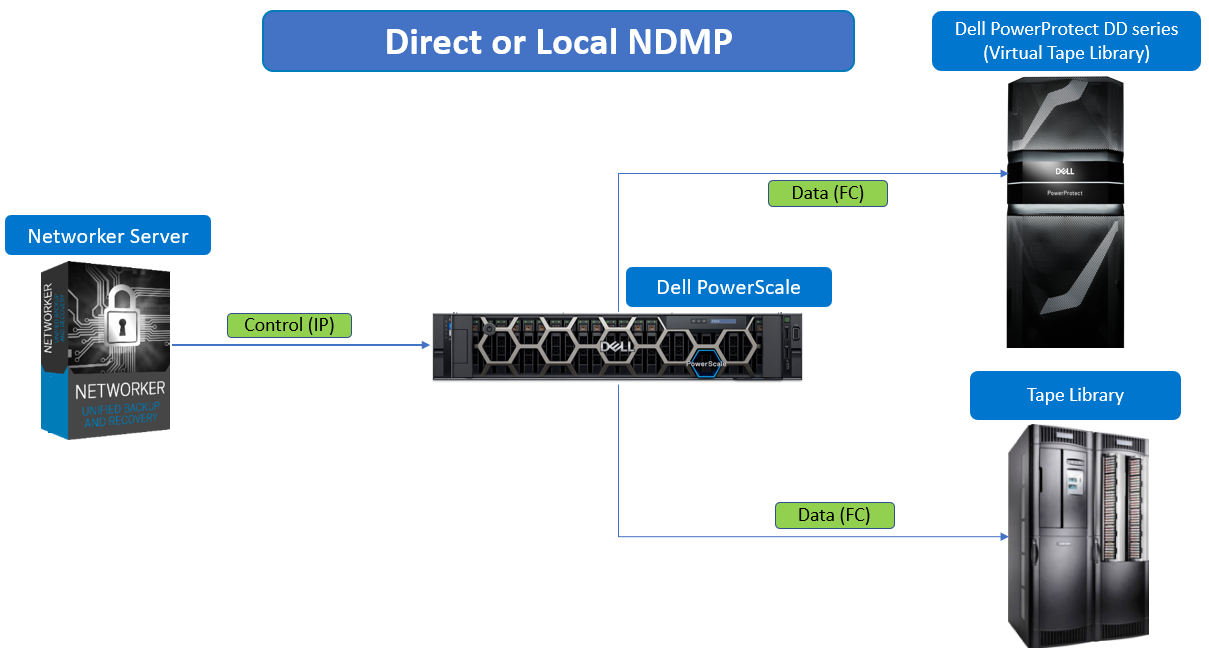 Figure 1. NDMP local backup (Direct-NDMP)
Figure 1. NDMP local backup (Direct-NDMP)
NDMP backups to non-NDMP devices (NDMP-DSA)
NetWorker software writes NDMP data to non-NDMP devices, including tape, virtual tape, AFTD, and Dell PowerProtect DD series appliances. A backup of NDMP data to a non-NDMP device is performed in one of two ways:
- NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that are local to the NetWorker server
- NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that reside on a NetWorker storage node
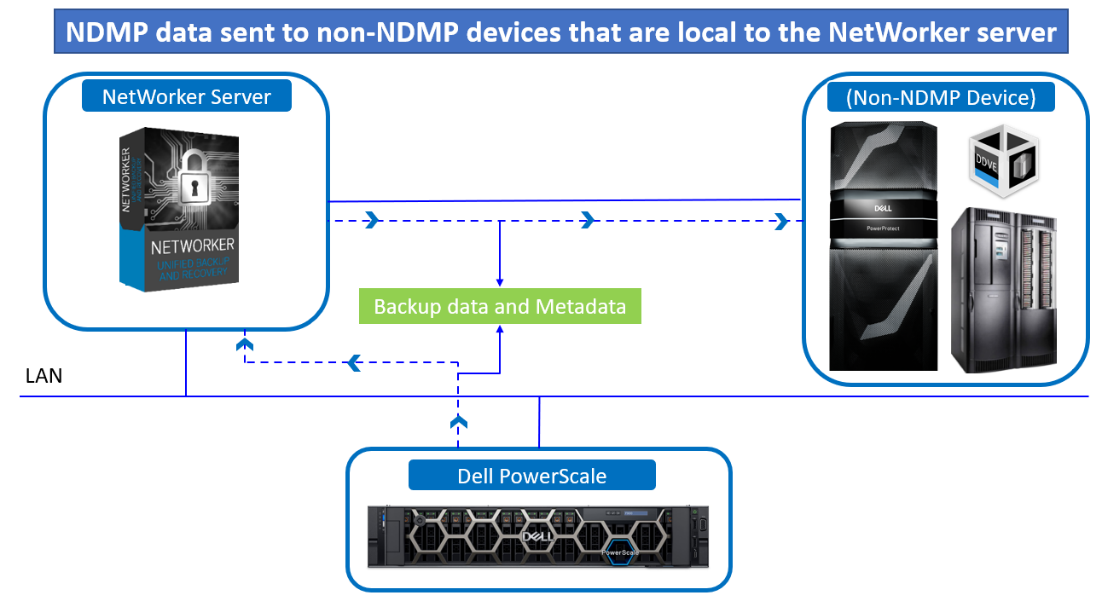 Figure 2. NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that are local to the NetWorker server
Figure 2. NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that are local to the NetWorker server
NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that are local to the NetWorker servers has the following characteristics:
- The backup data traverses the network between the NetWorker server and the NDMP data server.
- The metadata, the NDMP control information, and the file history (FH) remains local to the NetWorker server and still traverse the network.
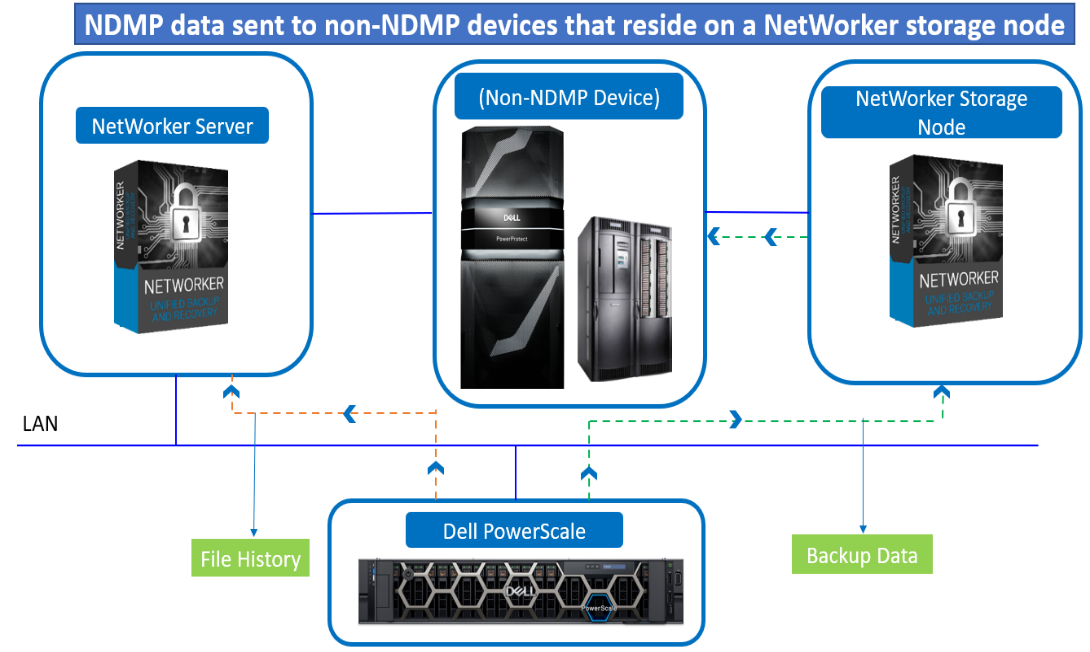 Figure 3. NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that reside on a NetWorker storage node
Figure 3. NDMP data sent to non-NDMP devices that reside on a NetWorker storage node
NDMP backups can be configured to write data to a NetWorker storage node in one of two ways:
- Immediate save (nsrdsa_save runs on storage node)
- Non-immediate save (nsrdsa_save runs on NetWorker Server)
Immediate save (nsrdsa_save runs on storage node)
The nsrdsa_save backup command runs on the NetWorker storage node. The NetWorker software uses TCP/IP and shared memory to communicate between the nsrdsa_save and nsrmmd processes.
Non-immediate save (nsrdsa_save runs on NetWorker Server)
By default, NDMP backups to a non-NDMP device use non-immediate save. When configuring an NDMP backup to use non-immediate save, the following actions occur:
- The nsrdsa_save backup command runs on the NetWorker server.
- The nsrdsa_save process uses TCP/IP to read the data in a local buffer.
- The nsrdsa_save process transmits the data to the nsrmmd process on the storage node.
- The nsrmmd process writes the data to the storage device.
Three-party backup
A three-party or three-way backup sends NDMP data to an NDMP Tape Server, however the NDMP Data Server and the NDMP Tape Server are not the same physical host.
There are two main types of three-party backups:
- In the first scenario, NetWorker sends the NDMP data to non-NDMP devices (NDMP-DSA). The NDMP Data Server and the NDMP Tape Server reside on different physical hosts. The NDMP Tape Server is always a NetWorker Server or a NetWorker Storage Node. Hence, NDMP-DSA is also a three-way NDMP backup.
- In the second scenario, NetWorker sends NDMP data to NDMP devices. The data flows from the NDMP Data Server to the NDMP Tape Server and then to a library that is locally attached to the NDMP Tape Server. In this configuration, the NDMP save sets cannot be archived
Dynamic drive sharing
Dynamic Drive Sharing (DDS) is a feature that provides NetWorker software with the ability to recognize shared physical tape drives.
DDS enables NetWorker software to perform the following operations:
- Skip the shared tape drives that are in use
- Route the backups or recoveries to other available shared tape drives
Benefits of DDS
Enabling DDS on a NetWorker system provides these benefits:
- Reduces storage costs
- Reduces LAN traffic
- Provides fault tolerance
- Provides configuration over a greater distance
References
Author: Vinod Kumaresan

