

Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies
Wed, 03 Aug 2022 21:41:04 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
A New Operating System for the Cloud
Cloud computing addresses distributed computing needs that arise from ever-increasing growth and mobility in the telecommunications industry. Cloud computing is performed in a data center that uses spine-leaf architecture. This architecture typically consists of two or three switching layers that use dual-homed connections to provide link redundancy.
The spine-leaf architecture, depicted in the following figure, is based on the following qualities:
- Simplicity
- Scalability
- Uniformity
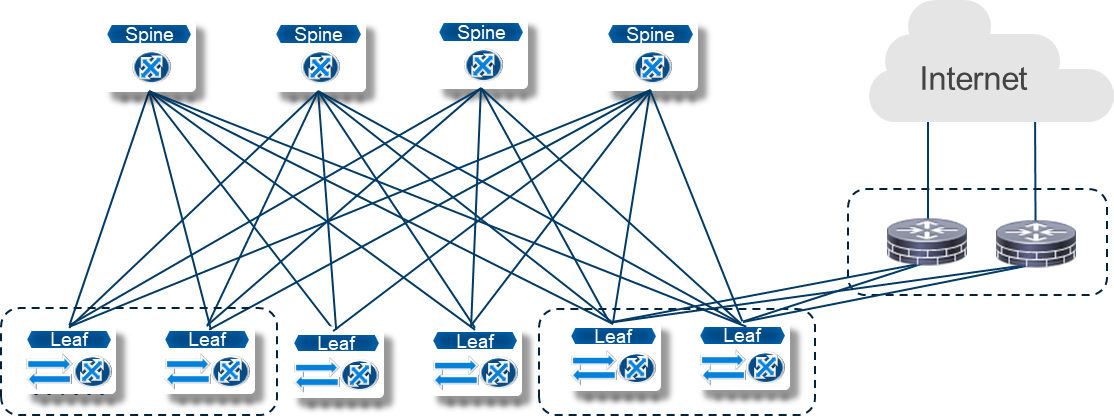 Figure 1—Spine-leaf architecture in a data center
Figure 1—Spine-leaf architecture in a data centerDell Technologies is a proponent of innovation in open networking, as evidenced by Dell Technologies enabling its data center switches to use third-party operating systems. Dell Technologies continues this innovation by adopting SONiC, a free and open-source network operating system designed for scalable infrastructure.
The Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies is based on the open-source SONiC architecture and includes an added set of features and world-class support. Enterprise SONiC Distribution enables network engineers to build a future-proof, scale-out, multitenant, and resilient network usable by single retail stores, large enterprises, or service providers. The following use cases describe how one network can be deployed for diverse uses.
Enterprise SONiC Distribution use cases
Enterprise SONiC Distribution supports several use cases, but three stand out. Each subsequent use case builds on key aspects of the previous use case. The use cases start with a Layer 3 underlay, continue to scalable networks, and end with routing to the host.
Use case 1—Simple network (Layer 3) underlay
To start, use Enterprise SONiC Distribution to build a Layer 3 underlay that leverages Border Gateway Protocol’s (BGP) scalability and active multilink connections between leaf, spine, and super-spine layers, as shown in the following figure.
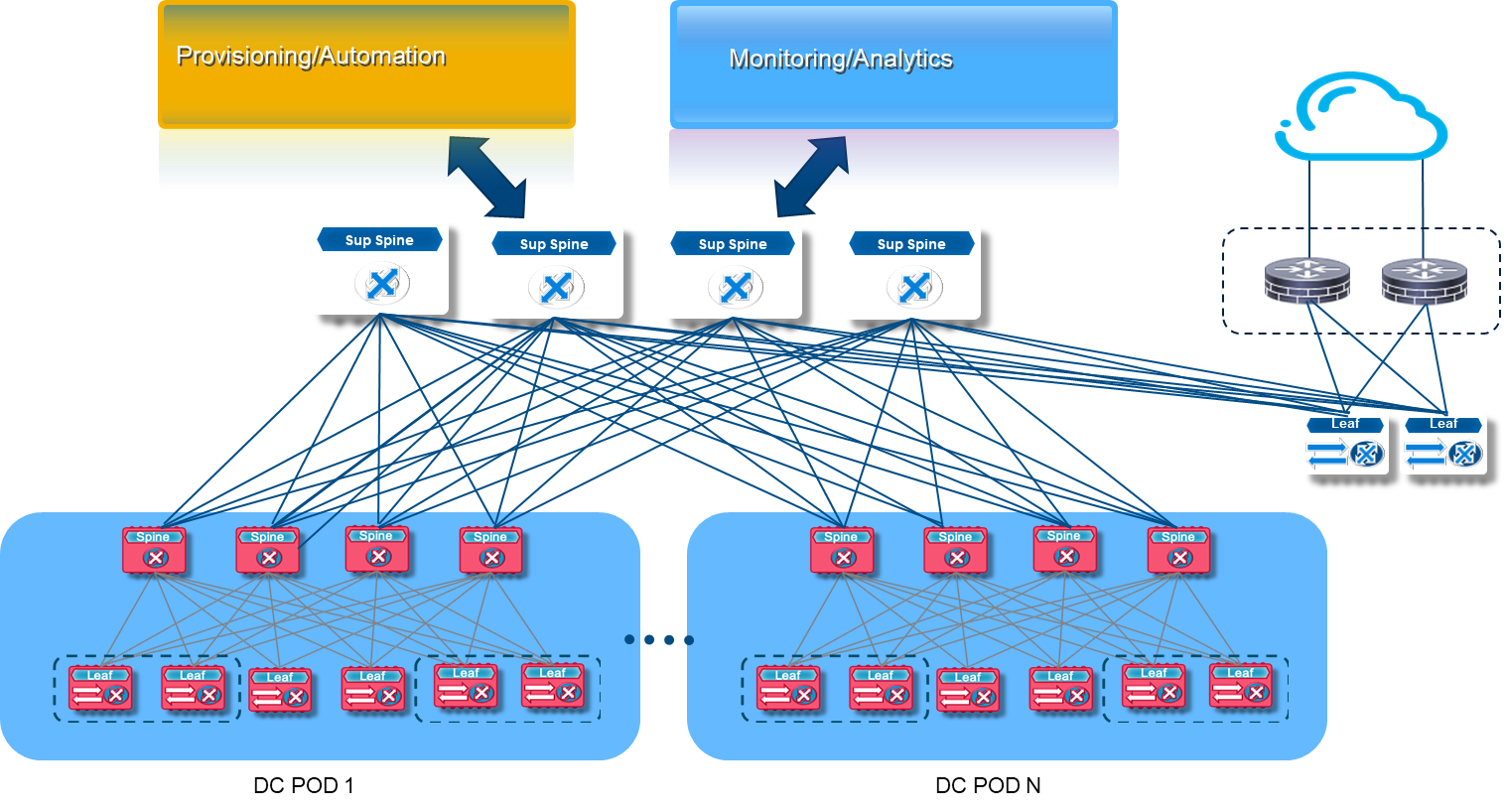 Figure 2—Scalable Layer 3 underlay in a data center
Figure 2—Scalable Layer 3 underlay in a data centerThe following benefits are worth noting:
- Simplicity—BGP-based configurations provide scale-out architecture and repeatable deployments with standards-based BGP, VLANs, unnumbered interfaces, ACLs, QoS, and VRRP implementations
- Cost Effective—The architecture is based on merchant silicon and Dell Technologies hardware with end-to-end support
Use case 2—Scalable multitenancy EVPN VXLAN
The second use case delivers fabric scalability by leveraging BGP EVPN VXLAN features. The following figure shows a fabric consisting of a spine layer and a leaf layer. Two tenants, A and B, are deployed and capable of communicating within and across each other while maintaining complete communications privacy between tenants.
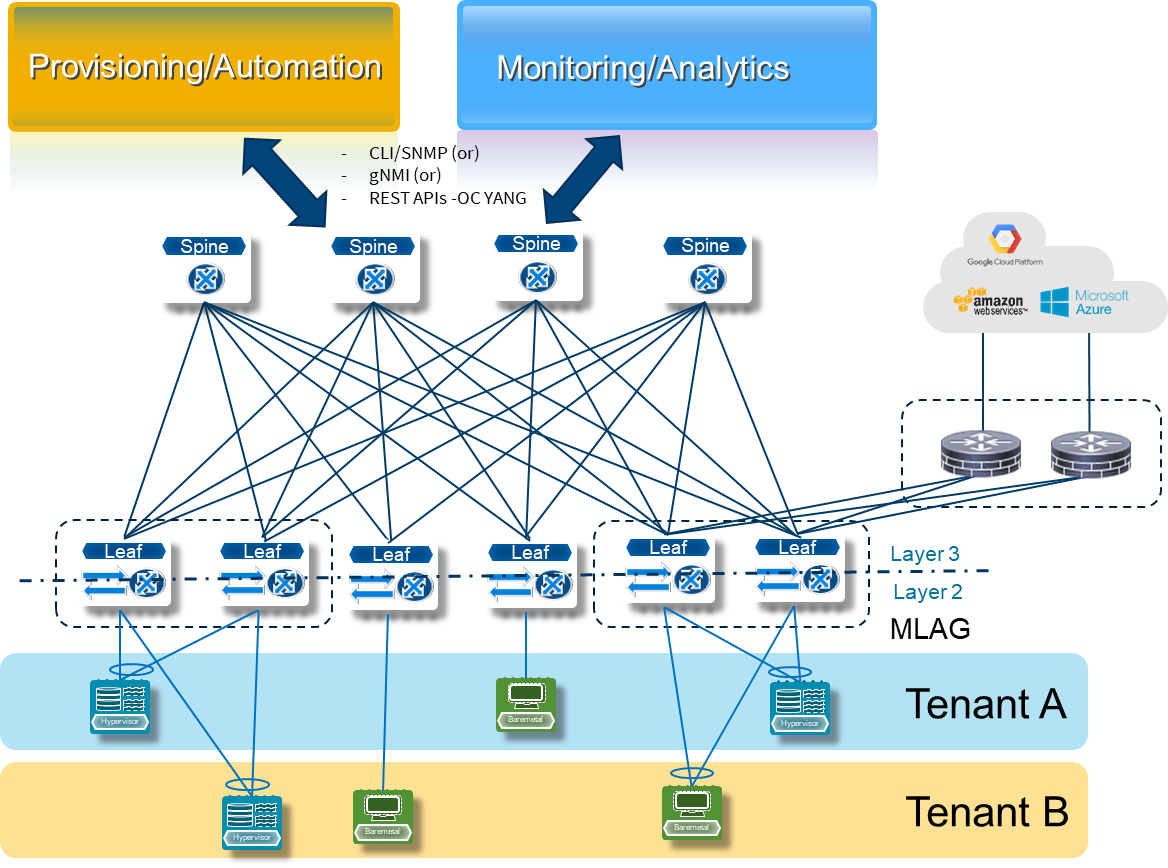 Figure 3—Multitenancy with VXLAN EVPN
Figure 3—Multitenancy with VXLAN EVPNA fabric that is based on EVPN VXLAN has two notable features:
- Scalability—VXLAN increases the number of VLANs from 4,000 (802.1q) to 16 million
- Efficiency—EVPN brings an efficient use in control plane across the network to establish full connectivity
Use case 3—Uniform routing to the host
The first use case provides a simple architecture that is based on open standards and builds the framework. The second use case expands the framework and makes it elastic. The third use case creates a uniform Layer 3 environment from the spine and leaf to the host, as shown in the following figure.
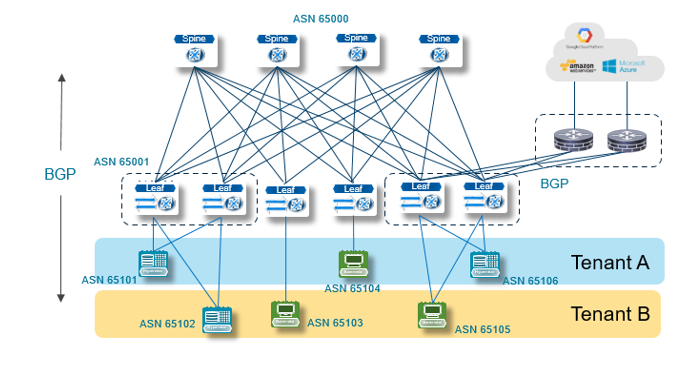 Figure 4—Routing to the host
Figure 4—Routing to the hostUniform routing to the host provides:
- Pure Layer 3 functionality—Basic Layer 2 features such as Spanning-Tree, VLANs, and MLAG are eliminated
- IP addressing efficiency—Efficient IP addressing that leverages BGP unnumbered configuration
- Host and VM agility—End-host physical rack decoupling and VM mobility
Additional information
For more about Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies, see the following:
Related Blog Posts

Be more agile with EVPN Multihoming (MH)
Thu, 04 Jan 2024 16:51:10 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Let’s talk about enhancing your basic EVPN fabric. In your typical data center EVPN fabric, an end host uses dual homed connections onto the leaf or Top of Rack (ToR) switches.
The ToRs are usually a pair of switches configured with multi-chassis link aggregation (MC-LAG) to provide end-host link redundancy if one of the ToRs failed.
These links are Layer 2 with spanning-tree deployed on the fabric. Spanning tree typically blocks half of the links to avoid any network loops. As a result, the fabric bandwidth is cut in half. This only happens when the LAG consists of single links, as demonstrated in Figure 2.
However, if there was a way to attain link redundancy, flexibility, and full link bandwidth utilization things could be more interesting in the EVPN landscape.
Dell Enterprise SONiC 4.2 brings EVPN multihoming into the data center. It is a standards-based replacement for multi-chassis link aggregation (Multi-chassis Link Aggregation Group) and legacy stacking technology.
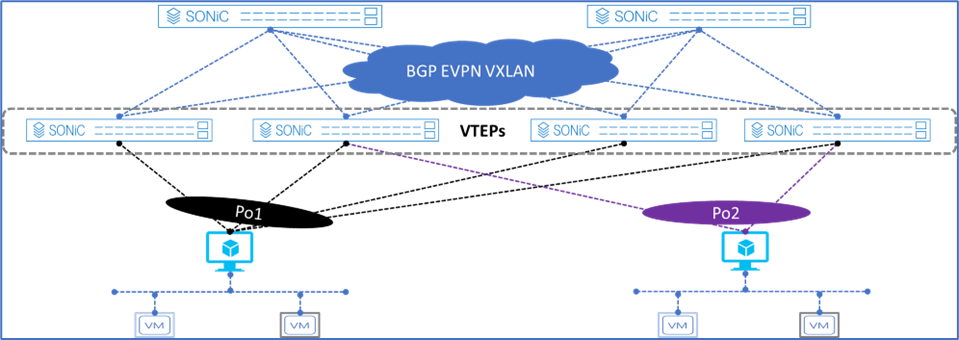
Figure 1. Dell Enterprise SONiC EVPN MH
Figure 1 shows the supported Dell Enterprise SONiC EVPN MH deployment. It shows the maximum number of VTEPs that can be connected to a single end host.
These connections are independent, meaning each link belonging to the link aggregation (LAG) can be connected to multiple independent upstream switches and these upstream switches do not have to be interconnected.
Deployment simplicity is the main benefit of EVPN MH, as all the connections only have to be connected from the end-host or server to the switches.
Achieve end host enhanced connectivity and link efficiency with EVPN MH
In an EVPN fabric, especially a data center fabric, the end hosts or servers are dual homed to a pair of Top of Rack (ToR) switches providing link redundancy. This deployment is common and it uses MC-LAG.
The other deployment option is known as stacking. This option involves several switches stacked together with a primary switch acting as the controller of the stack. All end-hosts or servers are connected to each of the switches part of the stack.
Note: A stack consisting of a single switch is also possible, but rarely deployed.
Both deployments offer link and device redundancy, but they have some limitations that EVPN MH can overcome. The benefits and limitations for each deployment option are described in the following lists.
MC-LAG deployment
- A minimum of two ToR/Leaf switches are required
- A single switch deployment is not supported
- An end host or server can connect only up to two ToRs/Leaf switches at any given time
- All connections from the end-host or server are Layer 2 based
Stacking deployment
- A maximum of eight switches are stacked with one primary or controller switch
- Specific types of stacking cables are required to form the stack
- A single switch deployment is not supported
- All end hosts or servers connect to each switch part of the stack to maintain link redundancy, resulting in a cable management situation
- All connections from the end-host or server are Layer 2 based
EVPN multihoming deployment
- A minimum of one ToR/Leaf switch is required
- An end-host or server can connect to four separate ToR/Leaf switches (VTEPs) at any given time
- All links from the end-host or server to the VTEPs are active
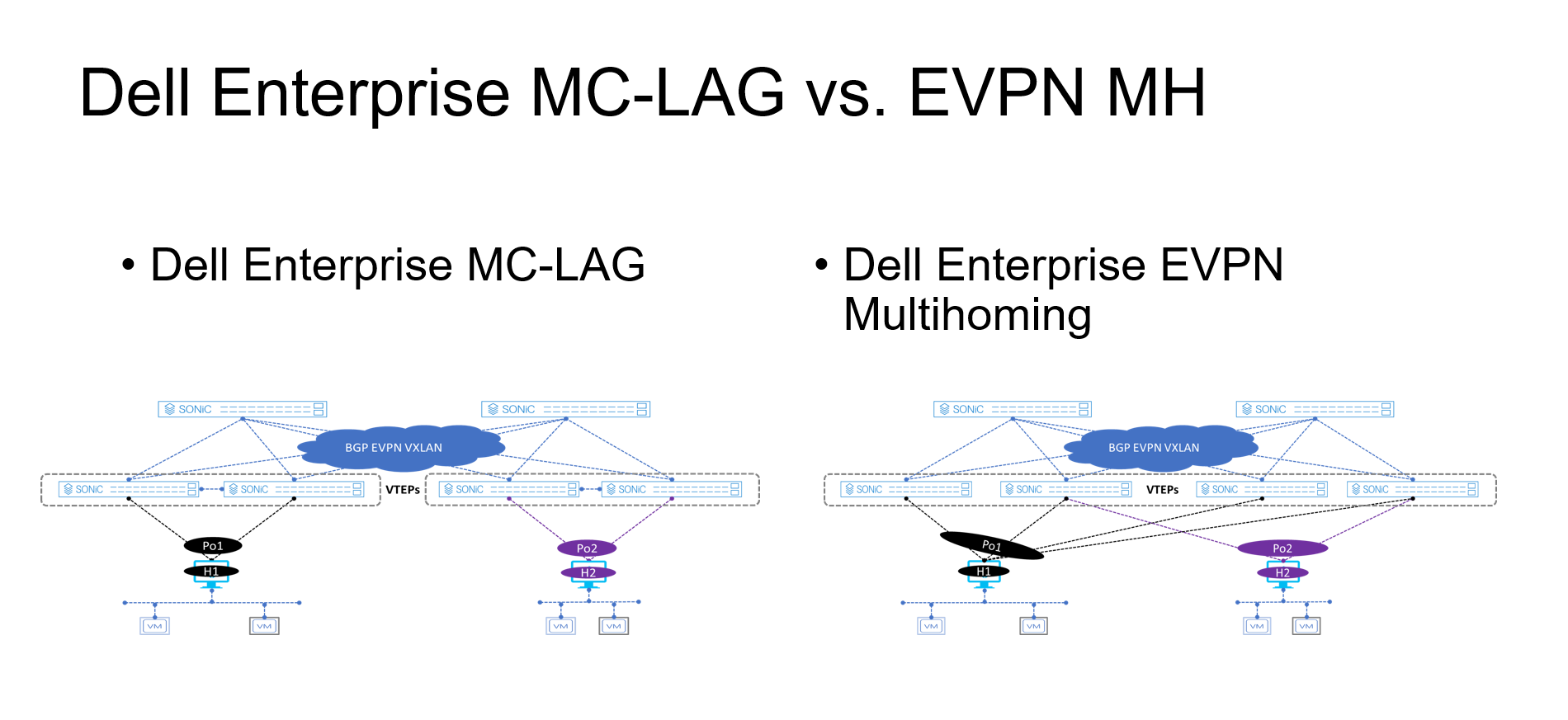
Figure 2. MC-LAG vs. EVPN multihoming deployment
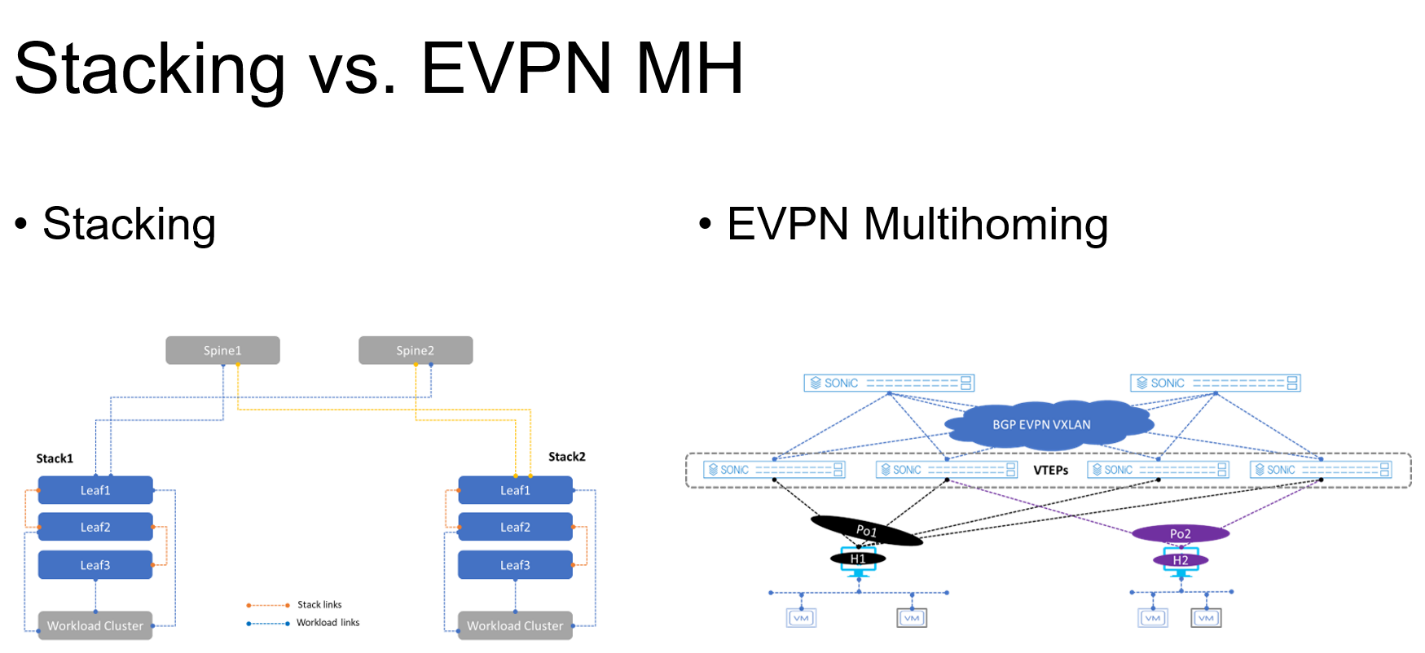
Figure 3. Stacking vs. EVPN multihoming deployment
The advantages offered by EVPN multihoming are clear when compared with the traditional stacking and MC-LAG. Table 1 summarizes these differences.
Table 1. Stacking compared to MC-LAG and EVPN-MH
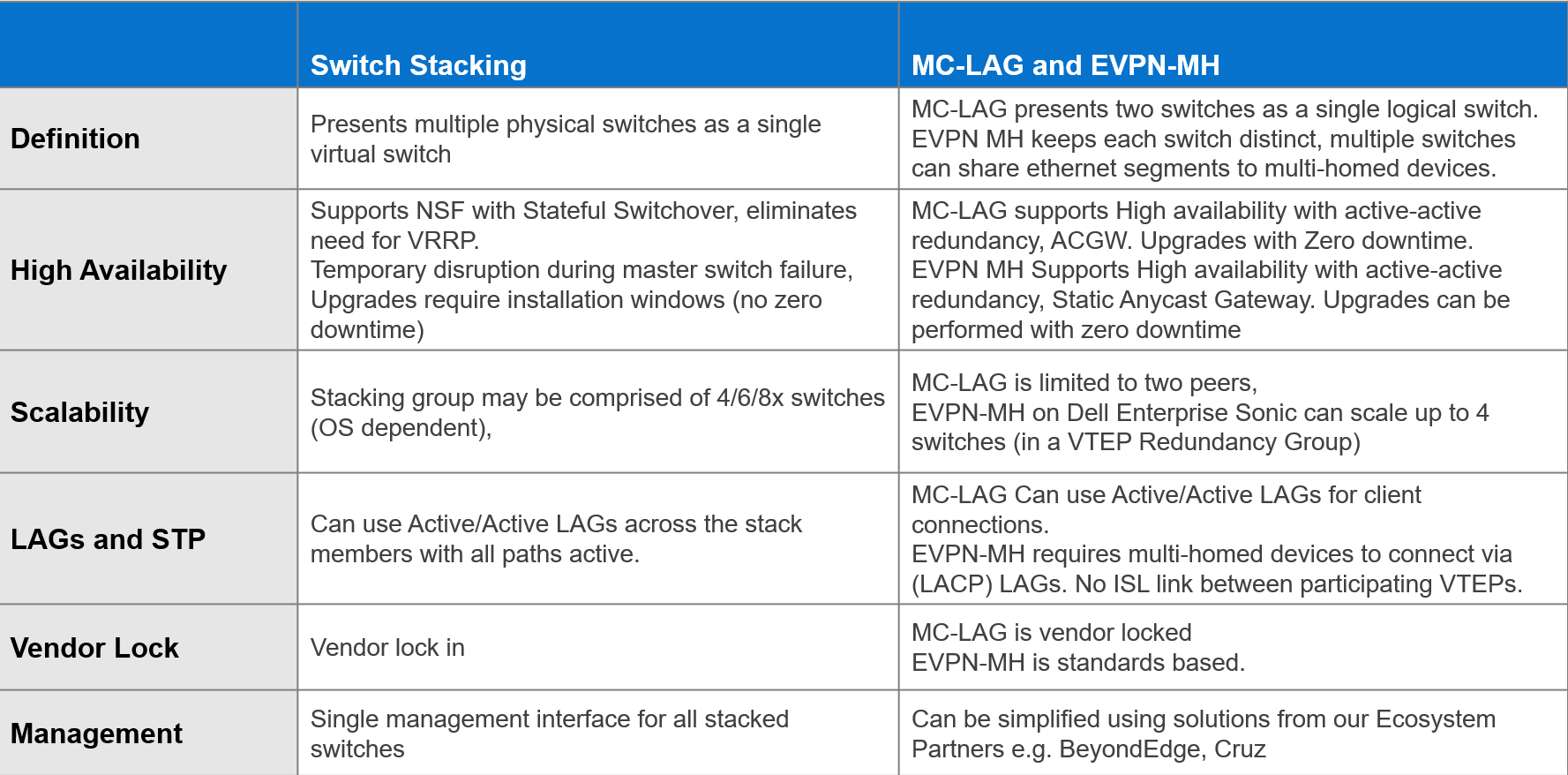
EVPN offers an upgrade to the legacy Layer 2 VPN technology. EVPN should be considered each time a new fabric is deployed, especially when virtualization is one of the workloads.
Dell Enterprise SONiC 4.2 offers even more simplicity into the adoption of EVPN in the data center.
Additional resources
Dell Enterprise SONiC 4.2.0 User Guide (log in required)

Transform Your Data Consumption with Dell Enterprise SONiC and PowerFlex Appliance
Thu, 28 Sep 2023 18:16:45 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Different types of data generated by our everyday needs defines our digital world. To survive the constant evolution of this world, transformation should be the first order of business. One way to spark transformation is by developing the ability to intelligently leverage the data we produce.
Data centers are the convergence of software and hardware elements that provide predictable outcomes for mission-critical workloads. These workloads need to reside and evolve within a well-defined infrastructure.
This infrastructure is known as hyperconverged or converged infrastructure, where compute, networking, and storage components work together in a single appliance.
Dell Technologies’ product portfolio has several hyperconverged/converged (H/CI) platforms, one of which is VxRail, and PowerFlex, which facilitates this transformation.
This blog introduces PowerFlex, as well as Dell Enterprise SONiC, an open-source networking operating system. These appliances complement each other and serve as a holistic solution for your H/CI needs.
Dell PowerFlex: The basic pillars of digital transformation
The Dell PowerFlex family empowers organizations to leverage the benefits of fully integrated, high-power appliances to achieve predictable outcomes. It brings three key pillars: flexibility, high performance, and linear scalability. These pillars work together to simplify infrastructure management, increasing IT agility overall.
PowerFlex offers the flexibility to meet the diverse and rapidly evolving needs of the modern data center and IT Enterprise. For example, PowerFlex allows for mix and match storage, compute, and hyperconverged nodes for a dynamic deployment. This flexibility allows users to scale their storage and compute resources together or independently.
PowerFlex also supports a wide range of operating environments: bare metal operating systems, hypervisors, and container platforms. It offers a robust toolset for simplifying IT operations for the entire infrastructure with PowerFlex Manager, automating complex life cycle management activities.
The transformation pillars of flexibility, performance, and scalability need a foundation on which to build to deliver the predictable outcomes. The infrastructure or fabric is that foundation—and Dell Enterprise SONiC is the networking operating system that builds this fabric.
Dell Enterprise SONiC: Open-source networking made real
SONiC is an open-source, Linux-network operating system. It started in the cloud-scale data center for a hyperscale deployment model. Its modular or container-based architecture allows it to expand into increasingly applicable edge, cloud, and Enterprise deployments.
Dell Enterprise SONiC is Dell’s own version of the SONiC community version. Dell’s version contains Dell proprietary features that provide the foundational fabric for our edge, cloud, and Enterprise customers delivering H/CI environments such as PowerFlex solutions.
H/CI environments require some basic networking features such as jumbo frames, link aggregation, line-rate performance, Quality of Service (QoS), simple Spanning-Tree port types (portfast/edge), and VLANs.
In addition to these basic Layer 2 features, Dell Enterprise SONiC provides VxLAN EVPN, Data Center Interconnect (DCI), MC-LAG, PoE, PoE+, 802.1x, and additional features for the edge, cloud, and Enterprise environments.
With Dell Enterprise SONiC, our customers can:
- Leverage the entire open networking product portfolio to facilitate transitions between platforms
- Deploy alert framework and streaming
- Have access to a growing third-party application ecosystem
- Count on round-the-clock, single-source, world-class support
 Dell Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies
Dell Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies
The best of both of worlds
By combing PowerFlex and Dell Enterprise SONiC, you get the best of both worlds. When working alongside each other, these solutions deliver scalable databases, provide deep insight with next generation analytics, and consolidate IT systems to improve efficiency. Additionally, these solutions help integrate your cloud native applications, and bring together bleeding edge applications such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to create revenue streams.
 PowerFlex Appliance plus Dell Enterprise SONiC – a good match
PowerFlex Appliance plus Dell Enterprise SONiC – a good match
Dell Enterprise SONiC brings open-source networking to the H/CI ecosystem by providing various competitive benefits. These include open architecture, community-driven development, vendor-neutrality, as well as enhanced scalability, performance, and security features. These benefits help to improve the efficiency, reliability, and security of an H/CI environment.
Together PowerFlex and Dell Enterprise SONiC deliver a unique solution based on innovative infrastructure open source for the next generation cloud, edge, and Enterprise IT providers for mission-critical workloads running on top of a hyperconverged or converged infrastructure.
For more information about these solutions, see the Dell Technologies Enterprise SONiC for PowerFlex Deployment Guide.


