Assets

Enabling Intel® TDX on Dell PowerEdge
Mon, 20 May 2024 15:04:01 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Summary
One of the primary targets for cyber attackers is data. Data breaches can have devastating consequences for businesses, ranging from financial to reputational damage. With the emerging threat of AI-powered cyber attacks alongside growing infrastructure complexity, implementing strong data protection measures is crucial. Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that ransomware attacks will result in an estimated annual cost of $265 billion by 2031 with attacks occurring every 2 seconds as cybercriminals refine their malware and extortion techniques. This projection takes into account the anticipated growth in damage costs.[1]
Prioritizing data protection empowers organizations to mitigate significant financial losses and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders. Historically, data protection efforts have primarily concentrated on securing data while it is at rest (stored) and in flight (being transferred over the network). Confidential computing is an advanced technology that provides protection for sensitive data during active processing. By incorporating techniques like trust domains and encryption, organizations can ensure that data is shielded from unauthorized access, modification, or theft while it is being actively processed.
Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (Intel® TDX) is Intel®'s newest confidential computing technology. This hardware-based trusted execution environment (TEE) facilitates the deployment of trust domains (TD), which are hardware-isolated virtual machines (VM) designed to protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access.
Intel® TDX uses virtualization technology to create these trust domains, which are isolated from the operating system and other software running on the system. This isolation helps prevent malware and other malicious software from accessing or tampering with sensitive data or processes.
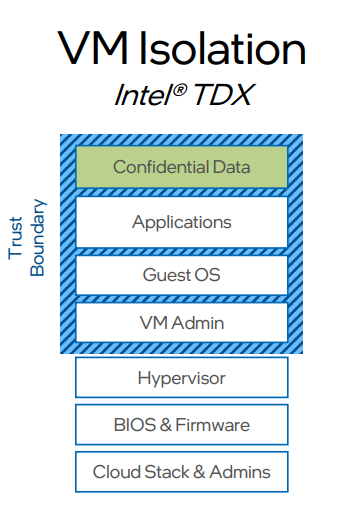
Figure 1: Trust Domain
One of the key benefits of Intel® TDX is that it can protect the system even if the host operating system or hypervisor is compromised because they are outside of the trust boundary. This is because the trust domains are created and managed by the CPU itself rather than relying on software-based security measures, which can also help protect against advanced threats such as rootkits, bootkits, and kernel-level attacks.
PowerEdge 16th-generation with 5th-generation Intel® Xeon® processors, secured with Intel® TDX, complements data-at-rest and data-in-flight protections with enhanced capabilities to safeguard data-in-use. Intel® TDX on PowerEdge enables businesses to put their workloads, containers, virtual machines, and/or processes in isolated secure enclaves in the CPU to minimize risk of data breaches and maintain the integrity of operations.
Intel® TDX on PowerEdge offers easy deployment, low-touch enablement, compatibility with existing software, and minimal performance overhead.
Intel® TDX on PowerEdge – supported platform processors and operating systems
Intel® TDX is currently available on select Intel® CPUs and is supported by certain hypervisors and guest operating systems.
Table 1: Intel® TDX on PowerEdge supported processors and operating systems
Supported Platforms and Processors | |
PowerEdge | PowerEdge 16th-generation with 5th-generation Intel® Xeon® processors – R760xs |
Early Preview Host OS/Hypervisor distributions enabled for Intel® TDX based on: | |
Host OS/Hypervisor
|
|
Guest OS |
|
Enabling Intel® TDX on Dell PowerEdge
1. Install Ubuntu 23.10, and run the script according to documentation from: https://github.com/canonical/tdx/tree/1.2?tab=readme-ov-file#setup-tdx-host
2. Install Ubuntu 23.10
a. Clone repository:

b. Run script:

3. Enable Intel® TDX in BIOS
a. Go to System BIOS > System Security
b. Set the following values:
- Intel(R) TXT: On
- Memory Encryption: Multiple Keys
- Global Memory Integrity: Disabled
- TME Encryption Bypass: Enabled
- Intel Trust Domain Extension (TDX): Enabled
- TME-MT/TDX Key Split to non-zero value: 1 (set non zero value)
- Disable excluding Mem below 1MB in CMR: Disabled
- TDX Secure Arbitration Mode Loader (SEAM): Enabled
- Intel(R) SGX: On
- PRMRR Size: 2G
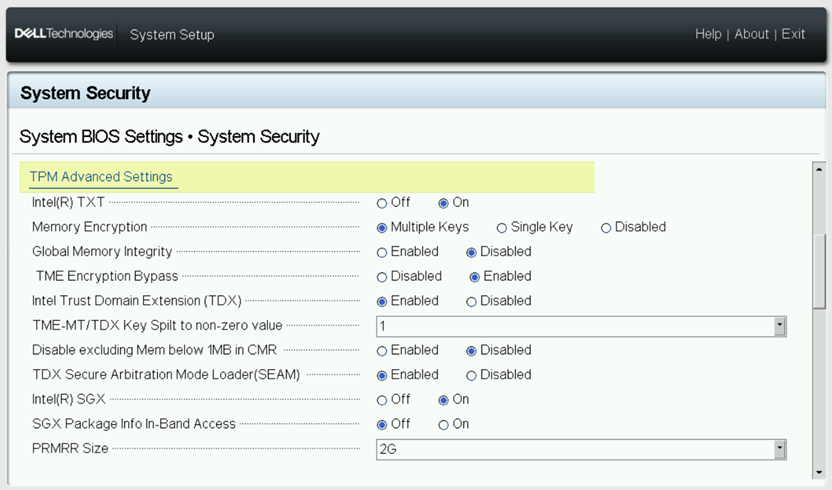
Figure 2. System BIOS System Security Settings
4. Verify if Intel® TDX is enabled according to documentation from:
https://github.com/canonical/tdx/tree/1.2?tab=readme-ov-file#verify-tdx-is-enabled-on-host
a. Run command:

b. Similar output is expected:

5. Create TDX VM image:
a. Follow the documentation on: https://github.com/canonical/tdx/tree/1.2?tab=readme-ov-file#setup-td-guest
6. Boot TDX VM:
a. Follow the documentation on: https://github.com/canonical/tdx/tree/1.2?tab=readme-ov-file#boot-td-guest-with-virsh-libvirt
7. Verify TDX VM: https://github.com/canonical/tdx/tree/1.2?tab=readme-ov-file#7-verify-td-guest
a. SSH to the VM
b. Run the following command to verify TDX:

c. Example output:
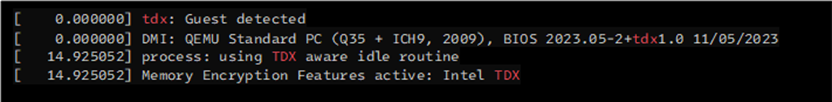
Enabling Intel® TDX in BIOS
The following steps describe how to setup BIOS to use Intel® TDX:
- Got to: System BIOS -> System Security
- Set the following values:
- Intel(R) TXT: On
- Memory Encryption: Multiple Keys
- Global Memory Integrity: Disabled
- TME Encryption Bypass: Enabled
- Intel Trust Domain Extension (TDX): Enabled
- TME-MT/TDX Key Split to non-zero value: 1 (set nonzero value)
- Disable excluding Mem below 1MB in CMR: Disabled
- TDX Secure Arbitration Mode Loader (SEAM): Enabled
- Intel(R) SGX: On
- PRMRR Size: 2G
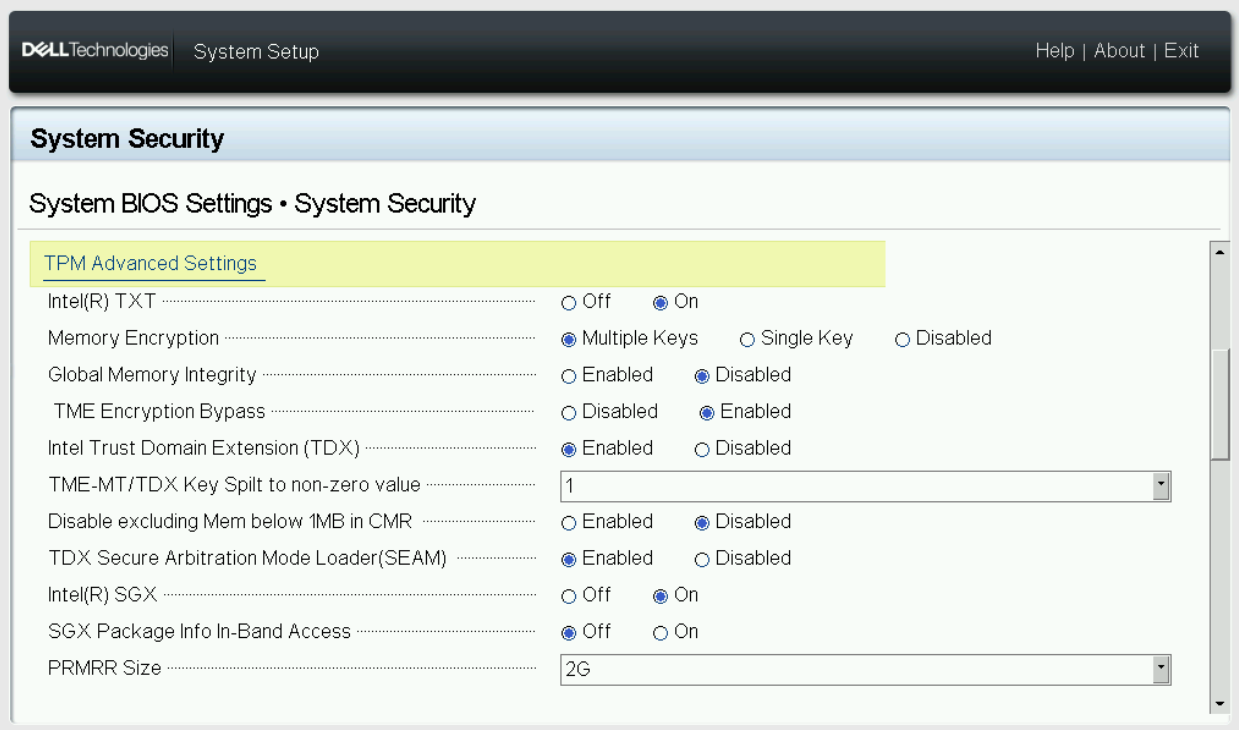
Figure 3. System BIOS System Security Settings
Conclusion
Organizations can bolster the security of data-in-use to mitigate the risks associated with data exposure or unauthorized access. PowerEdge 16th-generation with 5th-generation Intel® Xeon® processors, secured with Intel® TDX, complements data-at-rest and data-in-flight protections with enhanced capabilities to safeguard data-in-use. Intel® TDX on PowerEdge offers easy deployment, low-touch enablement, compatibility with existing software, and minimal performance overhead.
Intel® TDX on PowerEdge helps to strategically narrow the attack surface and increase data and application protection and confidentiality in the data center or in the cloud through hardware-level isolation within a virtual machine (VM). This approach helps maintain the confidentiality and integrity of both the data and applications while they are actively being processed.

