Assets

Introduction to the PowerStore Platform Offerings and their Benefits
Wed, 24 Apr 2024 14:00:55 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
In May 2020, we released Dell EMC PowerStore, our groundbreaking storage family with a new container-based microservices architecture that is driven by machine learning. This versatile platform includes advanced storage technologies and a performance-centric design that delivers scale-up and scale-out capabilities, always-on data reduction, and support for next-generation media.
PowerStore provides a data-centric, intelligent, and adaptable infrastructure that supports both traditional and modern workloads.

Figure 1. Overview of PowerStore
Let’s start by going over the hardware details for the appliance. The PowerStore appliance is a 2U, two-node, all NVMe Base Enclosure with an active/active architecture. Each node has access to the same storage, with Active-optimized/Active-unoptimized front-end connectivity.
Hardware
The following figures show the front and back views of the PowerStore appliance:

Figure 2. Front view of PowerStore appliance

Figure 3. Back view of PowerStore 1000-9000 appliance
The PowerStore models start at the PowerStore 500 all the way up to the PowerStore 9000. The configurations available vary by model. This table provides a comparison of the different models:
| PowerStore Model | 500 | 1000 | 3000 | 5000 | 7000 | 9000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
NVMe NVRAM drives | 0 | 2 | 4 | ||||
Capacity (cluster) | 28.57 TB to 11.36 PB Effective (11.52 TB to 3.59 PB Raw) | ||||||
Max drives (appliance / cluster) | 25 | 96 / 384 | |||||
Expansion (appliance) | None | Add up to three expansion enclosures per appliance | |||||
AppsON | N/A | X models | |||||
Drive types | NVMe SSD, NVMe SCM | NVMe SSD, NVMe SCM, SAS SSD (Only on the expansion enclosures) | |||||
Clustering | Up to four appliances: Mix and match appliances of any model/config of the same type | ||||||
Embedded ports | 4-port card: | 25/10/1 GbE | 25/10/1 GbE optical/SFP+ and Twinax or 10/1 GbE BaseT | ||||
2-port card: | 10/1 GbE optical/SFP+ and Twinax | None | |||||
IO Modules (2 per node) | 32/16/8 Gb FC or 16/8/4 FC | ||||||
Front-End Connectivity | FC: 32 Gb NVMe/FC, 32/16/8Gb FC | ||||||
For more details about the PowerStore hardware, see the Introduction to the Platform white paper.
Model types
PowerStore comes in two model types: PowerStore T and PowerStore X. Both types run the PowerStoreOS.
PowerStore T
For the PowerStore T, the PowerStoreOS runs on the purpose-built hardware as shown in Figure 4. PowerStore T can support a unified deployment with the option to run block, file, and vVol workloads, all from within the same appliance.
PowerStore T supports the following:
- SAN (NVMe/FC, FC and iSCSI)
- NAS (NFS, SMB, FTP and SFTP)
- vVol (FC and iSCSI)
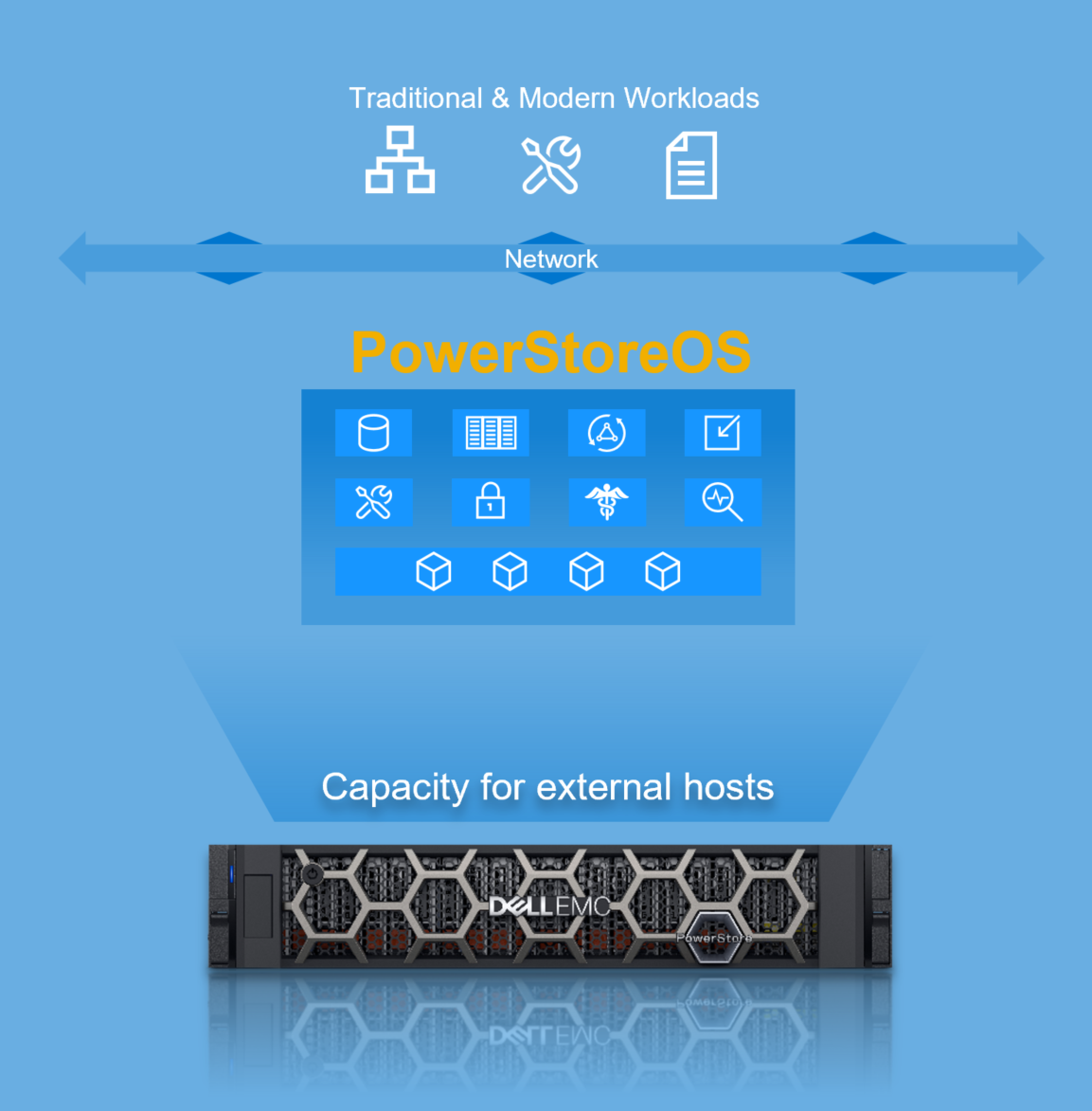
Figure 4. PowerStore T
PowerStore T has two deployment modes to ensure that the platform delivers maximum performance for each use case. The deployment mode is a one-time setting configured when using the Initial Configuration Wizard. The following describes the two deployment modes available as part of the storage configuration: unified and block optimized.
- Unified:
- Default storage configuration (factory state)
- Supports SAN, NAS, and vVol
- Resources shared between block and file components
- Block Optimized:
- Alternate storage configuration (requires a quick reboot)
- Supports SAN and vVol
- Resources dedicated to block components
Depending on the storage configuration you set, the PowerStore T can cover various use cases, and and fulfill many of the use cases that a traditional storage array would, but with added benefits.
Some use cases that the PowerStore T can cover:
- With the Unified storage configuration: file workloads are supported. This entails support for home directories, content repositories, SMB shares, NFS exports, multiprotocol file systems (access through SMB and NFS in parallel), and more. For more details, see the File Capabilities white paper.
- With the Block Optimized storage configuration: For customers running block only workloads, you can leverage PowerStore T with the traditional FC and iSCSI protocols, in addition to running NVMe/FC.
Now for our second model type, PowerStore X.
PowerStore X
PowerStore X also runs the same PowerStoreOS as the PowerStore T but it is virtualized as Virtual Machines (VMs) running on VMware ESXi hosts that run directly on the purpose-built hardware. This model type includes one of the key features known as AppsON. As the name suggests, it can run your typical block workload in conjunction with running customer and application VMs. Figure 5 provides a glimpse of this model.
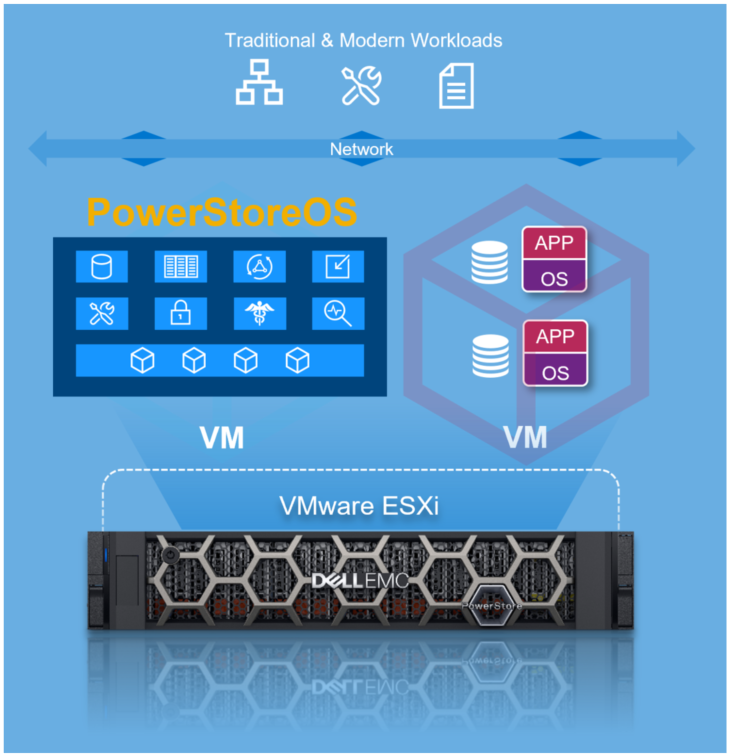
Figure 5. PowerStore X
PowerStore X supports the following:
- SAN (NVMe/FC, FC, and iSCSI)
- vVol (FC and iSCSI)
- Embedded Applications (Virtual Machines)
You can leverage AppsON for multiple use cases that span Edge, Remote Office, data intensive applications, and so on.
Some example use cases are:
- Applications: As organizations thrive to simplify, while continuing to keep up with ongoing accelerated demands, AppsON can be leveraged to help consolidate the infrastructure that is running business-critical applications. It can host a broad range of applications, such as MongoDB (MongoDB Solution Guide, Microsoft SQL Server (Microsoft SQL Server Best Practices), or Splunk (Capture the Power of Splunk with Dell EMC PowerStore) to name a few. For white papers regarding databases and data analytics, see the databases and data analytics page.
- VM Mobility: As mentioned previously, with AppsON we can host VMs natively within PowerStore. This allows for greater flexibility through VMware vSphere because we can leverage Compute vMotion and Storage vMotion to seamlessly move applications between PowerStore and other VMware targets. For example, you can deploy applications on external ESXi hosts, hyperconverged infrastructure (that is, Dell EMC VxRail), or directly on the PowerStore appliance that migrate transparently between them.
We have provided a high-level overview and some examples. There are additional use cases that PowerStore can cover.
Resources
Technical documentation
To learn more about the different features that PowerStore provides, see our technical white papers.
Demos and Hands-on Labs
To see how PowerStore’s features work and integrate with different applications, see the PowerStore Demos YouTube playlist.
To gain firsthand experience with PowerStore, see our Hands-On Labs site for multiple labs.
Author: Kenneth Avilés Padilla LinkedIn

