Assets

Running Machine Learning Workloads Using Red Hat OpenShift on Dell APEX Bare Metal Compute
Thu, 25 May 2023 23:20:31 -0000
|Read Time: 0 minutes
Today’s IT infrastructure is challenging, and customers are looking for solutions to help mitigate or solve the issues they face. Keeping up with constantly evolving business and workload demands can be difficult, but it doesn’t have to be that way. Dell APEX has a robust catalog of solutions to address these challenges, bringing customers on-premises solutions and assisting in modernizing their legacy environments. Dell APEX has solutions that work with several cloud environments including Red Hat, Microsoft Azure, and VMware, to name a few. The APEX Technical Marketing team decided to create a Kubernetes environment using Red Hat OpenShift on APEX bare metal compute nodes to create an AI/ML on-premises work environment.
What is Red Hat OpenShift?
OpenShift is a collection of containerization software products developed by Red Hat and built around Linux containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes. Dell Technologies and Red Hat have partnered to bring Red Hat containerized infrastructure to Dell platforms. Dell has expanded its longstanding strategic relationship with Red Hat by offering innovative solutions to simplify deploying and managing on-premises, containerized infrastructure in multicloud environments. Red Hat OpenShift allows users to choose where they build, deploy, and run applications through a consistent experience.
Simplify your cloud experience with Dell APEX
We introduced Dell APEX to help our customers with the challenges of infrastructure ownership and simplify their cloud experience. Dell APEX has rapidly expanded to give customers more flexibility and solutions to address their business needs. Our bare metal Dell APEX solutions are available for configuration and subscription through the Dell APEX Compute or Dell APEX Custom sections of the Dell APEX Console. Dell APEX Compute gives customers the option to select PowerEdge servers through a fixed monthly subscription model, while Dell APEX Custom expands on this option with more flexibility and server selection.
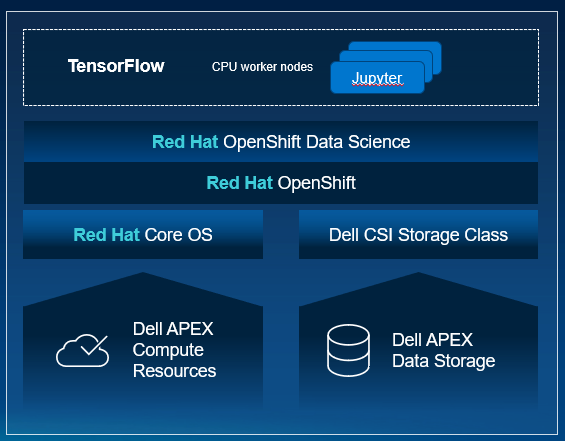
Delivering containerized machine learning workloads at scale
The APEX Technical Marketing team wanted to evaluate the full deployment of a Red Hat OpenShift cluster on Dell APEX bare metal compute resources to deliver containerized machine learning workloads at scale. We analyzed how to do this with simplified orchestration on-premises by using OpenShift deployed on Dell APEX compute connected to APEX Data Storage Services. In addition to connecting Dell APEX Data Storage Services, we were able to deploy a Red Hat OpenShift Data Science and Jupyter Notebook environment to leverage as a platform for a real-world AI/ML application. Red Hat OpenShift Data Science offers organizations an efficient way to deploy an integrated set of common open-source and third-party tools to perform AI/ML modeling. Jupyter Notebook is an interactive web application used for creating and sharing computational documents.
 "
"
Installing OpenShift
Assisted Installer is a user-friendly OpenShift installation solution for various platforms but is focused on bare metal. It is a web interface for performing cluster installation without having to create the installation configuration file. Deploying Red Hat OpenShift on our bare metal environment was straightforward with the help of Red Hat OpenShift Assisted Installer. Prerequisites included having a valid Red Hat account and a properly configured network for our nodes to connect to the OpenShift console. Once the prerequisites and networking requirements were met, we were able to start the Assisted Installer for our targeted data center.
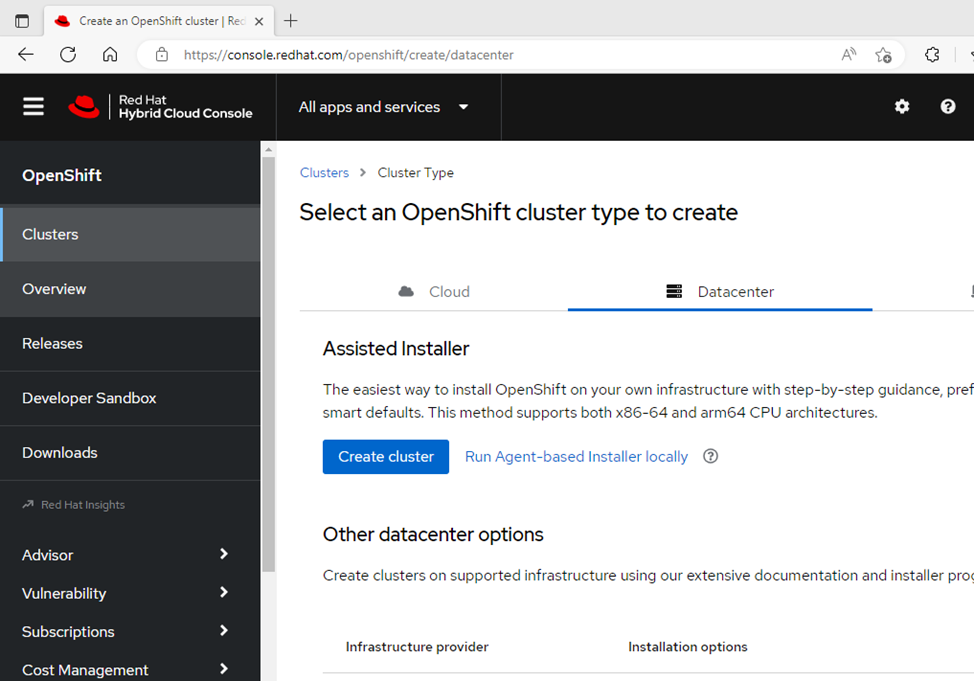
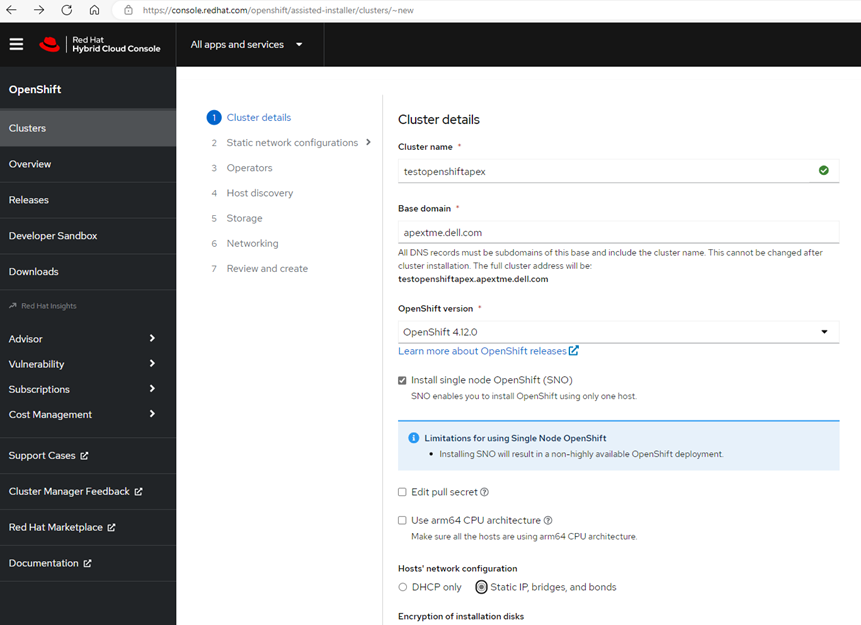
The Assisted Installer takes you through a series of seven straightforward steps for creating your cluster. During the installation, there were a few spots that we had to pay close attention to so that we reduced the chance of having cluster configuration issues later. We had to ensure that we had our bare metal nodes' MAC addresses and IP addresses associated with the node's NIC during step 2, Static network configurations. Had we not correctly entered this information, we would have had issues during the host discovery.
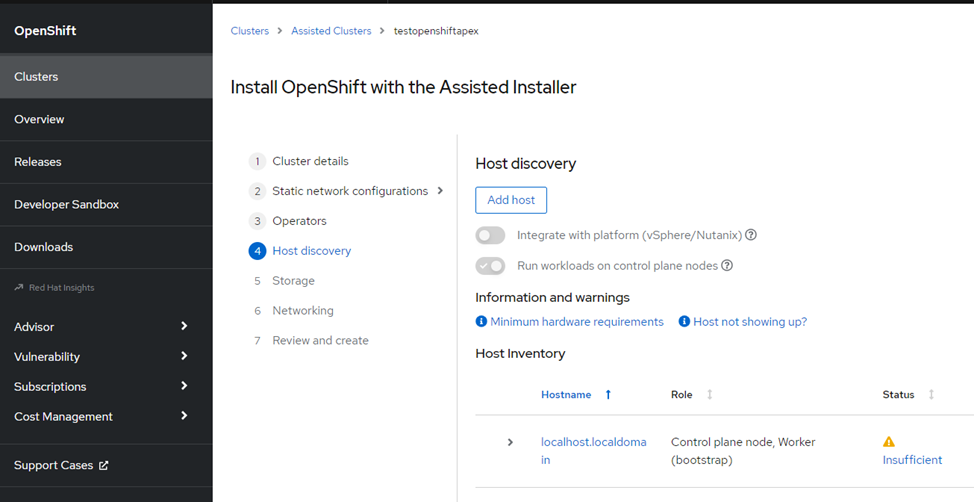
In step 4, host discovery, we downloaded our unique discovery ISO from the Assisted Installer and saved it to our local machine to be used on the bare metal nodes. This unique discovery ISO is created to be used for the cluster that you created with the Assisted Installer. There is a time limit for how long the ISO is usable as well. We were then able to successfully install and boot the ISO on all our bare metal nodes used in the cluster. The Red Hat console discovered the host nodes being used in the cluster, allowing us to continue to the next steps of the Assisted Installer.
Once we finished the remaining steps, we were able to review all the information that we put into the installer and make additional changes as we saw fit before creating the cluster. Once the cluster was created, a cluster admin username, password, and kubeconfig file were provided, and we saved and stored them in a secured location as best practice. The admin username and password will be used to log in to the cluster console. Another useful feature is being able to manage the admin login information and add other users if needed.
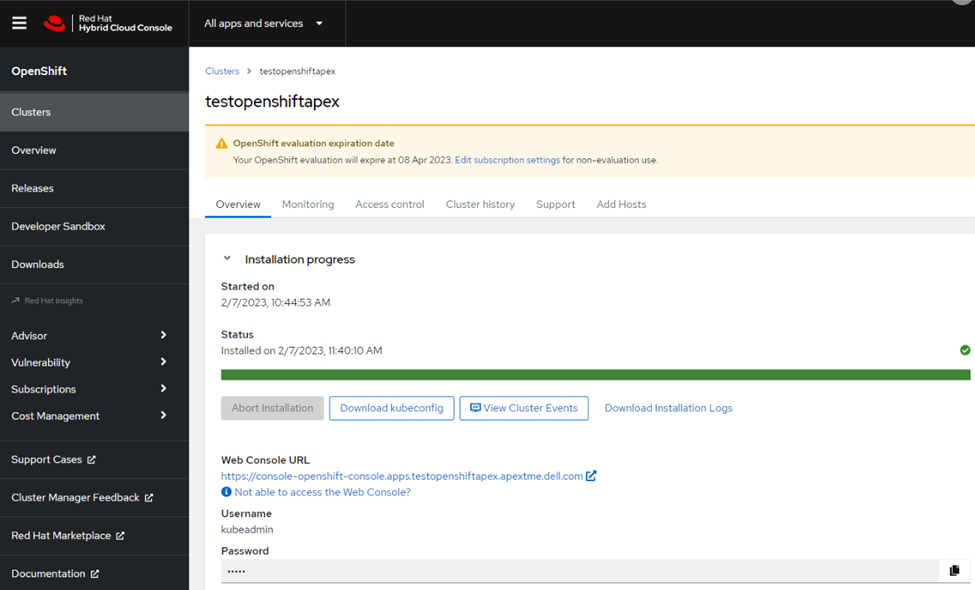
From this point forward, we could access our cluster’s Red Hat OpenShift environment and start deploying workloads and creating test environments, developers’ sandboxes, and much more. Once we logged into our cluster, we were able to install the Dell Container Storage Interface (CSI) drivers to connect our Dell APEX Data Storage Block Services as a container workload persistent storage location and install the Red Hat Data Science operator for the Jupyter Notebook application. The Jupyter Notebook application came online without any issues, allowing us to successfully run a test ML clothing image classification workload found on Kaggle.com.
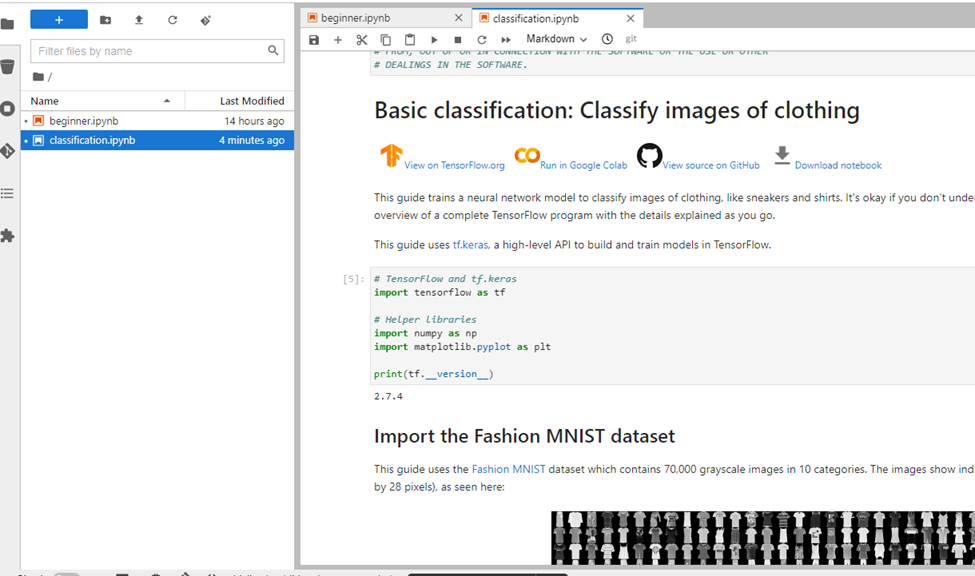
Many organizations today are starting a shift toward cloud-native constructs such as containers with Kubernetes orchestration, in addition to their existing virtualization environments. This deployment example shows how it is possible to deliver containerized machine learning workloads at scale with simplified on-premises orchestration using Red Hat OpenShift deployed on Dell APEX bare metal resources connected to Dell APEX Data Storage Services as persistent storage for the container volumes. This is just the beginning of workable solutions leveraging Dell APEX bare metal resources.
Author: Sevan Woods, Principal Engineer, Technical Marketing
